Choosing the Best Protection: Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol in Heat Pump Systems
Discover the pros and cons of anti-freeze valves vs. glycol in heat pump systems. Make informed decisions for your heating projects!

If you’re deciding how to protect your heat pump system from the clutches of cold, understanding the difference between anti-freeze valves and glycol is crucial.
This article cuts through the complexity, providing a head-to-head comparison of anti-freeze valves vs. glycol to help you choose the best freeze protection strategy.
Explore the technical differences, costs, and maintenance requirements of anti-freeze valves vs. glycol, setting the stage for an informed decision without prematurely revealing the in-depth analysis you’ll find ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Anti-freeze valves and glycol are two methods used to protect heat pump systems from freezing. The valves provide a mechanical solution while glycol offers a chemical prevention by lowering the freezing point of fluids.
- Each system has its advantages and disadvantages: Anti-freeze valves are cost-effective, low maintenance, and enhance system efficiency. Whereas glycol is high maintenance, reduces efficiency due to lower heat capacity and higher viscosity, and can be toxic, especially ethylene glycol.
- Considerations for choosing between anti-freeze valves and glycol include: climate conditions, heat pump system requirements and efficiency, maintenance and cost implications, and manufacturer recommendations, as well as safety and environmental impact.
Understanding Anti-Freeze Valves and Glycol
In the field of heat pump systems, anti-freeze valves and glycol are hailed as protectors against the icy clutches of freezing temperatures.
But what do they do, and how do they do it?
Anti-freeze valves function as protective overseers, releasing pressure and maintaining consistent system temperatures, thereby preventing freezing.
On the other hand, glycol, serving as a heat transfer fluid, inhibits freezing by reducing the fluid’s freezing point within the system.
Despite their shared goal, their strategies differ significantly.
While anti-freeze valves use a mechanical approach, glycol resorts to a chemical one.
Anti-Freeze Valves
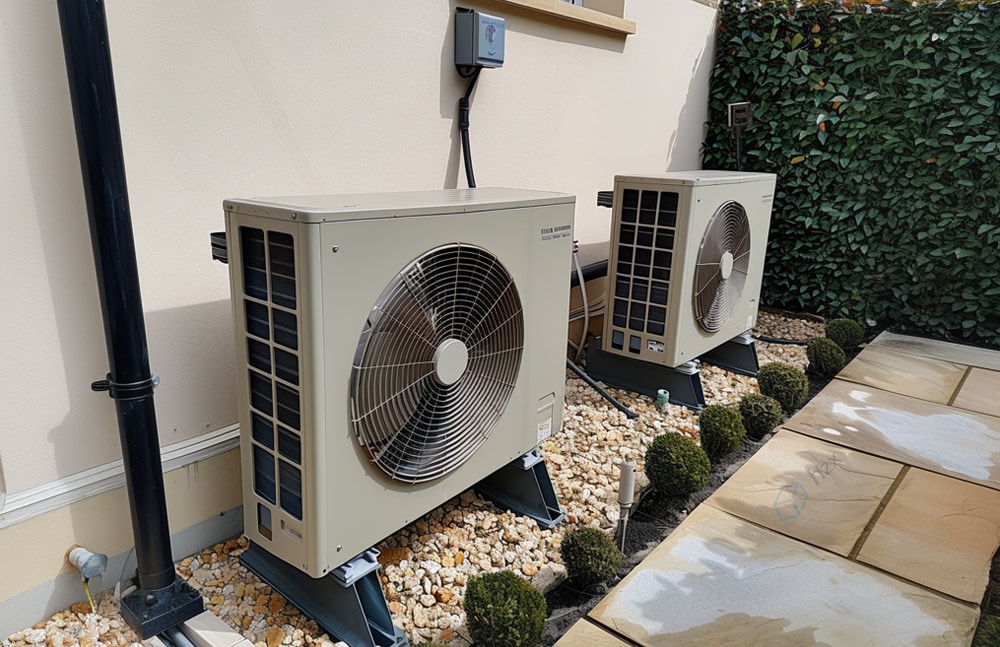
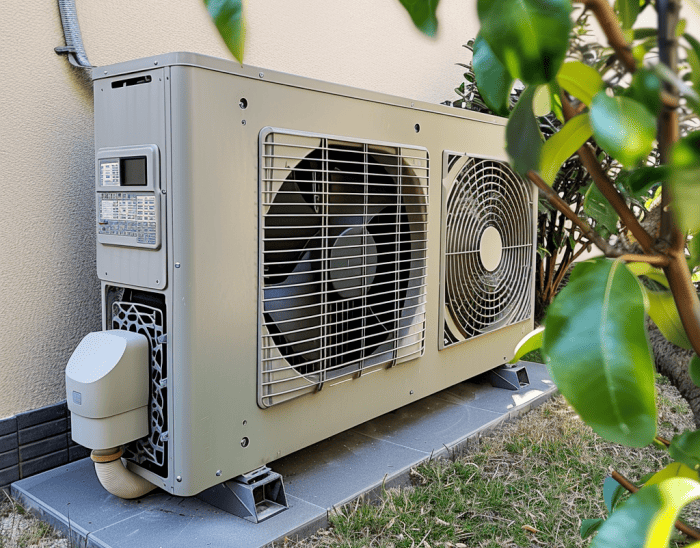
Heat pump systems heavily rely on the role of anti-freeze valves for protection.
They work tirelessly to avert the formation of ice, eliminating potential damage to the equipment.
Acting as attentive overseers, these valves drain the system at temperatures of approximately 3°C to 4°C, serving as a trigger to prevent freezing.
Once activated, these valves perform a dual function – draining water and admitting air.
However, this action necessitates bleeding the system to resume operation, a step not required in glycol systems, which can restart swiftly after a freeze event.
Glycol
The second key player, glycol, acts as an antifreeze solution in heating systems.
By reducing the freezing point of the fluid, glycol guarantees system operation even in extremely cold conditions.
Glycol comes in two popular varieties – ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
Ethylene glycol, though effective, carries a higher toxicity risk compared to its counterpart, propylene glycol, which is considered safer and even used as a food additive in certain scenarios.
Comparing the Pros and Cons
As we head deeper into the world of heat pump protection, it becomes evident that both anti-freeze valves and glycol have their unique strengths and weaknesses.
The initial cost for both methods is similar, making this factor neutral in the selection process.
However, the choice isn’t as simple as a coin toss.
Various types of glycol exist, such as ethylene and propylene, each boasting specific properties that make them suitable for different operating temperatures in heat pump systems.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Anti-Freeze Valves
Anti-freeze valves offer a host of benefits that make them an attractive option for many.
Primarily, they are cost-effective.
Unlike glycol solutions which require ongoing maintenance, anti-freeze valves are a one-time purchase.
In fact, purchasing two antifreeze valves can be a smart investment for larger systems.
Moreover, they are low-maintenance and have a typical lifespan of about 7-8 years without needing attention.
They also enhance the efficiency of HVAC systems by allowing the system to operate with the inherent fluidity of water, thereby improving performance.
One downside of anti-freeze valves is their potential to complicate the system by necessitating extra components, leading to possible points of failure.
Additionally, they may pose a risk of system leaks if not properly installed, potentially causing fluid loss and damage to other components.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Glycol
Glycol offers several advantages, including freeze protection by preventing water in the heat pump system from freezing during cold temperatures, safeguarding against cold-induced damage.
Additionally, it contains corrosion inhibitors, extending system component lifespan and reducing maintenance needs.
Moreover, glycol solutions can be customised to meet specific temperature and performance requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications and climates.
Many glycol formulations are biodegradable and environmentally friendly, minimising the impact on the ecosystem if accidental spills did occur.
However despite its benefits, glycol does have some drawbacks.
To start, it’s considerably expensive, with a 20-liter container setting you back around £200 / $250, and you may need multiple containers.
Moreover, glycol systems demand regular fluid testing and periodic replacement, making them high maintenance.
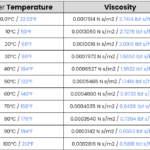
Added to this, glycol reduces system efficiency due to its lower heat capacity and higher viscosity, causing the heat pump to consume more energy to circulate the fluid and achieve necessary temperatures.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Protection
Several considerations come into play when deciding between anti-freeze valves and glycol.
For example, the potential for system failures or extended power outages during cold weather could influence your decision.
Other influencing factors include the regularity and intensity of power outages, system failures, power lines, environmental temperatures, and water temperature in your decision with anti-freeze valves vs. glycol.
A modern twist in this tale is that built-in safety features in contemporary air source heat pumps, like the outdoor unit, may reduce the need for additional antifreeze measures like glycol or anti-freeze valves.
Climate and Weather Conditions – Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol
Your decision to use glycol or anti-freeze valves is highly influenced by climate and weather conditions.
The frequency and duration of sub-zero temperatures in your region can dictate the necessity for either of these protections in your heat pump system.
In colder climates or sudden drops in temperature, using glycol or anti-freeze valves becomes crucial to provide extra protection against freezing risks.
For areas particularly prone to freezing conditions, glycol could be the preferred choice, especially in parts of the heating system that may be unoccupied or not heated continuously.
System Requirements – Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol
The unique needs and requirements of each heat pump system can sway the choice of freeze protection.
For instance, when selecting pumps for glycol usage, it’s essential to ensure the pump manufacturer approves glycol use to maintain the pump’s warranty.
Interestingly, heat pumps are more efficient with anti-freeze valves due to water’s better fluidity compared to glycol-based fluids.
This insight brings another dimension to the decision-making process.
Maintenance and Cost – Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol
The intertwined factors of maintenance and cost can significantly impact your heat pump system protection choice.
Anti-freeze valves offer the advantage of a longer working life and require no maintenance post-installation, making them a one-time expense.
On the other hand, glycol may need replacement over time due to degradation, leading to recurring costs, and contamination from degradation can increase viscosity, thus leading to higher pumping costs.
However, remember that post-activation of anti-freeze valves might necessitate manual system refills, adding to maintenance efforts.
It’s also important to note that using both methods concurrently is typically discouraged due to the lack of additional benefits and associated cost inefficiency.
Heat Pump Manufacturer Recommendations
Considering expert advice is always beneficial when exploring the complex world of heat pump protection.
Heat pump manufacturers often have varying recommendations about the use of anti-freeze valves and glycol.
For instance, Mitsubishi specifically endorses the use of anti-freeze valves, provided the freeze stat function on the FTC6 controller is activated.
On the other hand, some manufacturers accept antifreeze valves as a valid solution for freeze protection without specifying any operational conditions.
However, Bosch advises against the use of glycol in their heat pump systems.
Safety Concerns and Environmental Impact
Safety concerns and environmental impact must be taken into account when deciding between anti-freeze valves and glycol.
Glycol, especially ethylene glycol, is toxic and can pose a health hazard if ingested, requiring careful handling and disposal.
Anti-freeze valves, on the other hand, are not associated with toxicity risks, providing a safer alternative to glycol-based systems in terms of chemical hazards and offering anti-freeze protection.
However, glycol can contaminate groundwater if leaks occur, leading to environmental damage and potential harm to animals and plants.
The use of corrosion inhibitors can help mitigate these risks.
Toxicity of Glycol
Awareness of glycol’s toxicity is crucial when using it in a heat pump system.
Glycol poses a risk if ingested, necessitating careful handling during system drainage.
Specifically, ethylene glycol, commonly used in heat pump systems, is highly toxic.
It can cause dermatitis upon skin contact, and ingestion can be lethal to adults.
Thus, handling glycol requires utmost caution to prevent toxicity issues.
Environmental Considerations – Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol
Glycol also hold significant environmental implications that demand attention.
Ethylene glycol is hazardous to the environment, and spills need to be reported to environmental authorities.
However, propylene glycol poses a lower indirect environmental impact due to its reduced toxicity.
The risk of borehole grout cracking due to the use of antifreeze additives can lead to cross-contamination between aquifers.
Furthermore, glycol contributes to environmental pollution, which is exacerbated by potential leaks and spills.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance are key to maximising the effectiveness of your chosen heat pump system protection.
Whether you opt for anti-freeze valves or glycol, here are some tips to follow:
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation and maintenance.
- Use qualified technicians for the installation to ensure proper setup.
- Regularly check and maintain the system to ensure optimal operation.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your heating system protection is working efficiently.
As for maintaining glycol levels, consult the manufacturer’s manual or a professional service, as specific maintenance instructions may not be readily available.
Installing Anti-Freeze Valves
The installation of anti-freeze valves necessitates accuracy and caution.
They must be positioned outdoors, in the system’s coldest area vulnerable to freezing.
Some manufacturers recommend to install them on both pipes (flow and return), away from heat sources that could disrupt operation.
First, locate the appropriate point on the lower pipe of the heat pump system where the valve should be installed.
Then, cut the pipework at the marked location and prepare for the valve installation.
Maintain a clearance of at least 15 cm from the ground to ensure unfettered water release and a minimum distance of 10 cm between valves.
Securely tighten the nuts to install the valve and ensure a firm fit on the flow and return pipes.
After installation, repressurise the heating circuit to the specified pressure level and check the valve for leaks.
Maintaining Glycol Levels
Ensuring optimal glycol levels is a key aspect of heat pump system protection.
Glycol requires routine testing for degradation and contamination, which may necessitate fluid replacement.
Implementing leak detection systems and secondary containment methods like drip pans can help manage leaks should they occur.
Lastly, the glycol concentration in the system water solution should match the system’s freezing protection requirements, typically a 30% glycol to 70% water dilution.
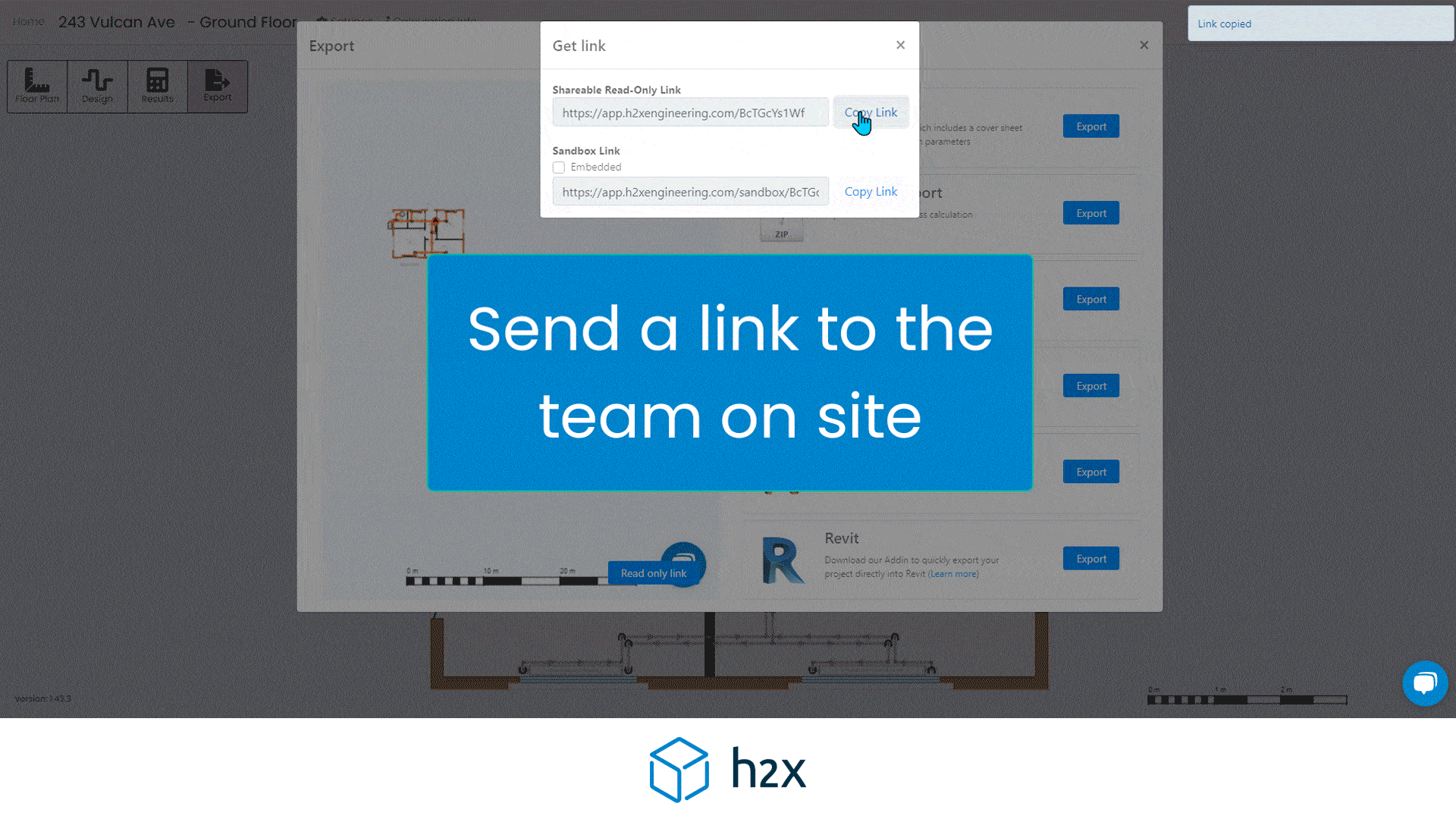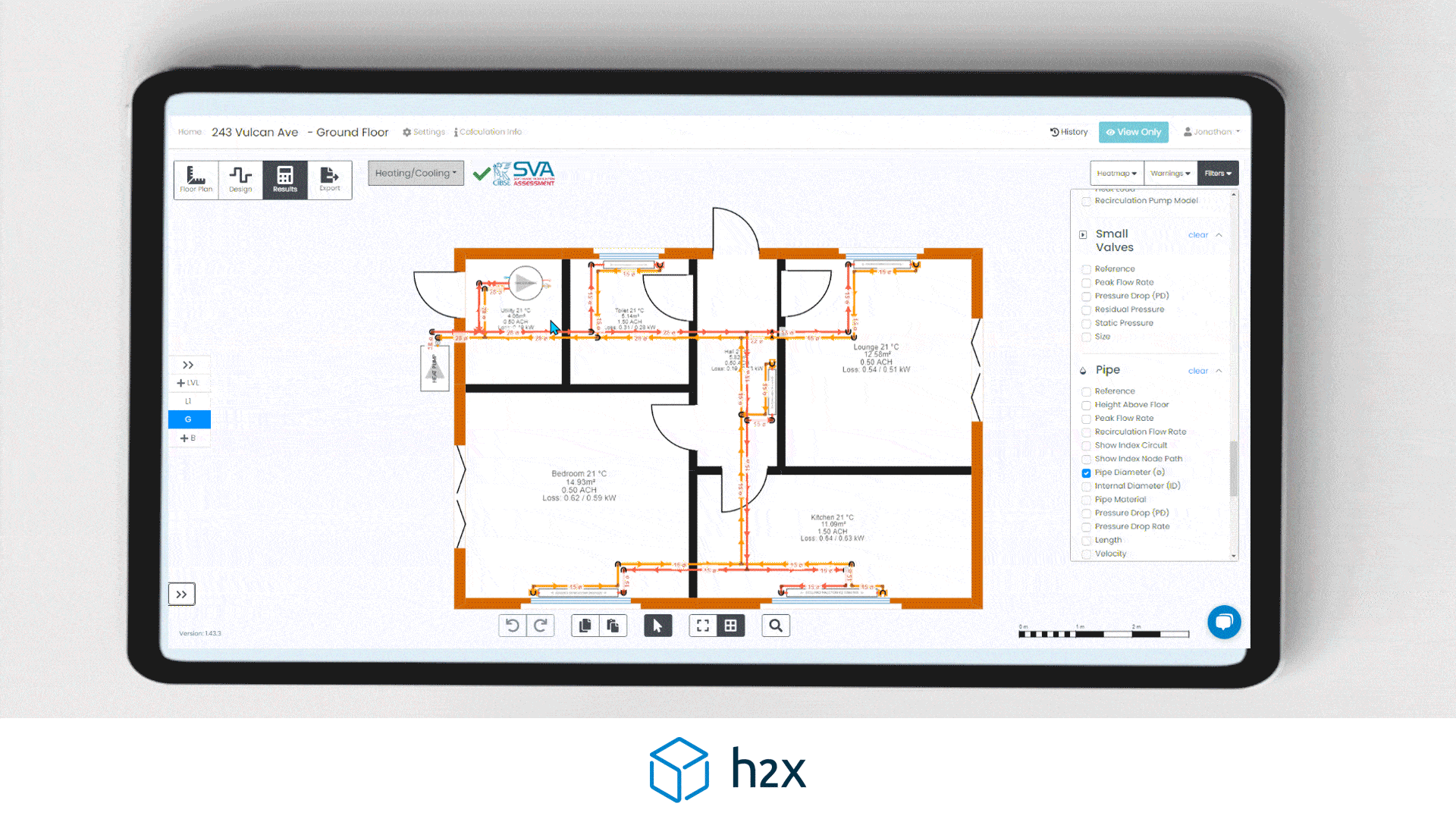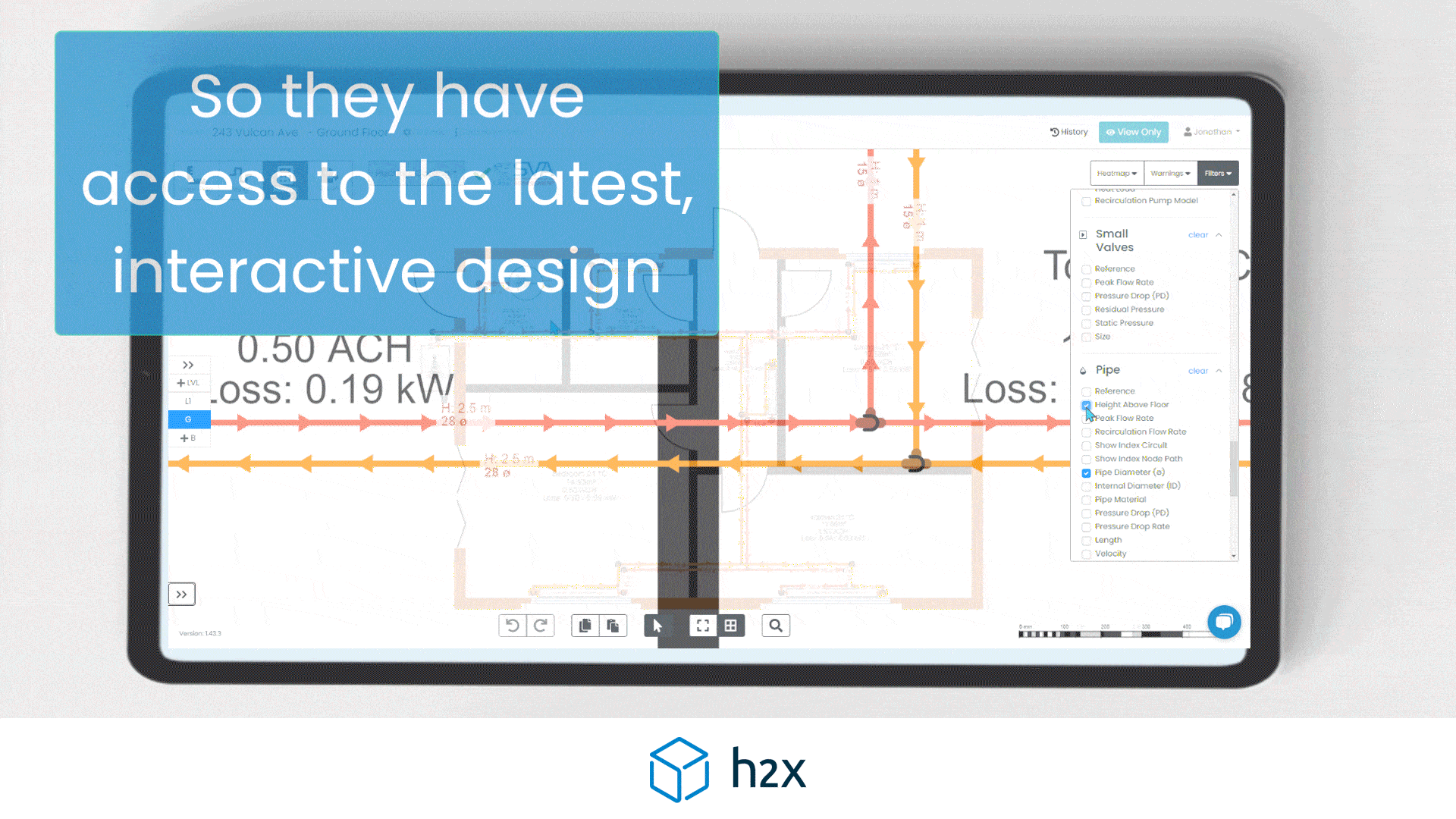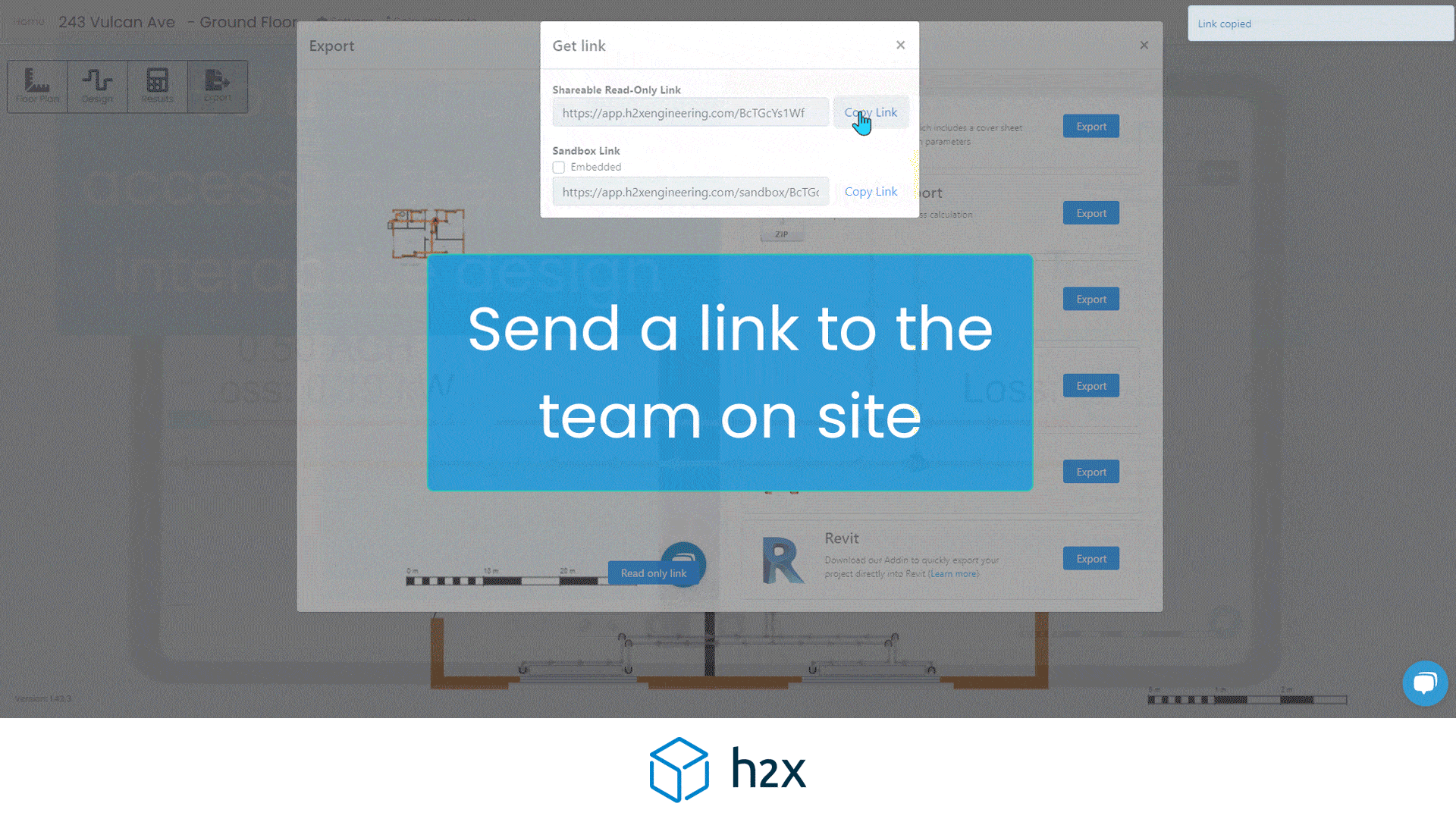
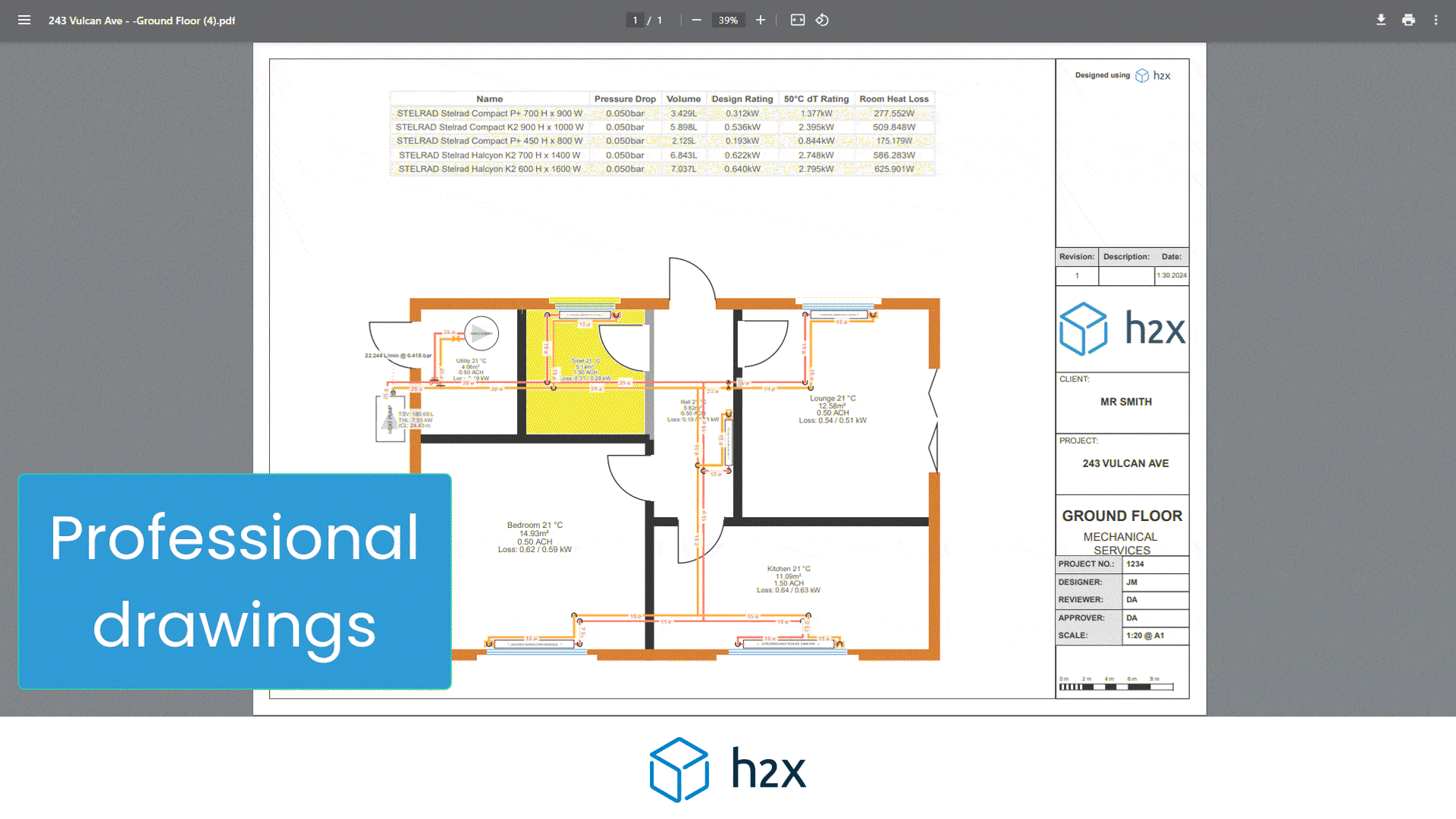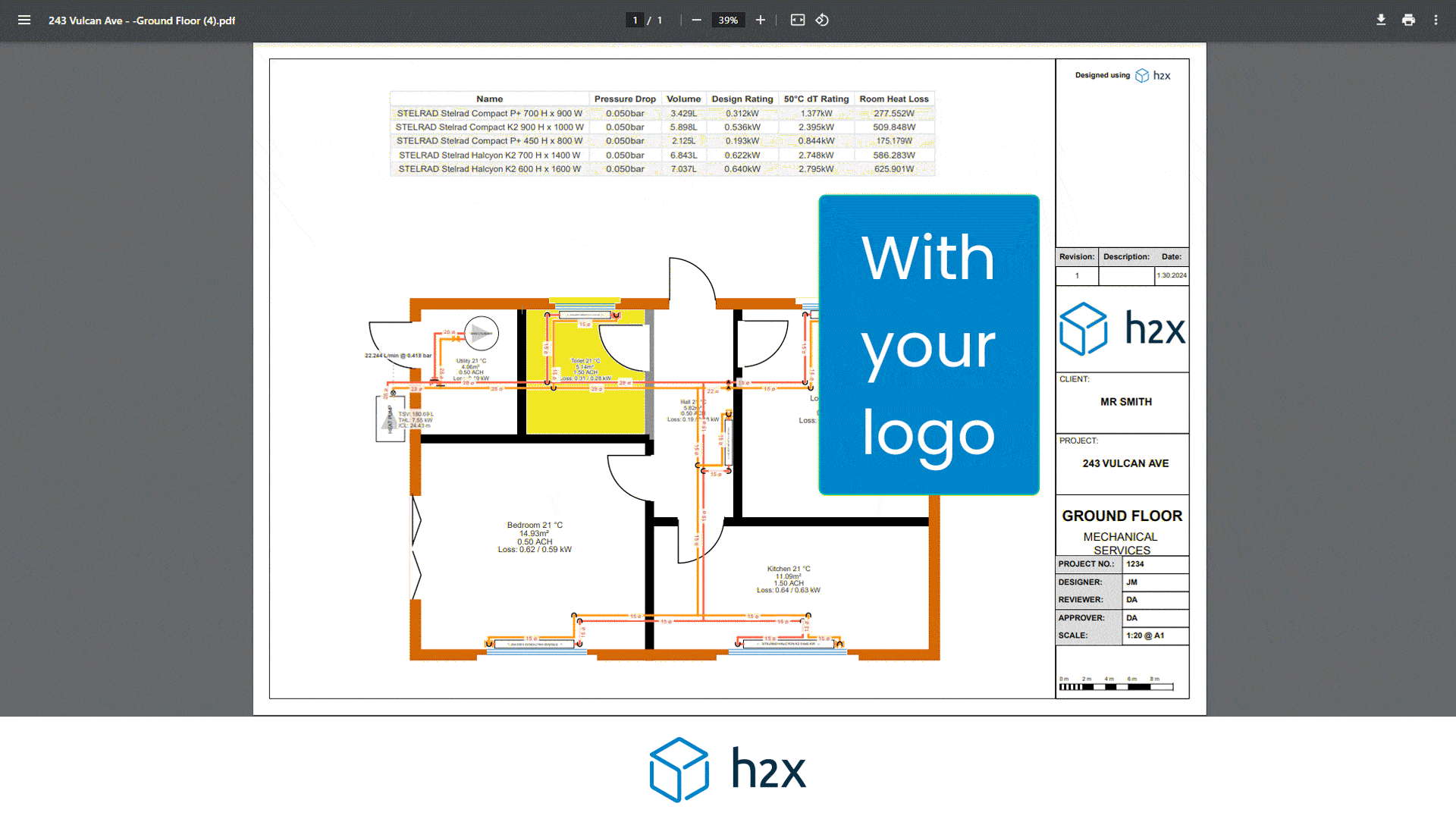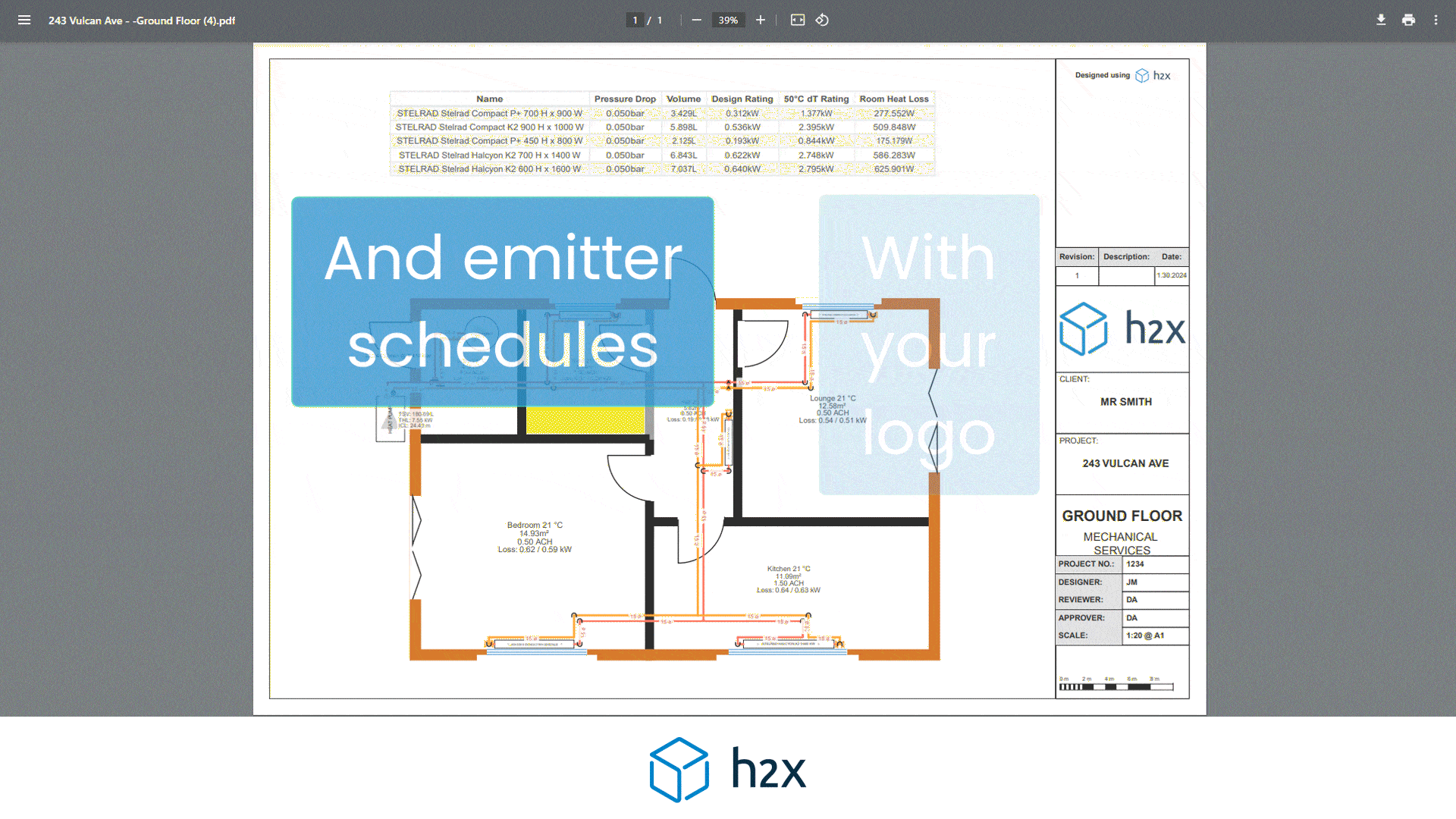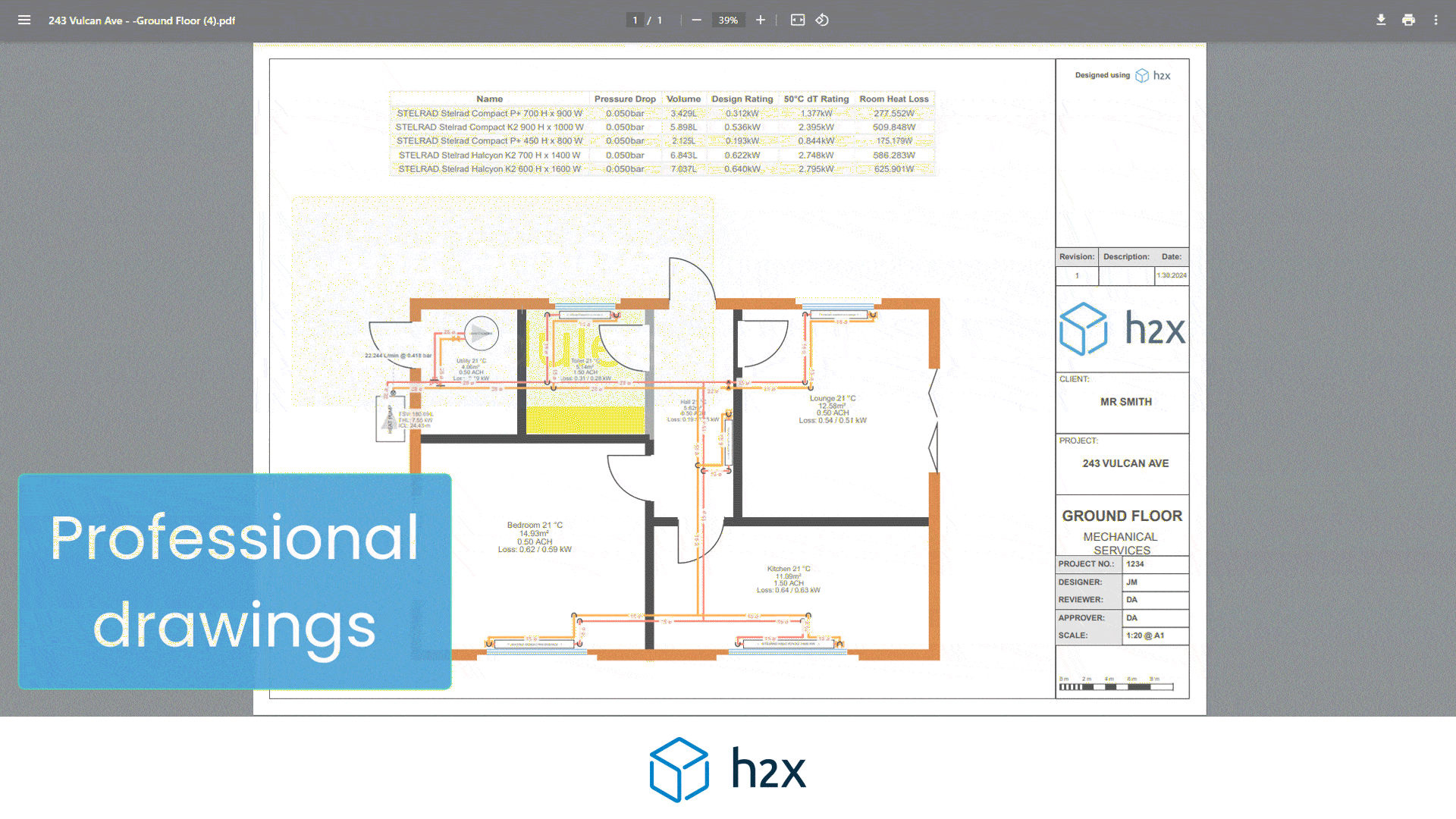
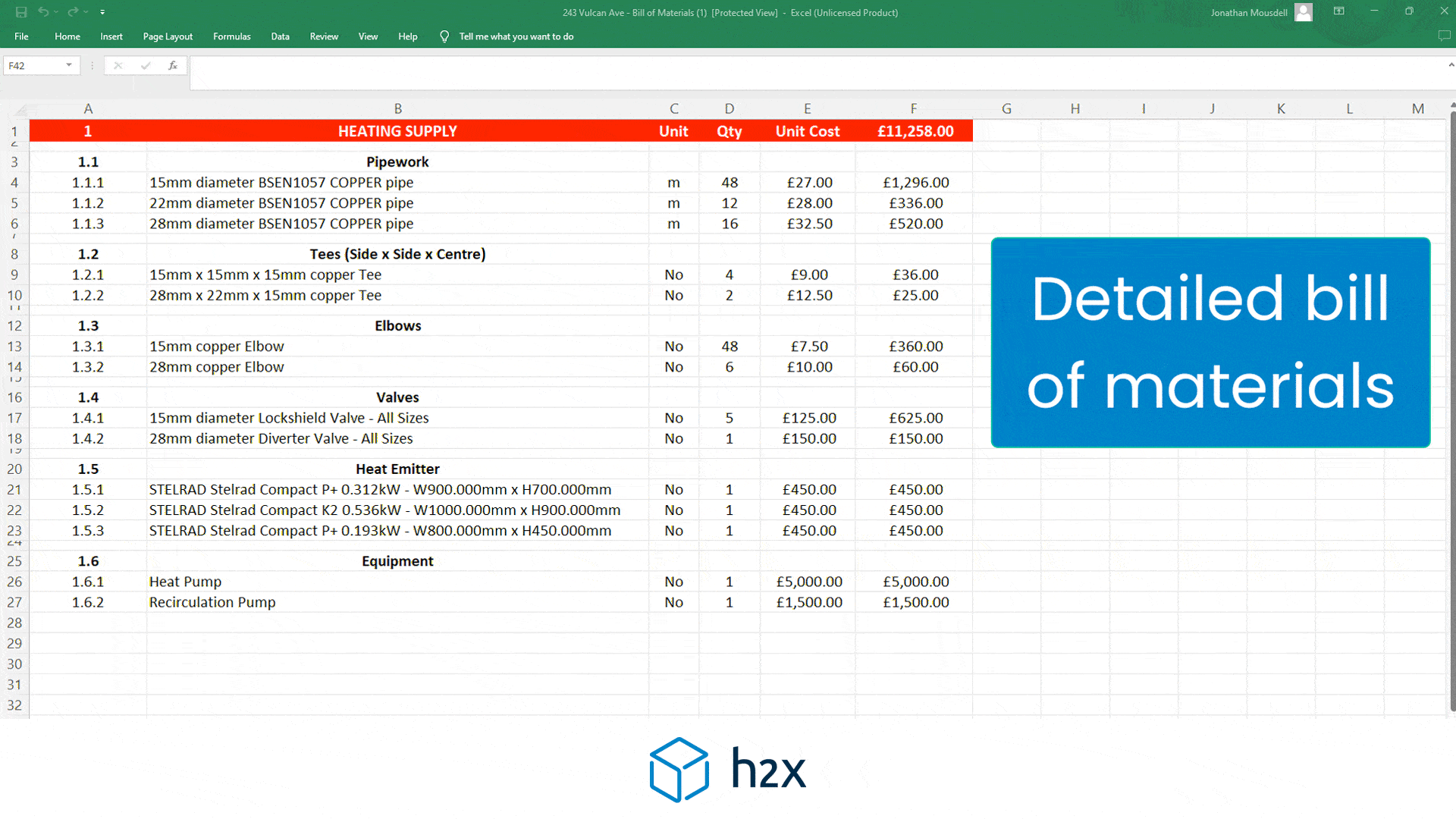
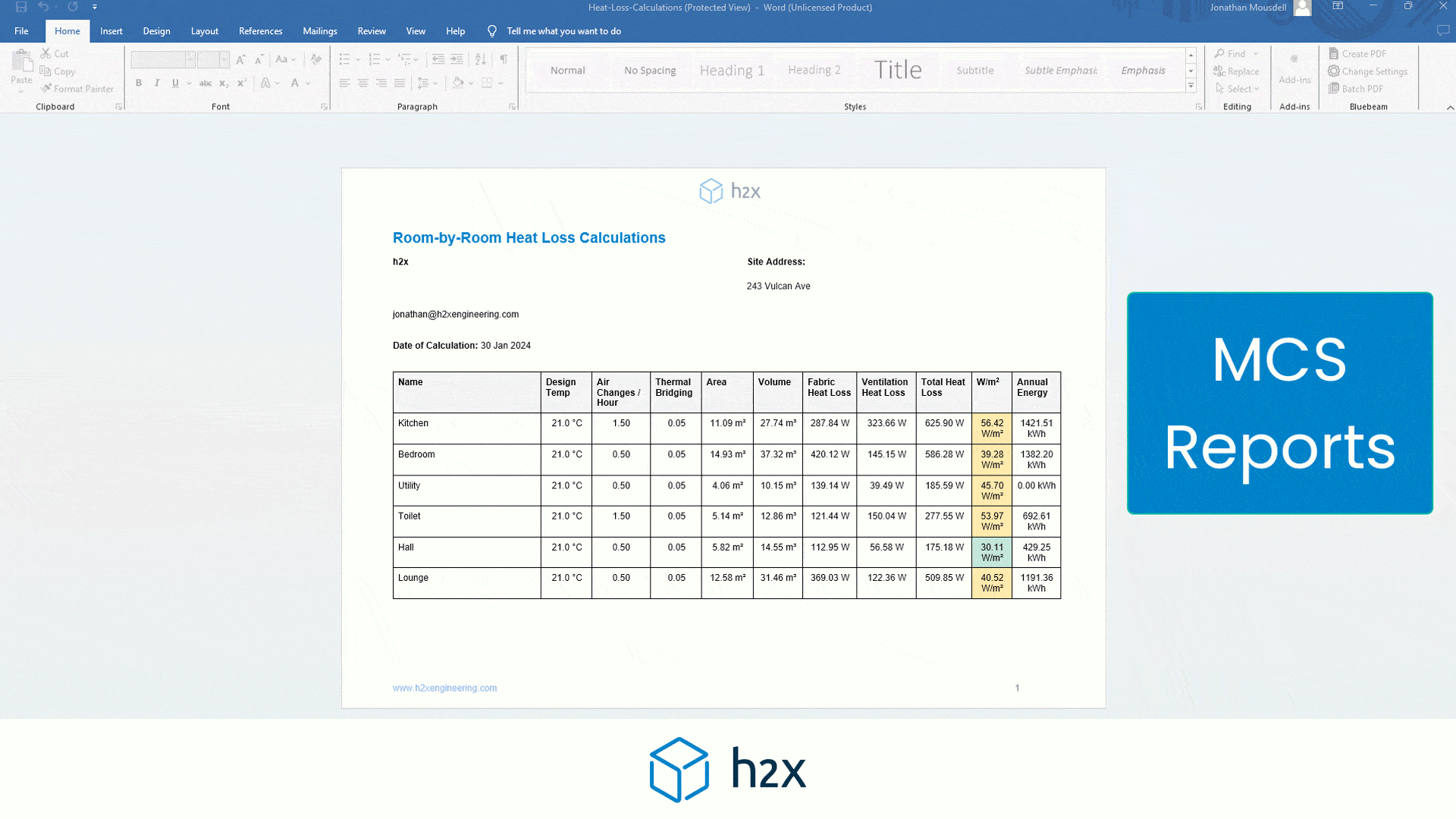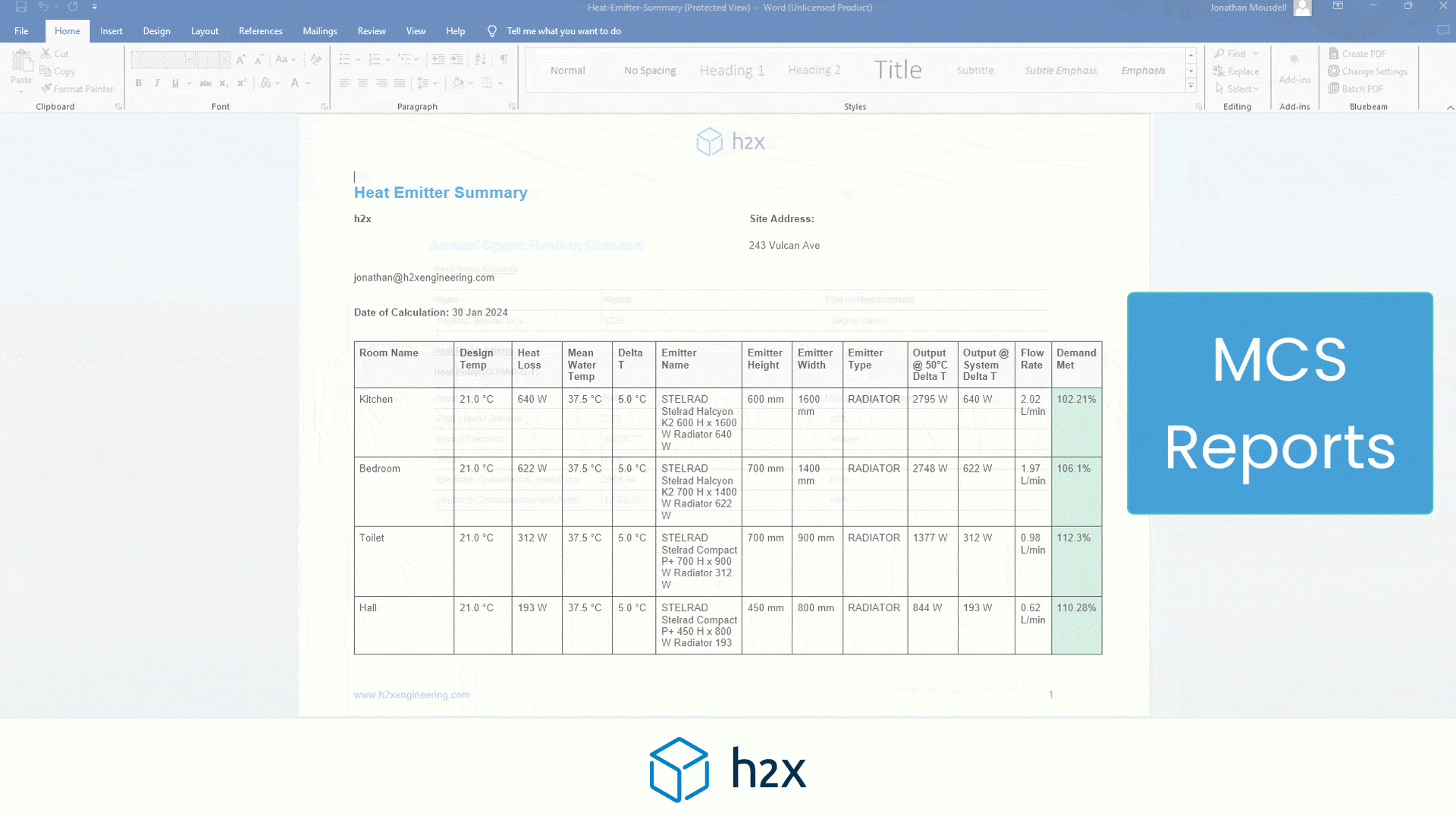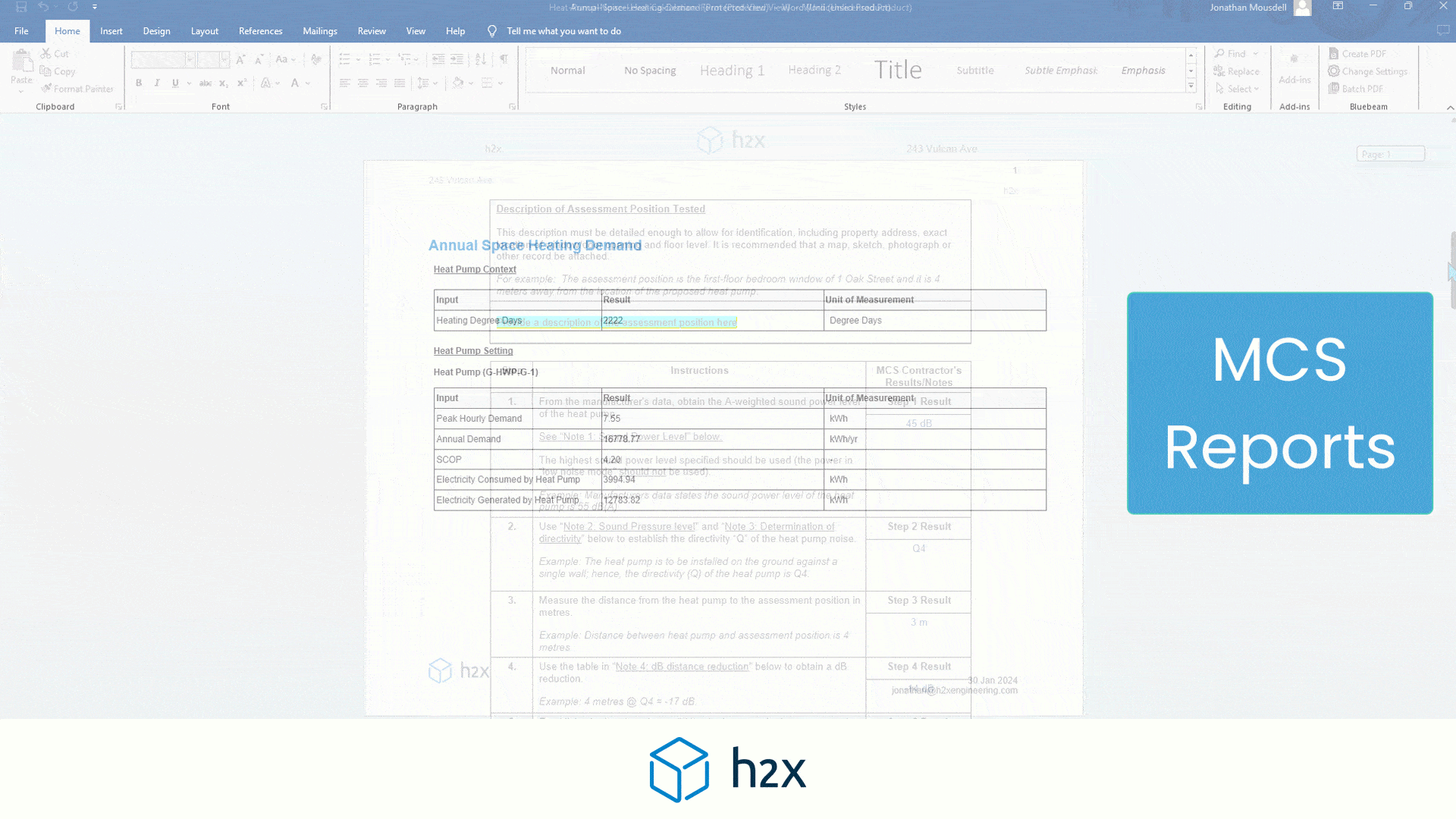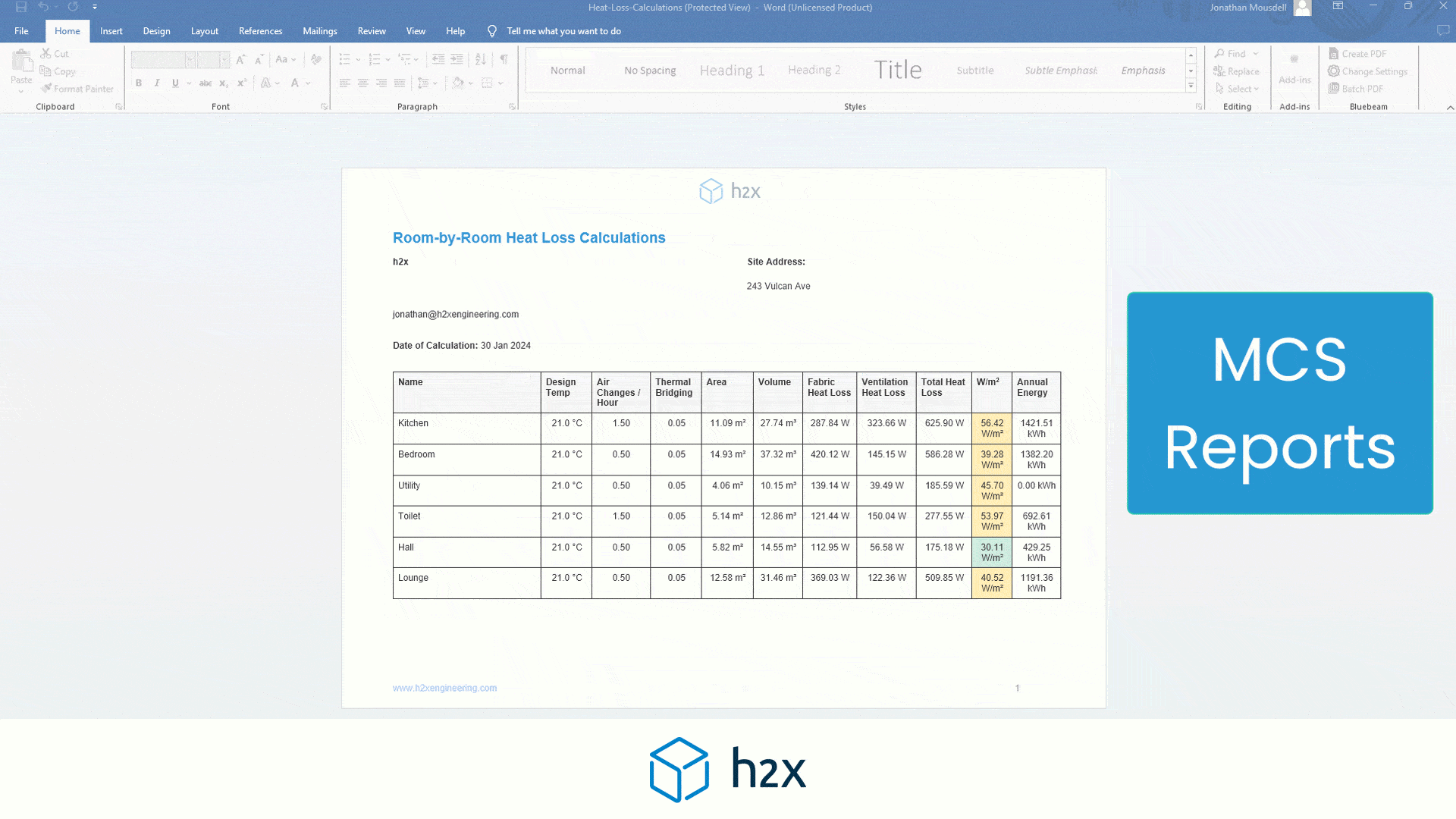
Heat Pump System Design with h2x

Successful heat pump installations require thorough design processes.
Undoubtedly, undersized pumps won’t suffice, and oversized ones waste energy.
However, h2x Engineering’s software tackles these challenges, enabling engineers to ensure quality and efficiency in clean heating and cooling systems.
Ready to experience h2x for yourself? Book your free demo or start your free trial today!
Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol Summary
In the battle against freezing temperatures, anti-freeze valves and glycol stand as two powerful defenders of heat pump systems.
While they both aim to protect, their strategies differ significantly.
From cost-effectiveness to environmental impact, their unique strengths and weaknesses make the choice between the two dependent on a variety of factors.
Ultimately, understanding your system’s specific needs and unique properties of each option will lead you to the most suitable solution.
So, equip your heating systems with the right protection and win your battle against the cold!
FAQs For Anti-Freeze Valves vs. Glycol
Should I put glycol or anti-freeze valves in my heating system?
For domestic applications and if the goal is to maximise efficiency in your heating system, we recommend anti-freeze valves.
However, for larger systems and commercial applications, you may find glycol to be more suitable to prevent freezing and potential damage to your pipes and property depending on the nature of your project.
What are the benefits of using anti-freeze valves?
Using anti-freeze valves is beneficial because they are cost-effective, require low maintenance, and enhance heat pump system efficiency.
What are the drawbacks of using glycol?
Using glycol can be costly due to its maintenance requirements and it can also decrease system efficiency.
How do climate and weather conditions influence the choice of freeze protection?
In colder climates or sudden temperature drops, glycol or anti-freeze valves becomes crucial to provide extra protection against freezing risks.
Glycol or anti-freeze valves help protect against freezing in such conditions.
What are the safety concerns associated with glycol?
Glycol, especially ethylene glycol, is toxic and poses a health hazard if ingested, thus requiring careful handling to prevent harm.
h2x: All-In-One Tool for Calculating, Designing, Estimating, and Paperwork
What's in the Pipeline?
Get technical resources delivered to your inbox weekly!
Testimonials
What Installers Say
What Consultants Say
A game changer for the humble plumber. Incredible.
Brad Winkel
Director at Queenstown Plumbing
Brilliant, simple and easy to use. Game changer.
James Major
Director at Hubb
Big time game changer to the industry!
Viv Jude
Director at UHC
Incredible software! Super user-friendly and allows you to save so much time.
Devni Gamage
Engineer at DMA
h2x is great software, our company use it nearly every day. It is easy to use with direct conversion from h2x to Revit.
Callum Craig
Engineer at WDE
h2x is fantastic software. It is very easy to use and the ability to output to Revit is a fantastic time saver.
Joe Kirrane
Engineer at MEP