Buffer Tanks 101: What They Are, How They Work, How To Size Them & Do You Even Need One?
Learn all about buffer tanks: what they are, how they work, worked examples, sizing tips, installation, maintenance, and more for optimal HVAC system efficiency. Most importantly, we'll explain why you likely don't need one.

Introduction
Welcome to the ultimate guide on buffer tanks! Whether you’re a seasoned HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) professional or a curious homeowner, understanding buffer tanks can greatly enhance your heating and cooling systems. Components like buffer tanks can play a role in maintaining system efficiency, reducing wear and tear, and improving overall comfort. However, their primary reason is to add volume to a system so the heat pump operates efficiently. If you undertake system volume calculations, you’ll often find that your system meets the minimum system volume simply through the pipes, equipment, and emitters you already have.
While buffer tanks can play a key role and are beneficial in certain situations, it’s important to recognise the efficiency advantages of designing systems without them. Eliminating the buffer tank reduces thermal losses and minimises the energy required to maintain the desired temperature levels. Therefore, by carefully analysing each project’s specific requirements and conditions, engineers can often find that a streamlined system, free of buffer tanks, not only meets but exceeds performance expectations, ultimately leading to more sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions.
What is a Buffer Tank
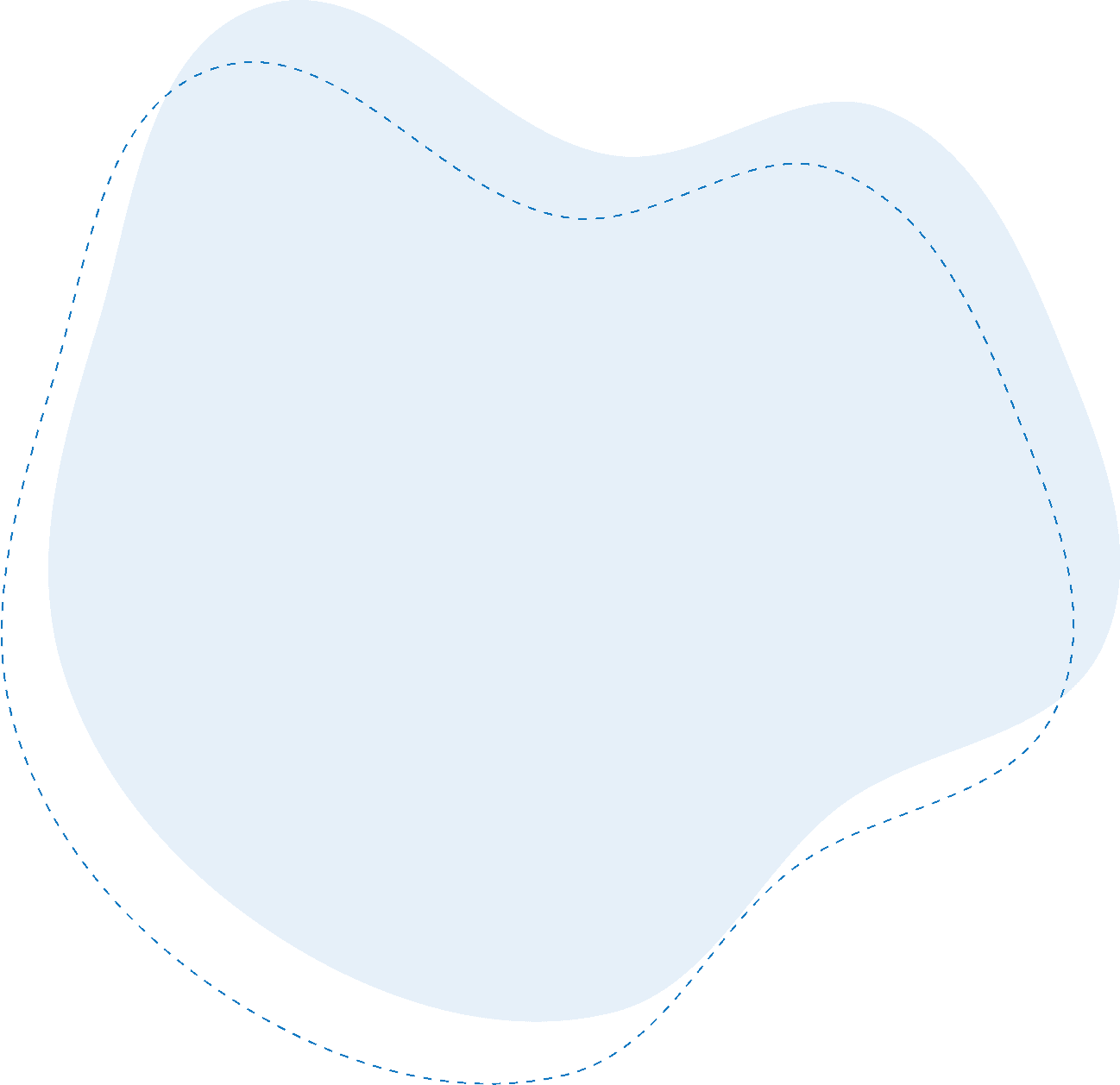
A buffer tank is a storage tank that helps manage the temperature, volume and flow of water in HVAC systems. These tanks act as a buffer between the heat source and the distribution system, ensuring a steady supply of heated or cooled water. They are particularly useful in systems with variable loads or frequent on/off cycling, such as air source heat pumps, ground source heat pumps and boilers.
Buffer tanks come in various sizes and configurations, but their primary purpose remains the same: to improve system performance by adding more volume. Also, by providing additional thermal mass, buffer tanks help prevent short cycling, reduce wear on equipment, and maintain consistent temperatures throughout the system.
Buffer Tank Alternative
When considering buffer tanks, there are two better options:
1. Utilise the Existing System Volume: If your calculations show that the volume within your equipment, pipes, and emitters meets the minimum system volume required by your heat pump, which they most likely do, you do not need a buffer tank.
2. Install a Volumiser: If your calculations indicate that you do not meet the minimum system volume requirement, installing a volumiser is better than a buffer tank. A volumiser has the following advantages:
• It does not mix the flow and return temperatures, maintaining a higher system efficiency.
• It can be installed on the return line, minimising its negative impact on overall system performance.
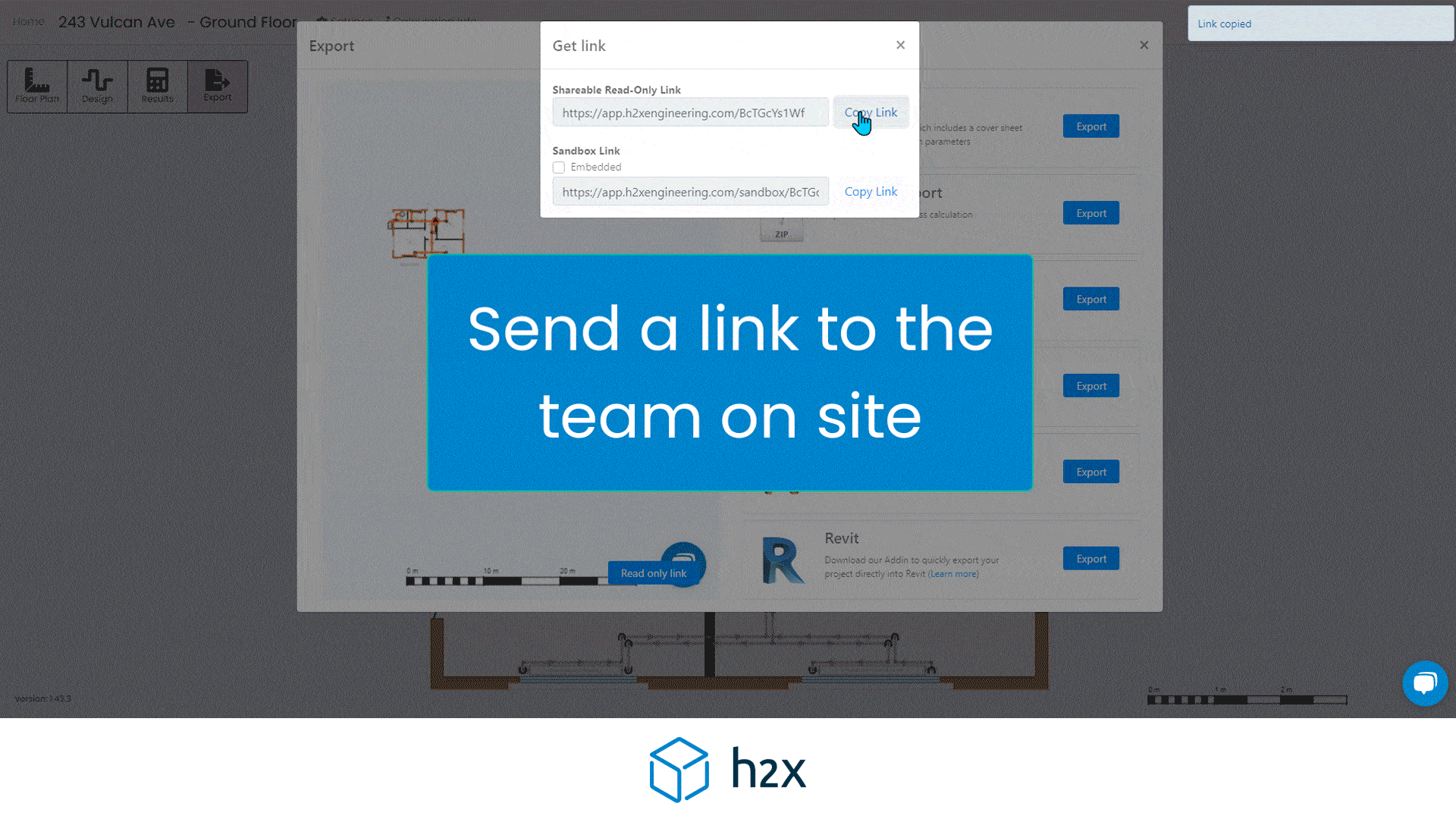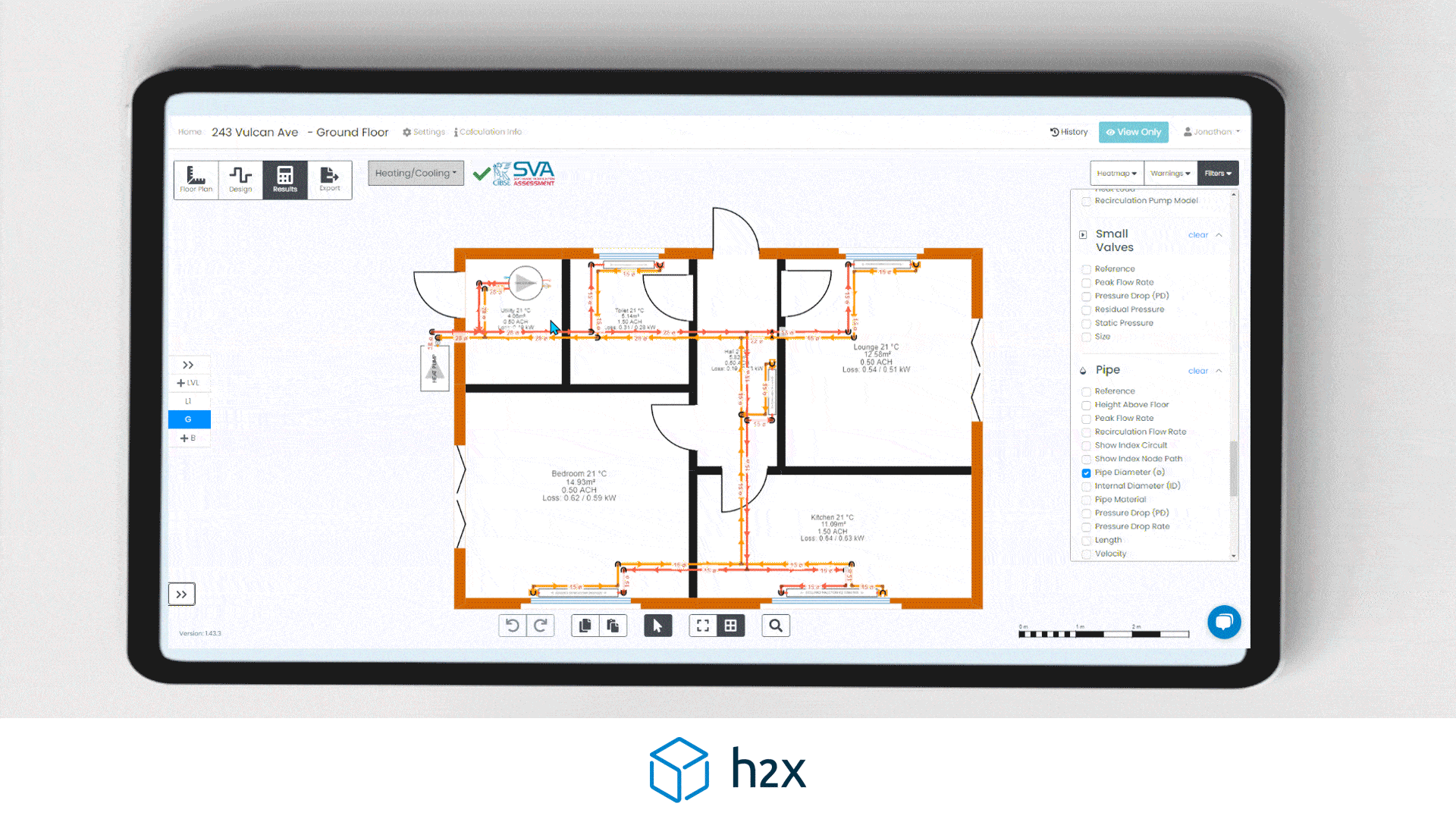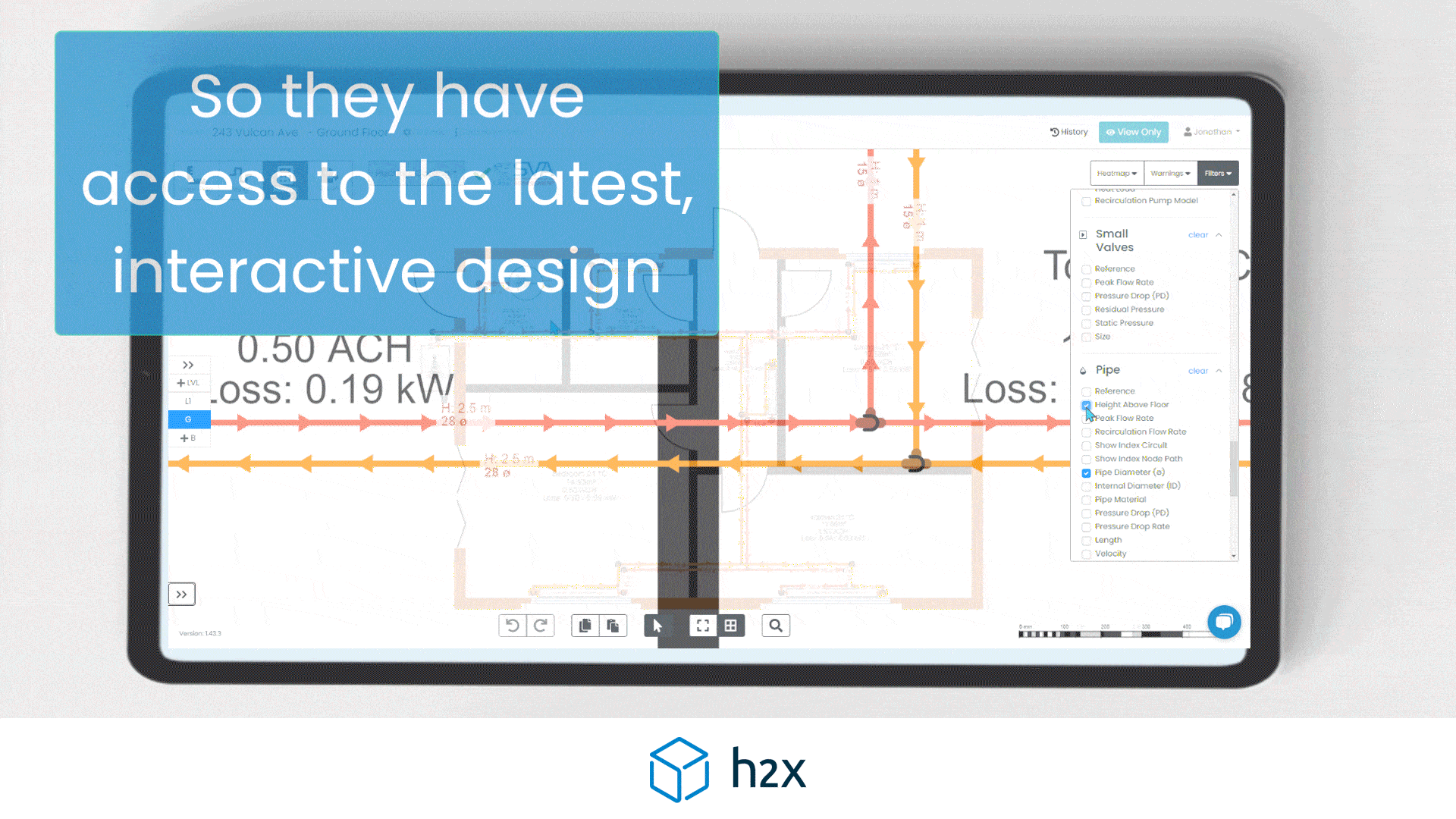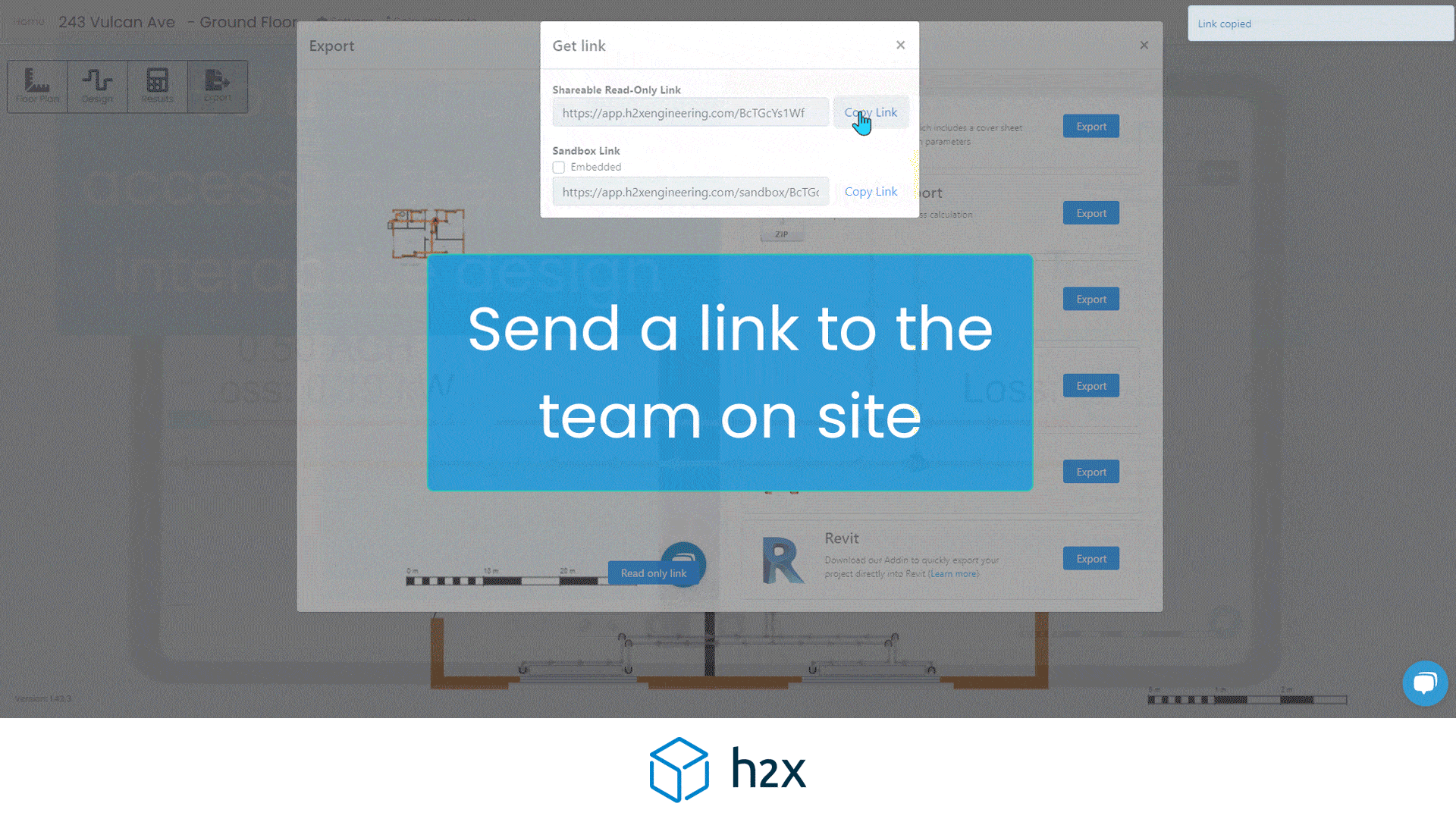
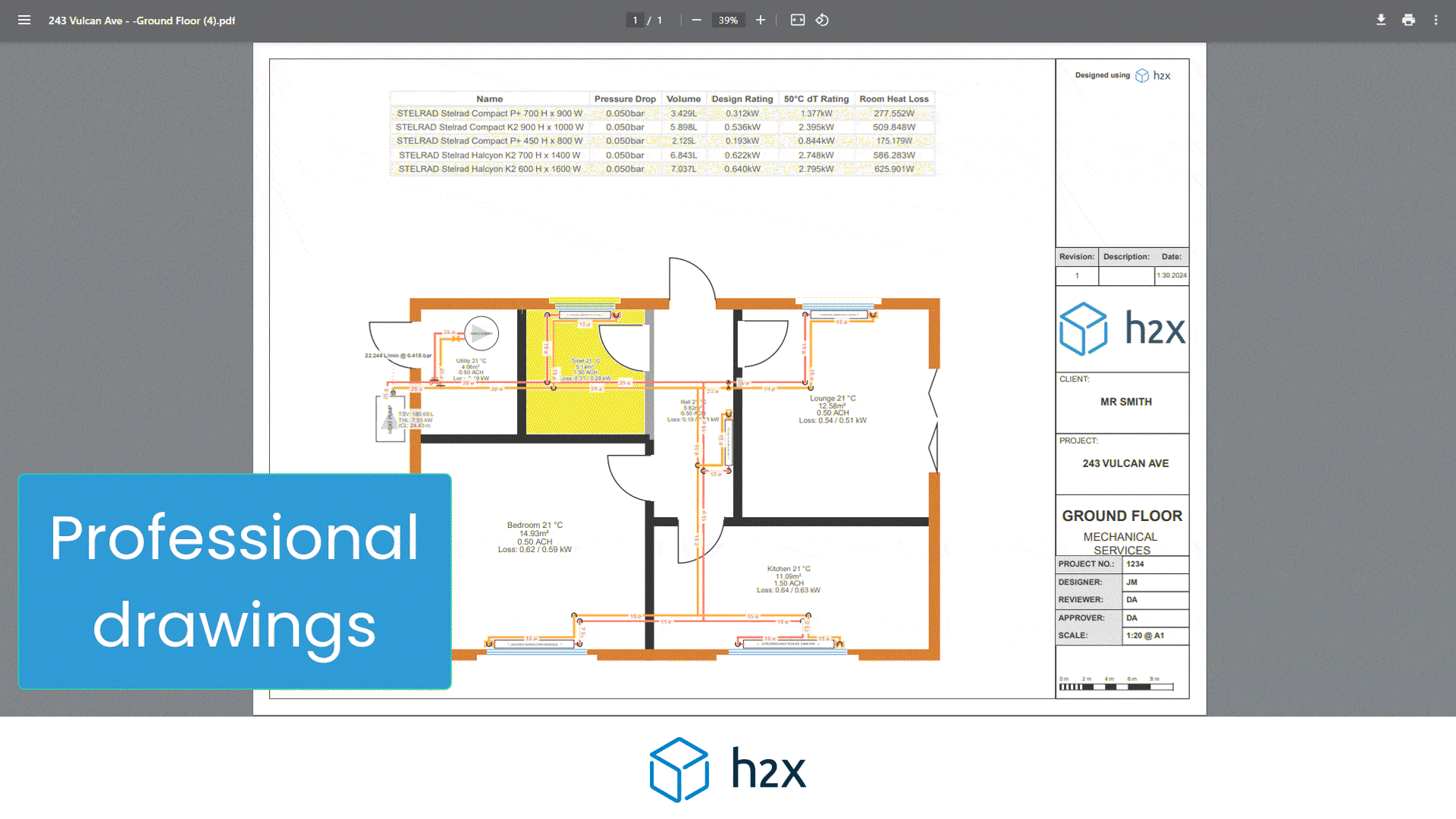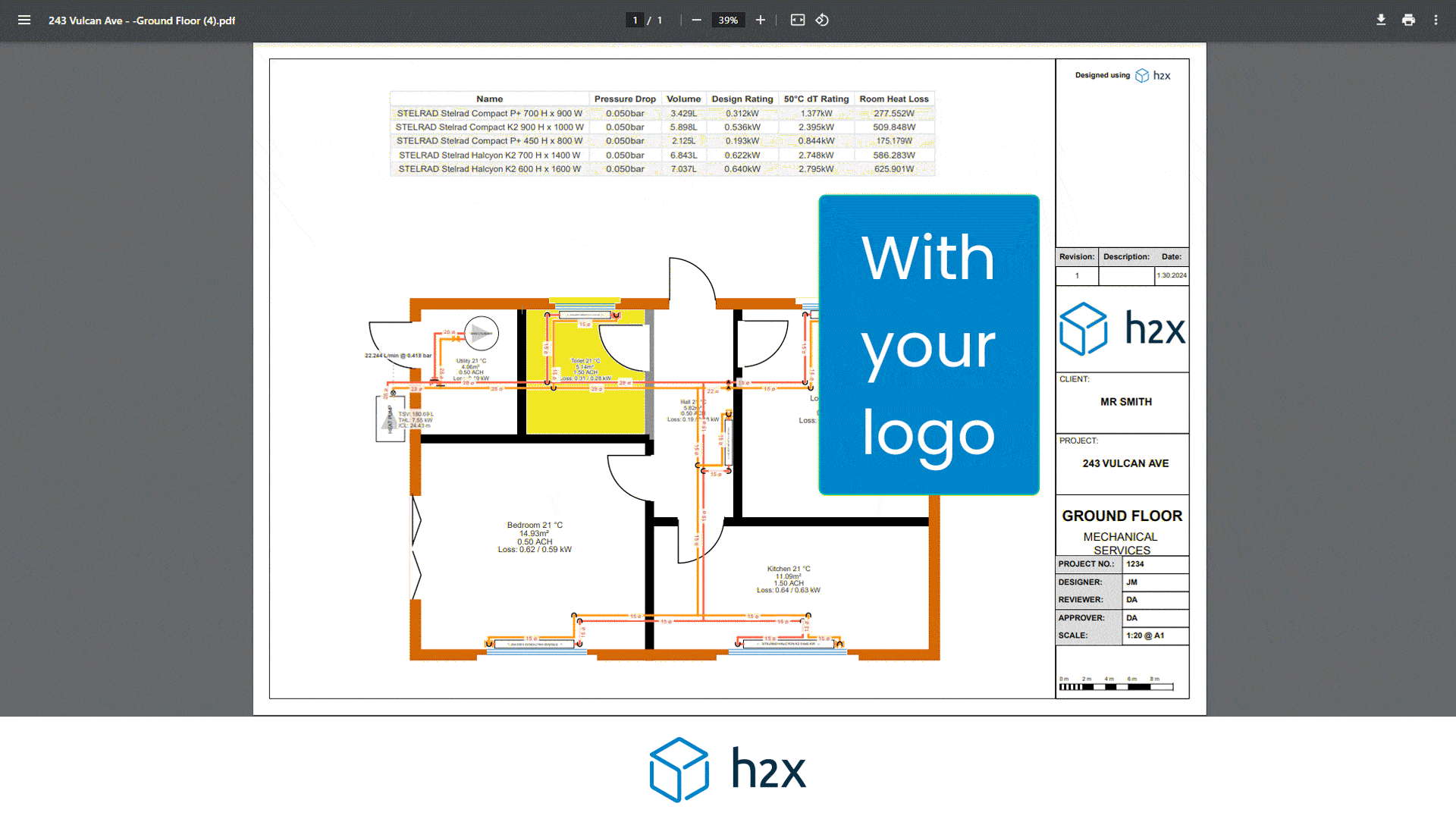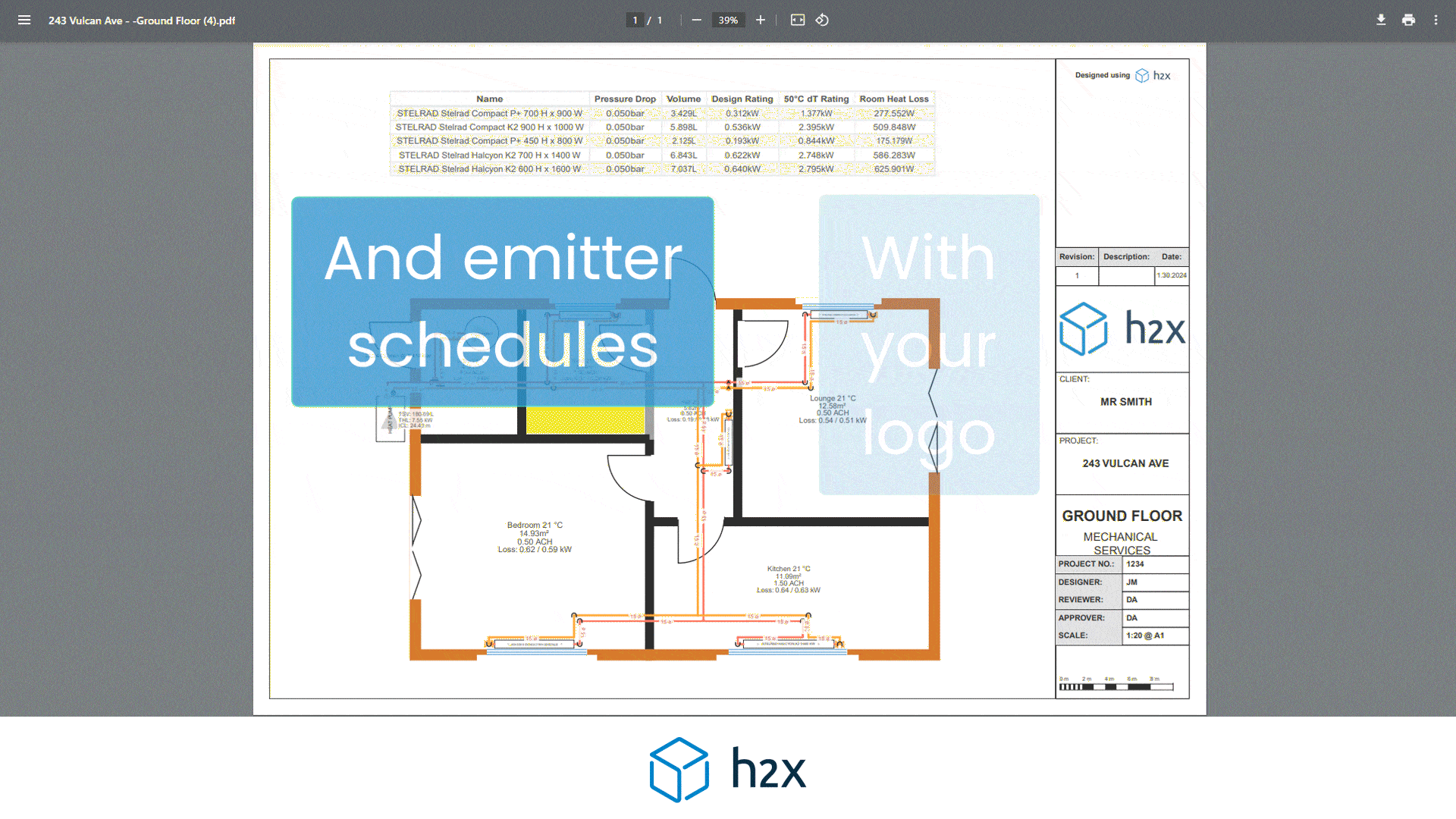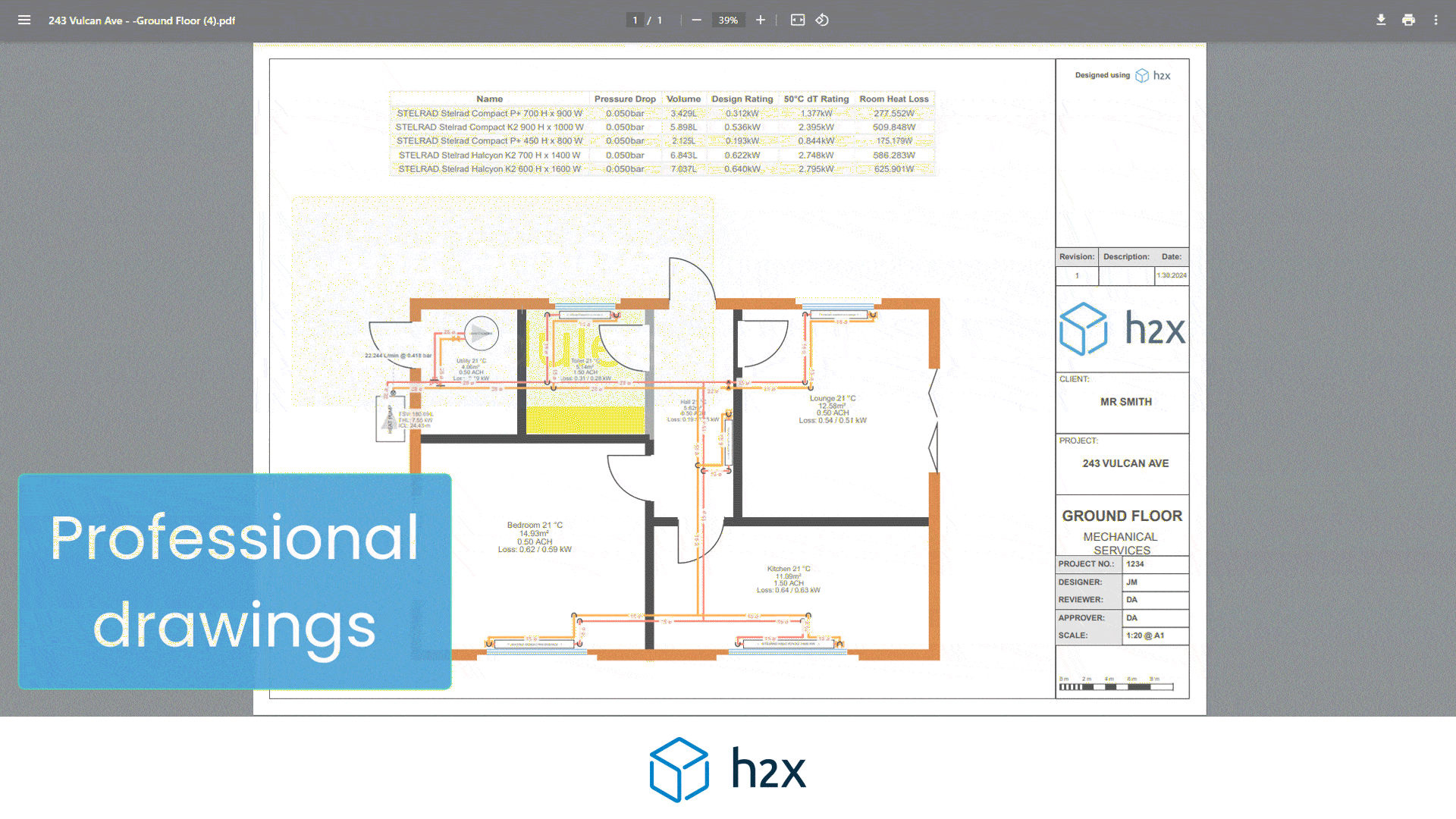
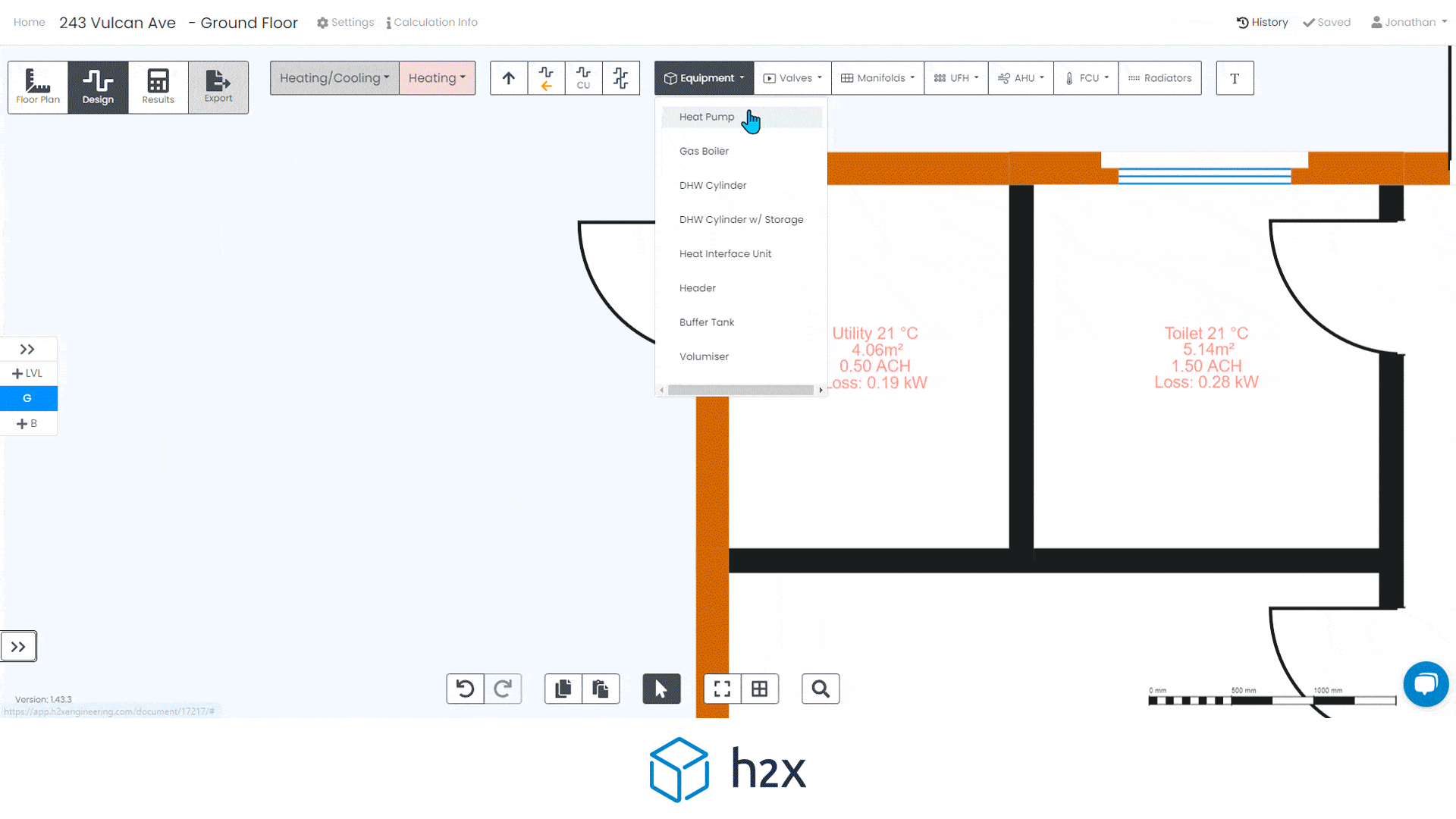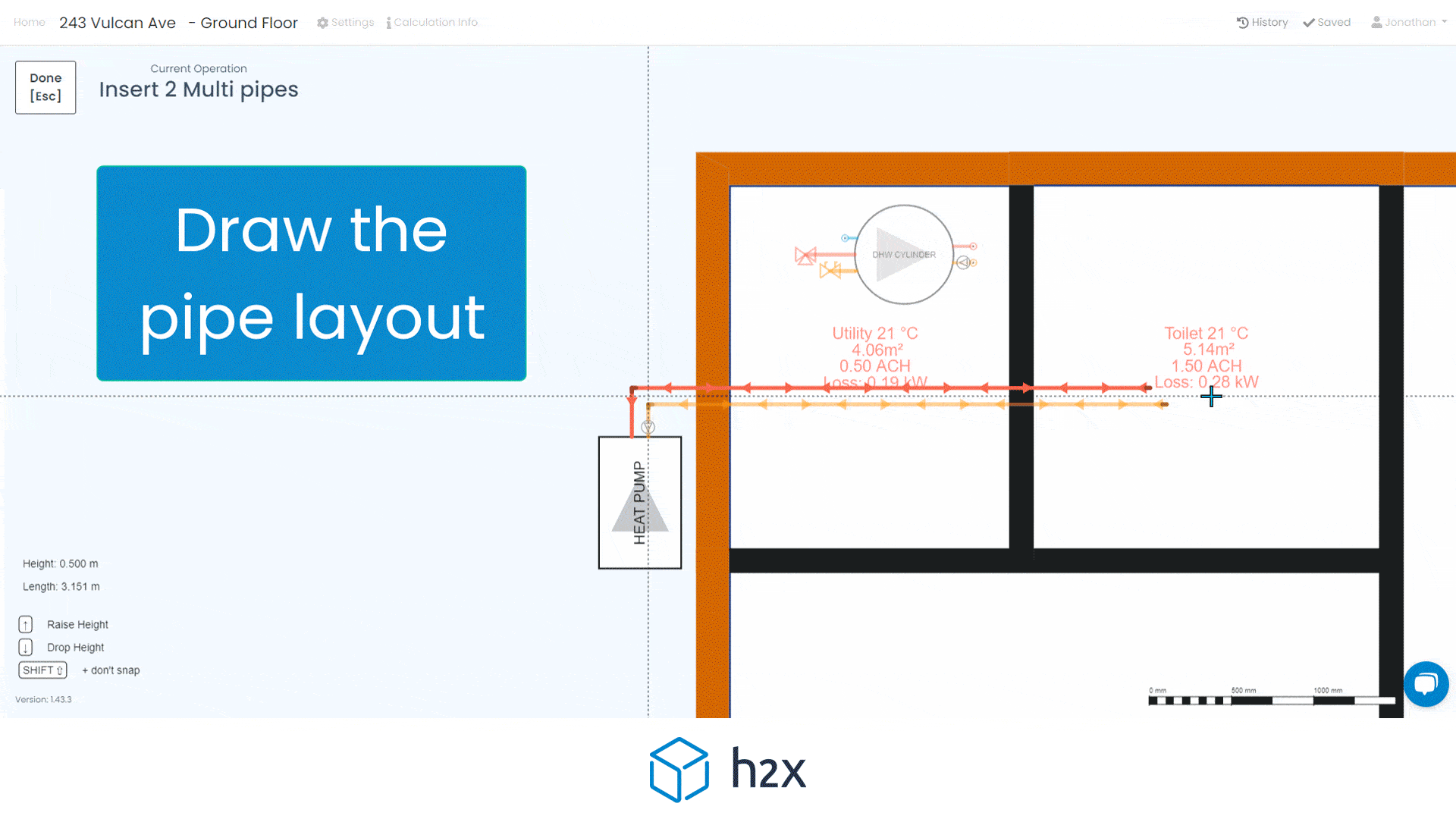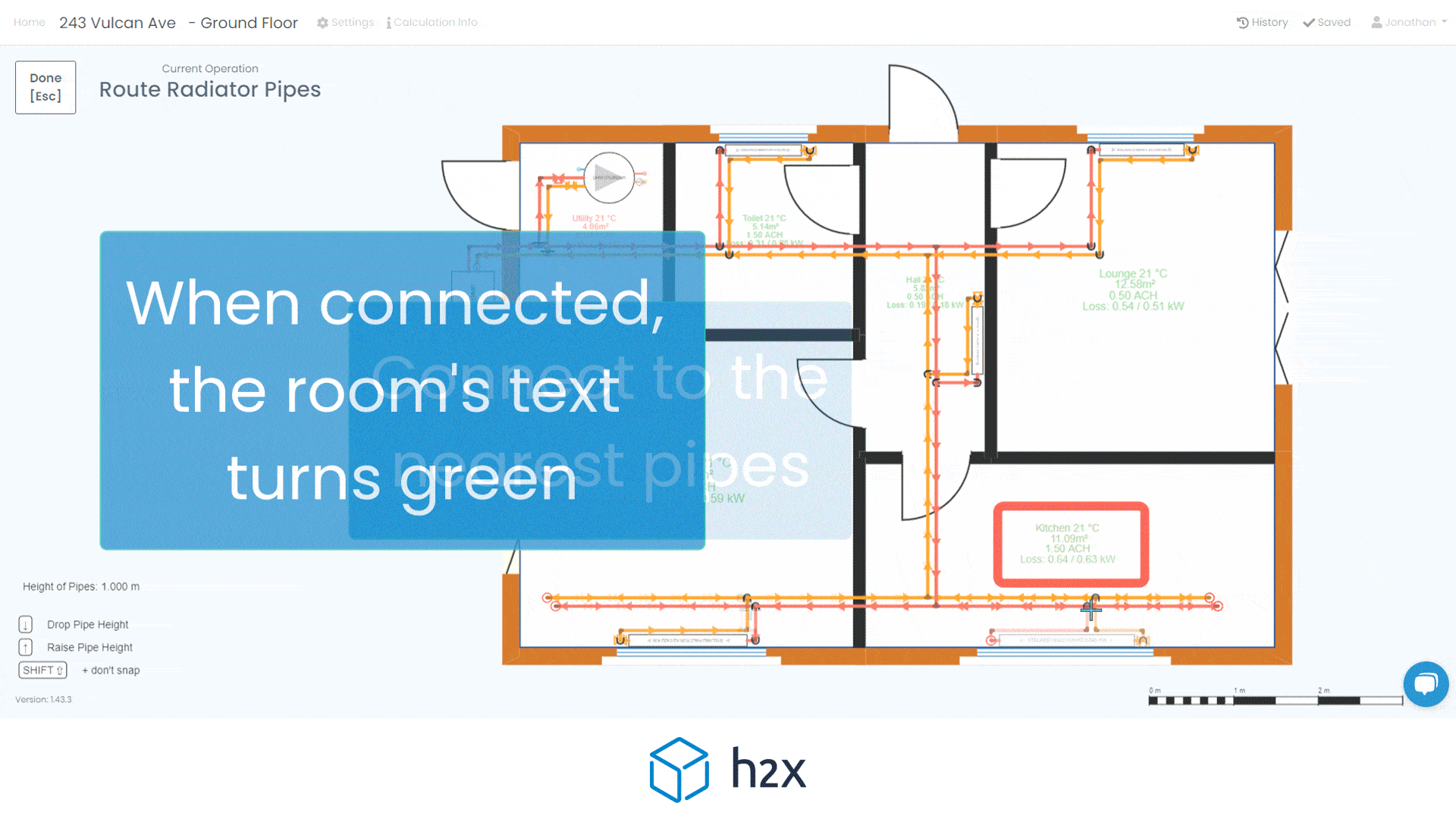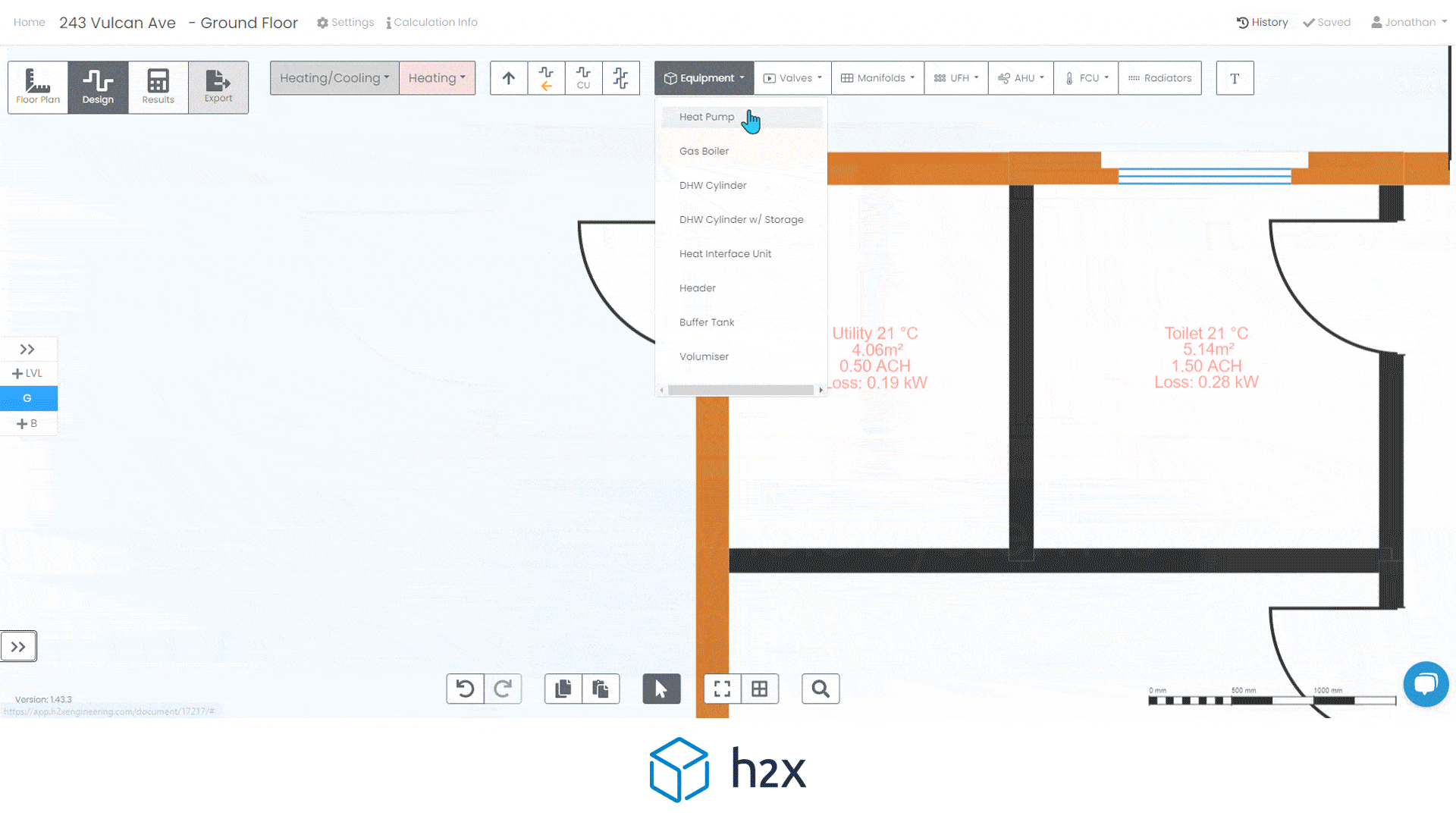
By choosing the right alternative, you can optimise your heat pump system for both efficiency and effectiveness. Using software like h2x can help you realise that you don’t need a buffer tank. By simply drawing your pipe layout and adding equipment, it will give you your system volume result. If it doesn’t meet the minimum requirement, you will receive a warning so you can fix it.
How Do Buffer Tanks Work
So, how does a buffer tank work? In essence, buffer tanks store excess heat or cooling energy generated by your system. When the system’s demand is low, the tank absorbs the extra energy, preventing the equipment from cycling on and off frequently. However, when demand increases, the stored energy is released, ensuring a smooth and efficient operation.
A typical buffer tank piping diagram shows connections between the heat source, the buffer tank, and the distribution system. The tank acts as a thermal reservoir, balancing the load and minimising fluctuations in temperature and flow. Consequently, this not only extends the life of your equipment, but also improves overall system efficiency.
Types of Buffer Tanks
There are several types of buffer tanks to choose from, each designed for specific applications. Primary buffer tanks are used in systems with a single heat source, while secondary buffer tanks are used in systems with multiple heat sources. Some buffer tanks are designed for specific applications, such as buffer tank heat pumps or chiller systems.
Another important distinction is between pressurised and non-pressurised buffer tanks. Pressurised tanks are sealed and operate at system pressure, while non-pressurised tanks are open to the atmosphere and operate at lower pressures. Understanding the different types of buffer tanks and their applications will help you choose the right tank for your system.
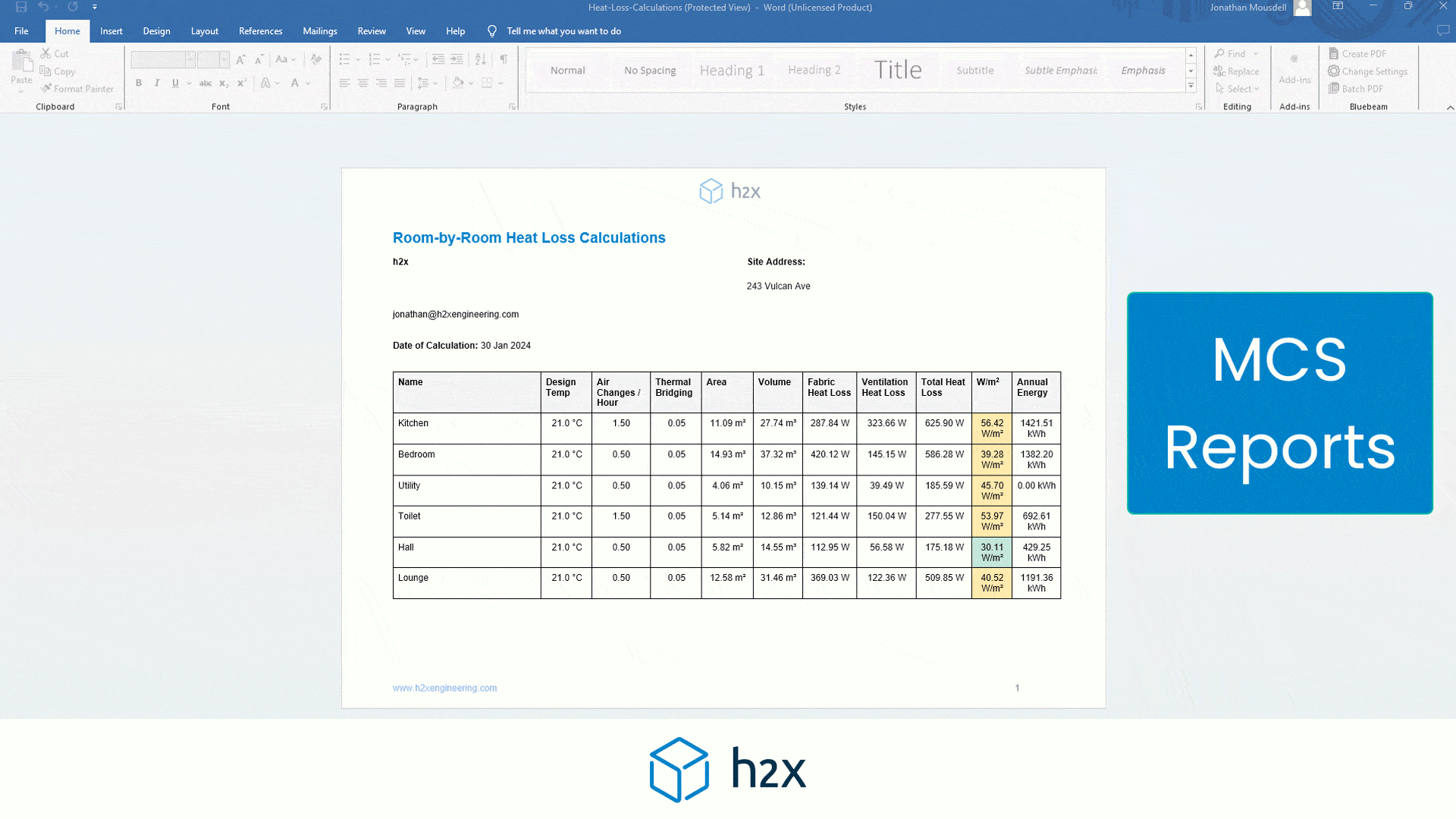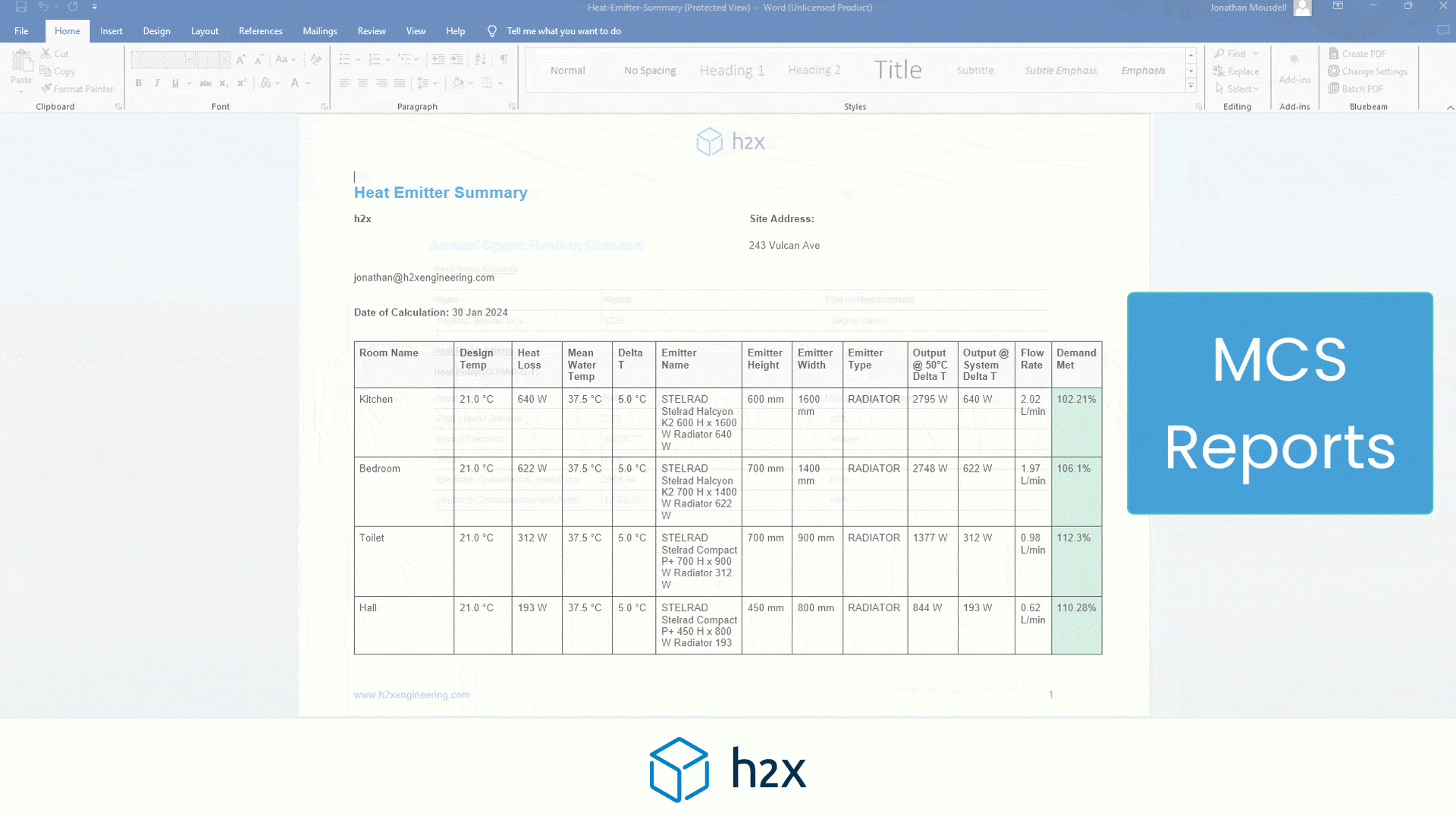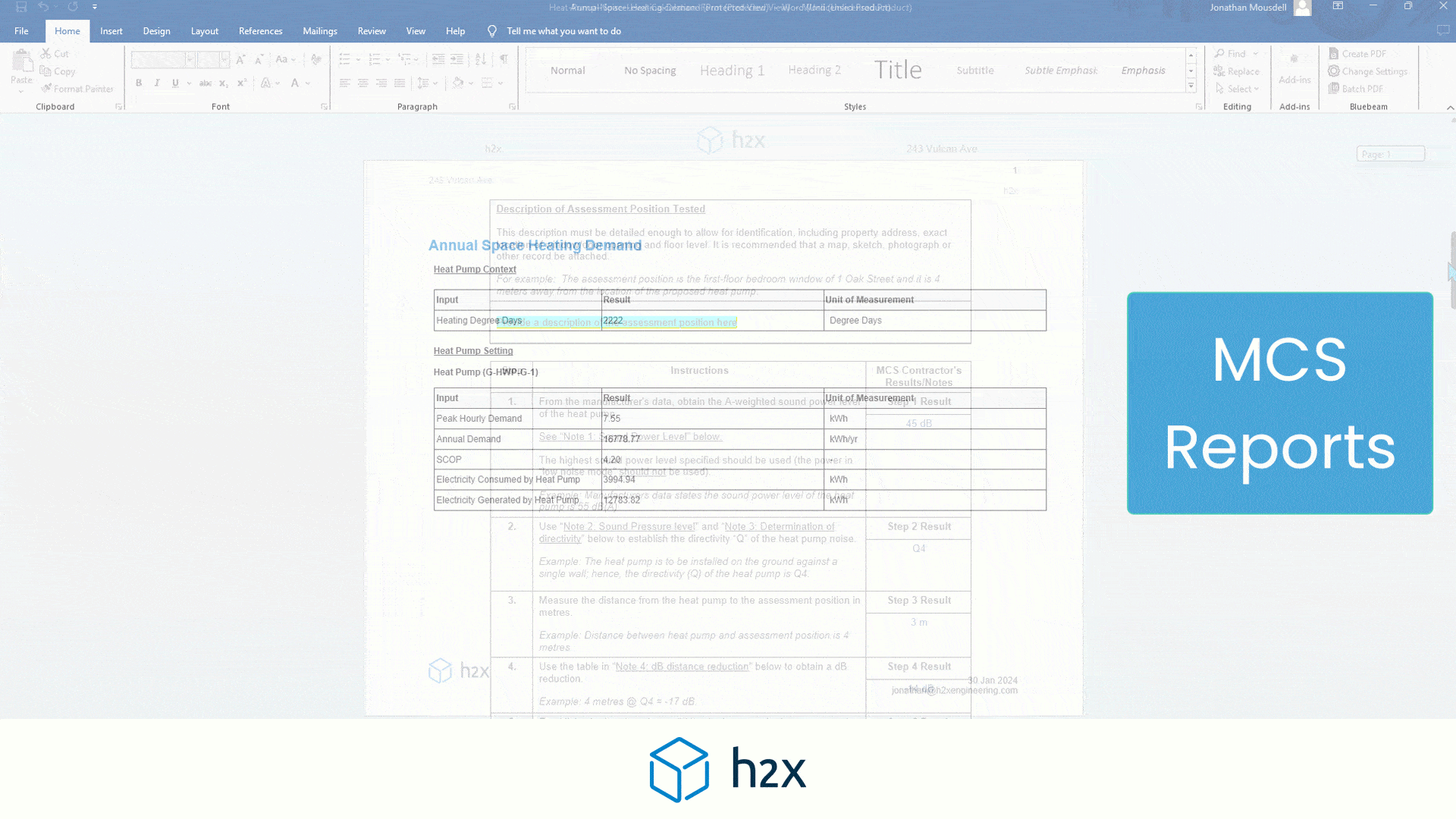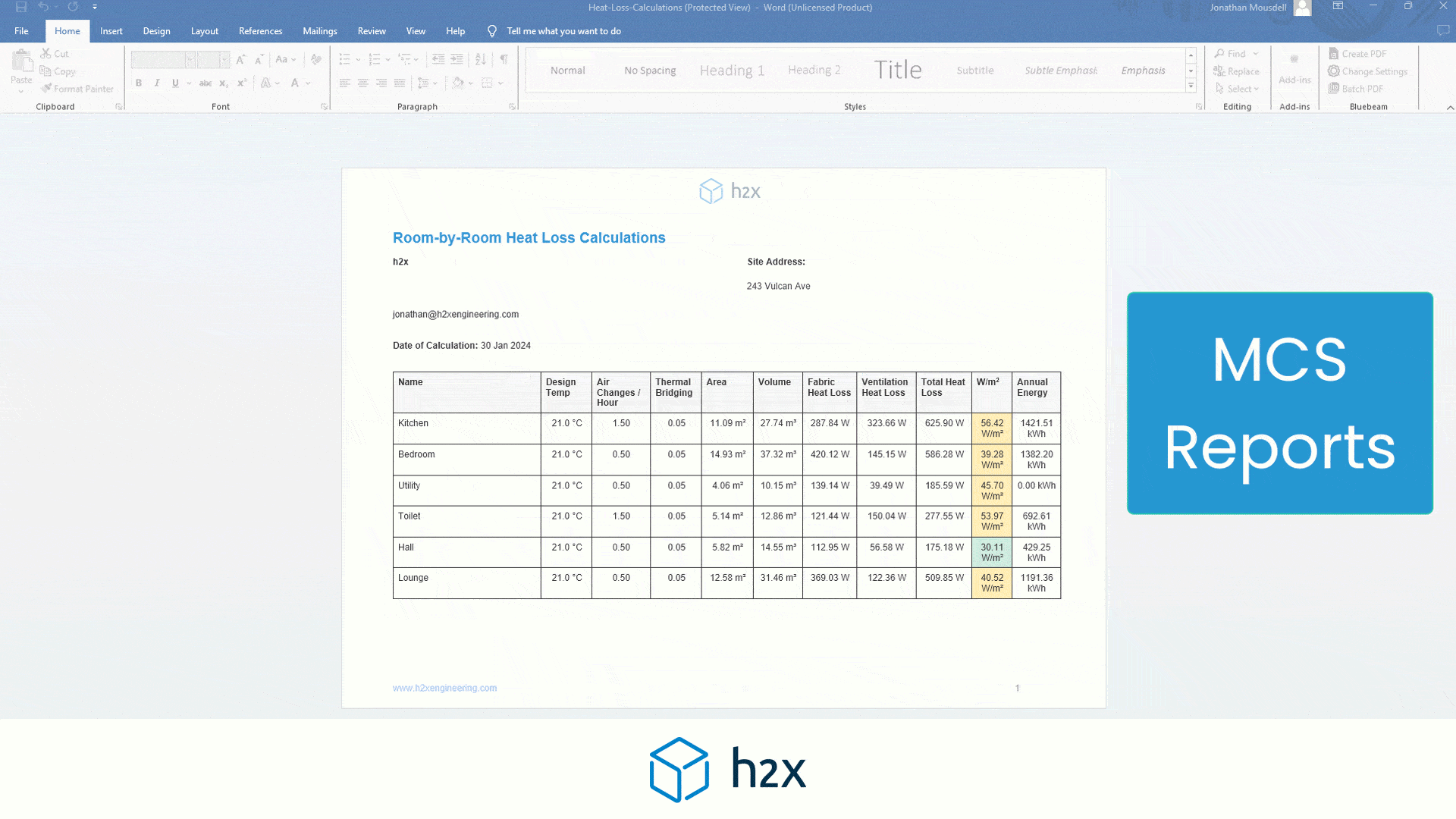
Do You Need a Buffer Tank – Worked Example
1. Determine the Minimum System Volume Requirement of the Heat Pump:
• The first step is to check the heat pump’s technical documentation for the minimum system volume requirement. For instance, let’s assume the heat pump requires a minimum system volume of 200 litres.
2. Calculate the Current System Volume:
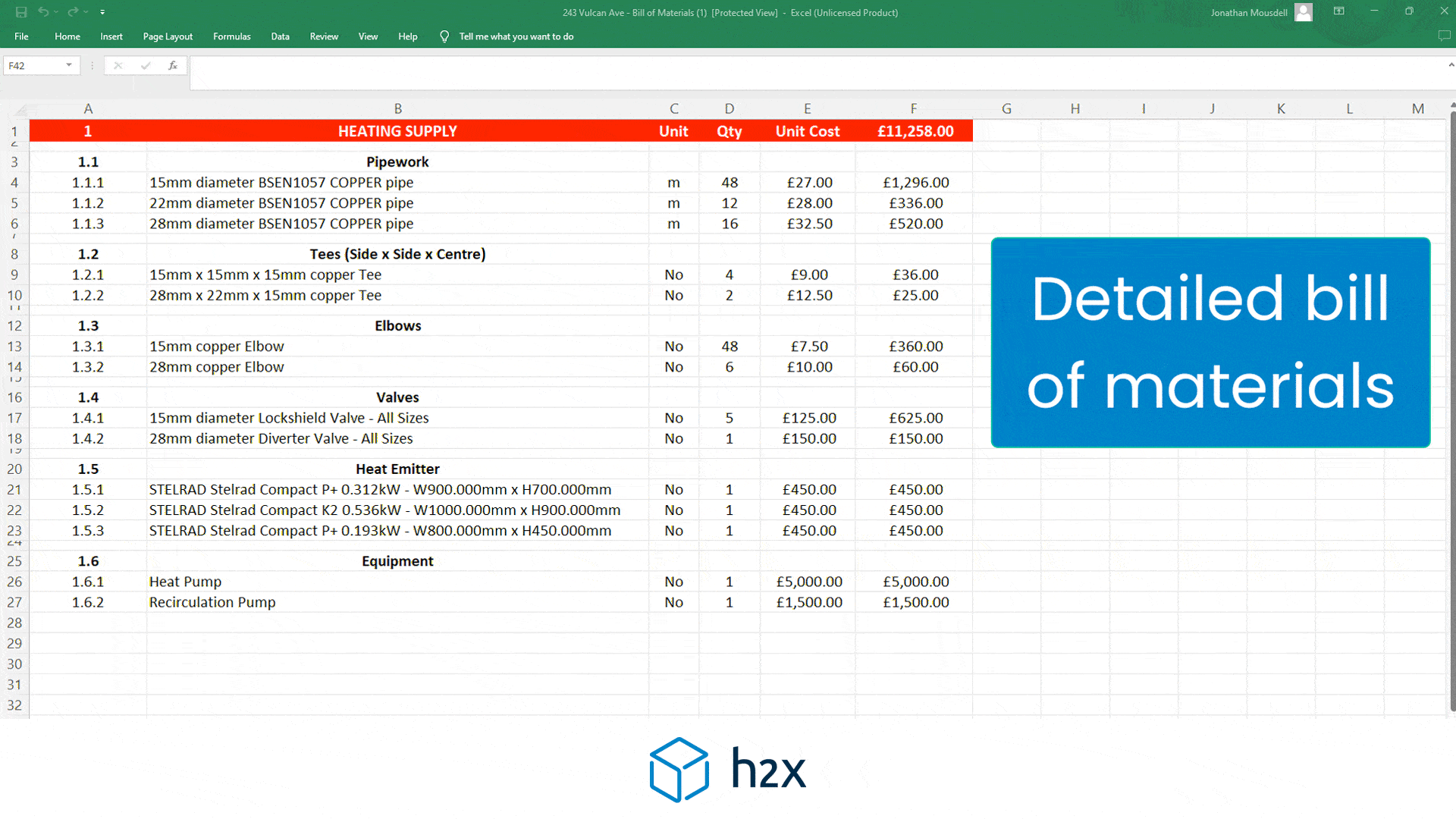
Next, add up the volumes of all the components in the system. This includes:
- Pipes: For example, let’s say the pipes have a total volume of 60 litres.
- Heat Emitters: Suppose the radiators and underfloor heating account for 80 litres.
- Other Equipment: The cylinder coil and other components add up to 30 litres.
3. Total system volume = 60 litres (pipes) + 80 litres (heat emitters) + 30 litres (equipment) = 170 litres.
4. Calculate the Volumiser Required:
• To find the volumiser size needed, subtract the current system volume from the minimum system volume requirement:
5. Volumiser required = Minimum system volume requirement – Current system volume Buffer tank required = 200 litres – 170 litres = 30 litres
In this example, a volumiser of at least 30 liters is required to ensure the system volume meets the minimum requirement of the heat pump. By installing a volumiser instead of a buffer tank, the system can operate efficiently, preventing issues such as short cycling and ensuring optimal performance.
Ensuring the correct volumiser size not only helps maintain the heat pump’s efficiency, but also extends its lifespan by reducing strain on the system. This calculation ensures your system is balanced and operates smoothly, providing reliable and efficient heating for your home or building.
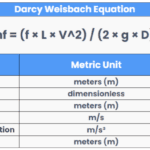
How to Size a Volumiser
h2x makes calculating your heating system’s volume easy. Start by entering the minimum system requirement in the heat pump properties. As you draw the pipe layout, h2x calculates volume based on size and length, combining it with the volume in any emitters.
You can exclude control valves from the calculation by isolating them. For equipment like cylinders with coils, input the volume. If the total volume doesn’t meet the minimum requirement, h2x will alert you to improve the system, including adding volumisers.
Maintenance and Care of Buffer Tanks
For long-term performance of your volumiser/buffer tank, regular maintenance and care is paramount. Start by inspecting your tank regularly for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Clean the tank and its components as needed, and check the insulation to ensure it’s in good condition.
It’s also important to monitor the tank’s pressure and temperature, as well as the performance of your overall system. Regularly check and replace any worn or damaged parts, and follow the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations. By taking good care of your buffer tank, you can extend its lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any system component, buffer tanks can experience issues from time to time. Common problems include leaks, pressure fluctuations, and temperature inconsistencies. To troubleshoot these issues, start by checking the tank and its connections for any signs of leaks or damage.
If you’re experiencing pressure or temperature issues, check the tank’s pressure relief valve and thermostat. Ensure that the tank is properly insulated and that the system is balanced and operating efficiently. By addressing these common issues, you can keep your buffer tank and system running smoothly.

Buffer Tanks in Software like h2x
Software tools like h2x can help simplify the design and sizing of buffer tanks in HVAC systems. h2x provides detailed simulations and calculations, helping you determine the optimal size and configuration for your buffer tank.
Using h2x software ensures you size and install your buffer tank correctly, improving system performance and efficiency. This will also save you time and effort, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your HVAC project.
If you’re interested in learning more about h2x, we’d love to hear from you. You can book a demostration or sign up for a 14-day free trial today!
Conclusion: Is a Buffer Tank Right for Your System?
In conclusion, buffer tanks are a valuable addition to many HVAC systems, offering numerous benefits in terms of efficiency, performance, and comfort. Whether you’re dealing with variable loads, short cycling, or inconsistent temperatures, a buffer tank can help address these issues and improve your overall system.
By understanding how buffer tanks work, how to size them correctly, and how to maintain them, you can make an informed decision about whether a buffer tank is right for your system. With the right buffer tank, you can enjoy a more efficient, reliable, and comfortable heating and cooling experience.
FAQs
What is a buffer tank in a chiller system?
A buffer tank in a chiller system stores excess cooling energy, helping to balance load fluctuations and maintain a steady temperature.
How do buffer tanks work in HVAC systems?
Buffer tanks store excess heat or cooling energy, reducing short cycling and ensuring a consistent temperature and flow in the system.
What are the benefits of using buffer tanks in a heating system?
Buffer tanks improve system efficiency, reduce wear and tear on equipment, enhance comfort by maintaining consistent temperatures, and can store excess energy in renewable systems.
How do I choose the right buffer tank for my system?
Consider factors such as the type of system, the specific application, the size and capacity of the tank, insulation, installation requirements, and maintenance needs.
How do buffer tanks benefit solid fuel heating systems and biomass boiler hydronic systems?
Buffer tanks improve the efficiency of solid fuel heating systems and biomass boiler hydronic systems by storing excess thermal energy, ensuring a consistent heat supply even when demand fluctuates.
What role do thermal storage tanks play in managing heat pump capacity?
Thermal storage tanks help manage heat pump capacity by storing surplus heat, allowing the heat pump to operate efficiently and providing a steady supply of thermal energy to the heating distribution system.
Why is mild steel construction preferred for buffer tanks in heating systems?
Mild steel construction is preferred for buffer tanks due to its durability and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for use in biomass boiler systems, domestic hot water applications, and other heating systems.
What are some of the most popular brands of buffer tanks?
Some of the most popular brands of buffer tanks include Amtrol, Lochinvar, Rheem, and Flexcon. These brands offer reliable, durable, and efficient options for various HVAC applications.
What are some common issues with buffer tanks and their solutions?
Common issues include leaks, pressure fluctuations, and temperature inconsistencies. Solutions involve checking for leaks or damage, ensuring proper insulation, and maintaining system balance and efficiency.
h2x: All-In-One Tool for Calculating, Designing, Estimating, and Paperwork
What's in the Pipeline?
Get technical resources delivered to your inbox weekly!
Testimonials
What Installers Say
What Consultants Say
A game changer for the humble plumber. Incredible.
Brad Winkel
Director at Queenstown Plumbing
Brilliant, simple and easy to use. Game changer.
James Major
Director at Hubb
Big time game changer to the industry!
Viv Jude
Director at UHC
Incredible software! Super user-friendly and allows you to save so much time.
Devni Gamage
Engineer at DMA
h2x is great software, our company use it nearly every day. It is easy to use with direct conversion from h2x to Revit.
Callum Craig
Engineer at WDE
h2x is fantastic software. It is very easy to use and the ability to output to Revit is a fantastic time saver.
Joe Kirrane
Engineer at MEP