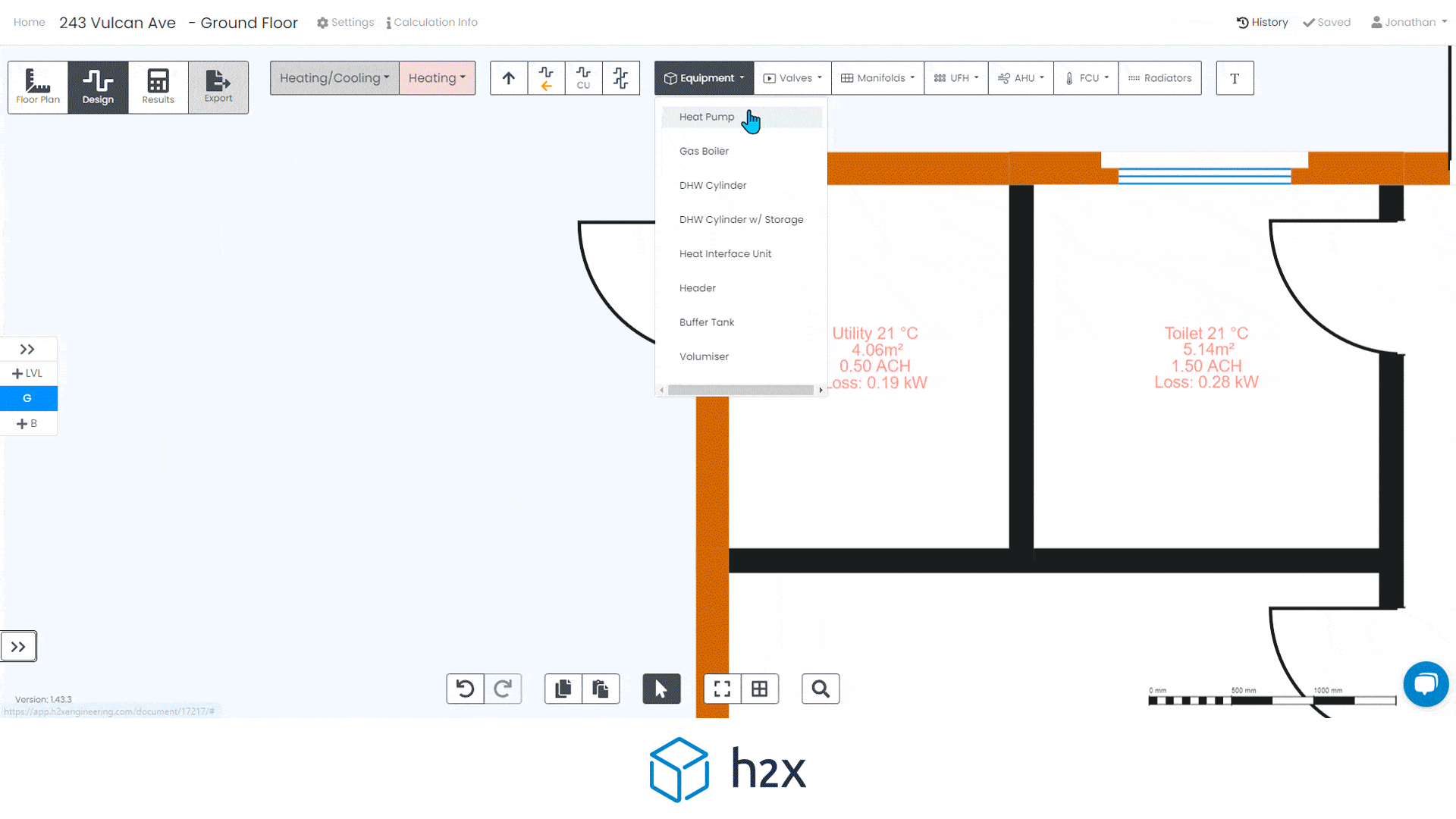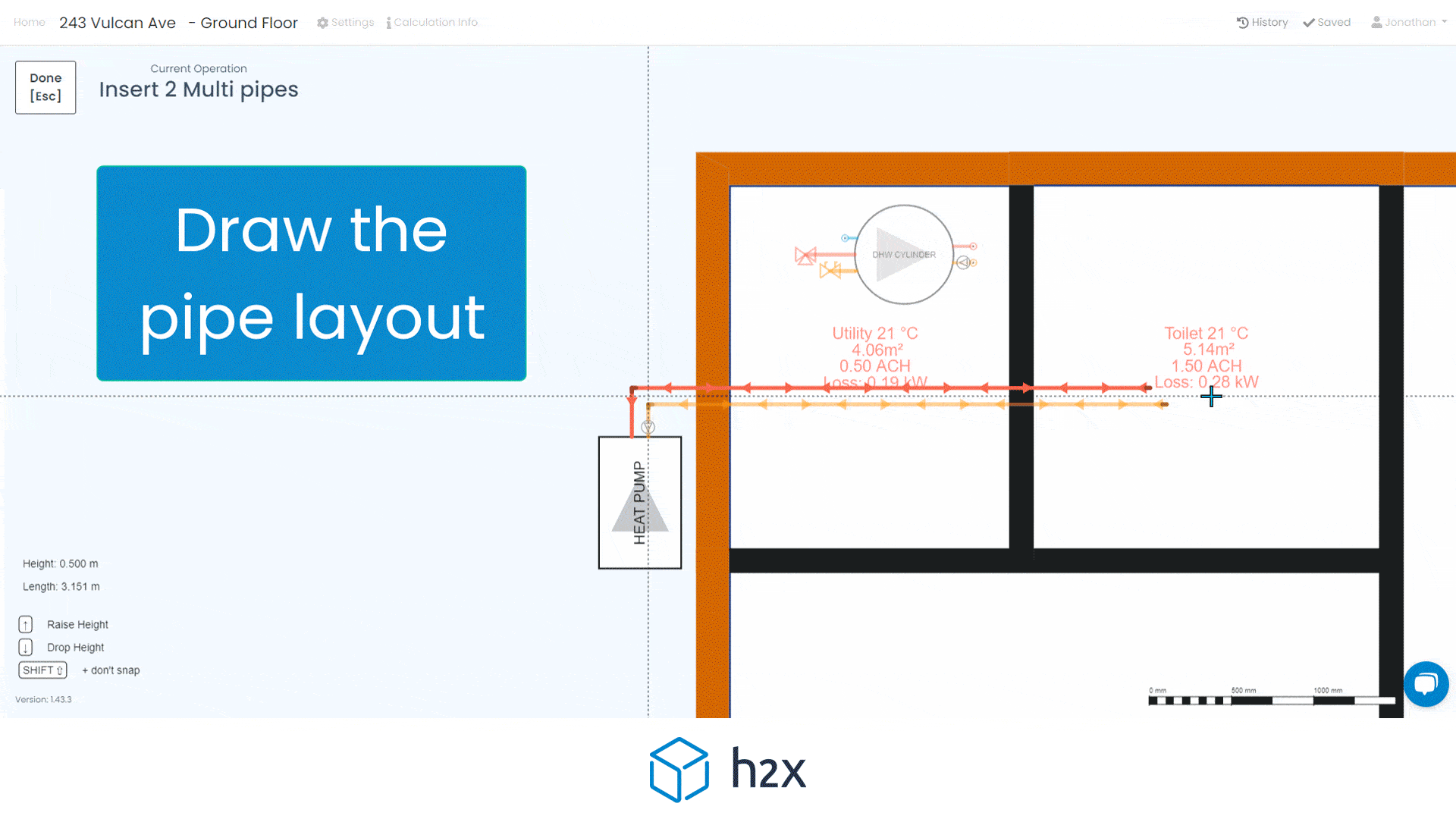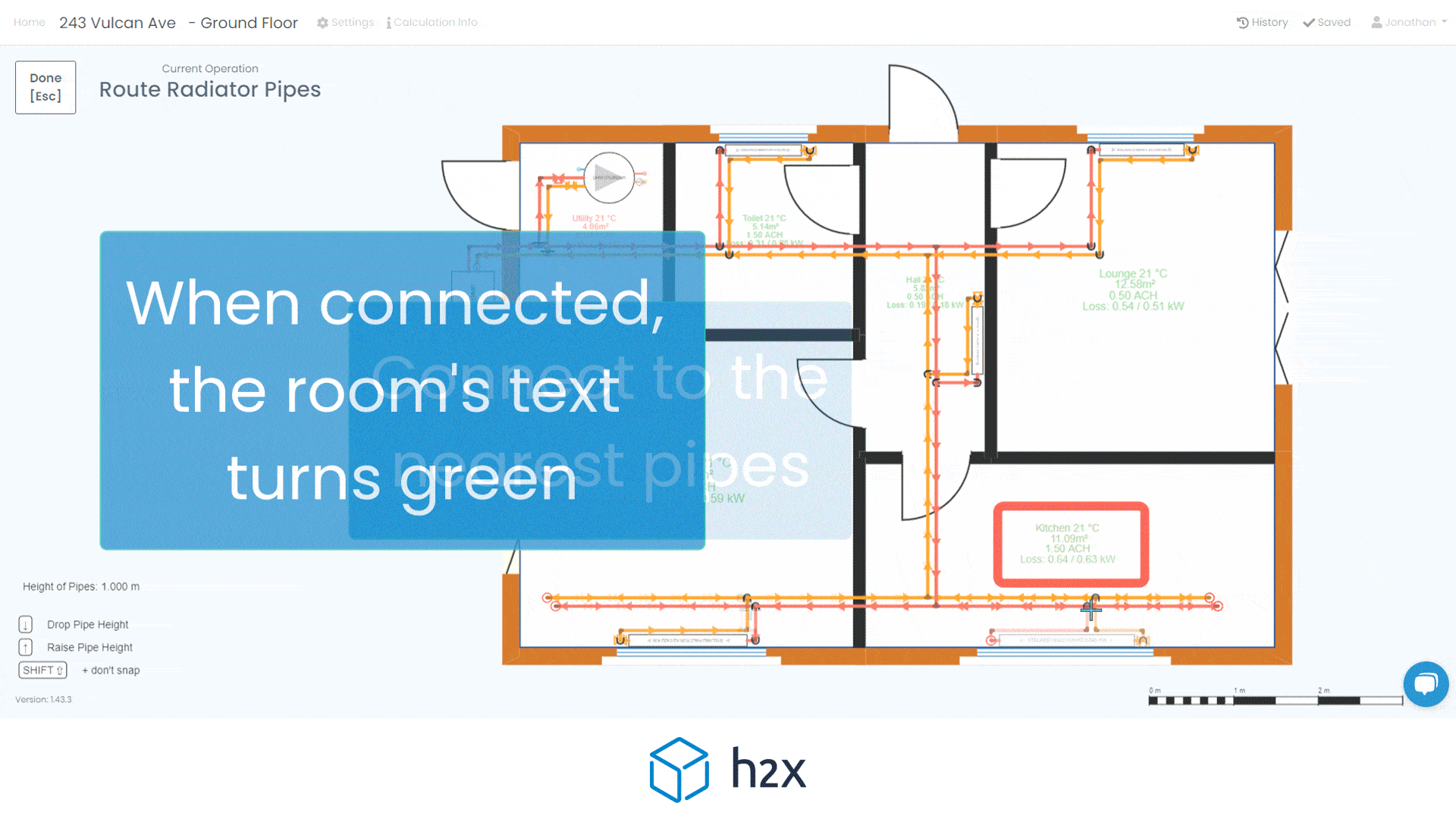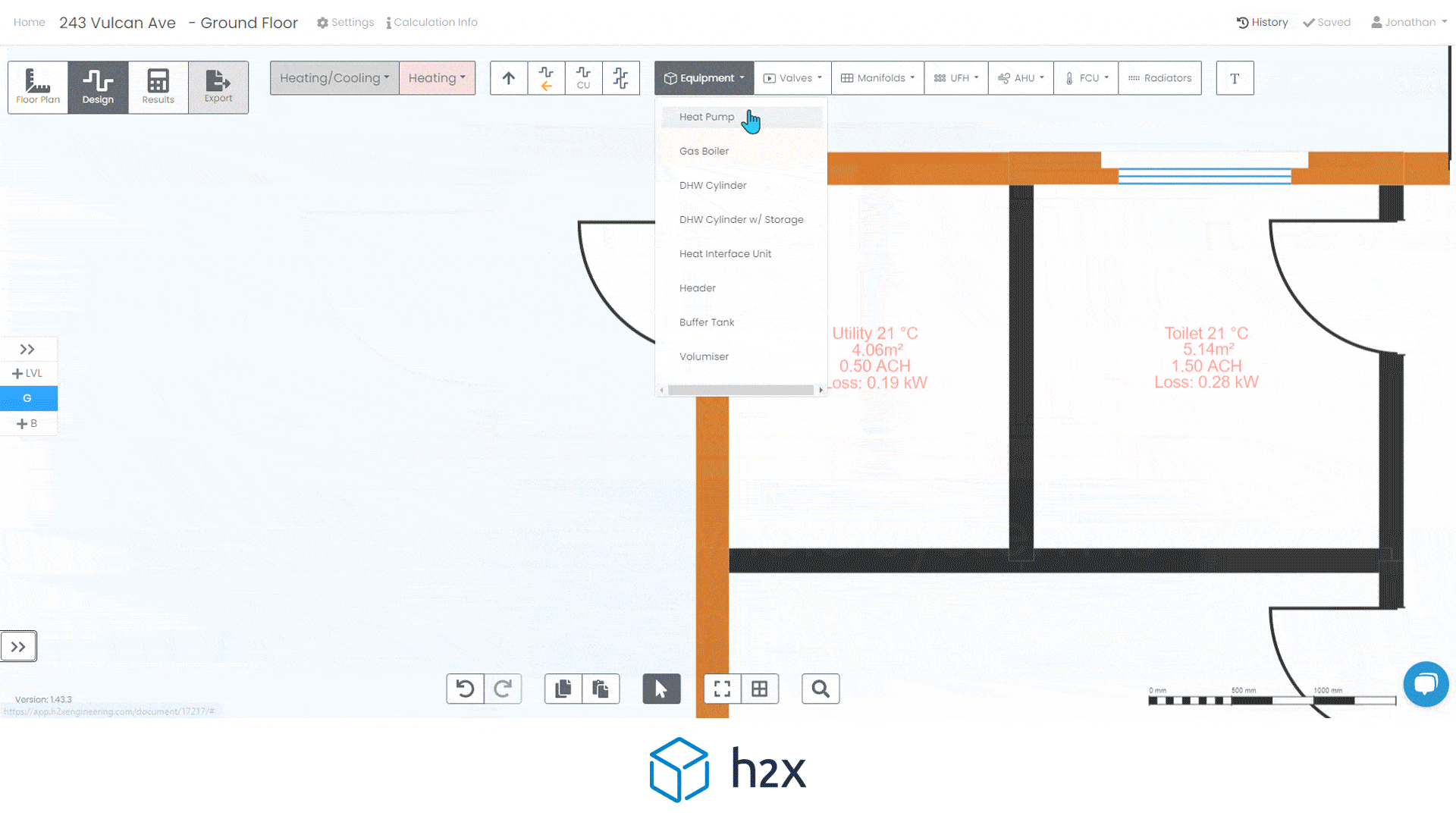
The Importance Of Correctly Sizing Recirculation Pumps In Heat Pump Systems (Includes A Worked Example)
Discover the importance of accurately sizing recirculation pumps in heat pump systems along with a worked example in this informative blog article.
Introduction to Recirculation Pumps in Heat Pump Systems
Recirculation pumps are required to do two things:
1. Circulating the water through the pipes fast enough to ensure the temperature of the water does not fall below the chosen Delta T
2. Provide enough pressure for the water to circulate at the required flow rate
Some good basics to understand about recirculation pumps are:
- The smaller the Delta T, the higher the flow rate.
- This is because the pump needs to move the water faster so it isn’t exposed to the cold surfaces of the pipes and heat emitters for as long, thus not losing as much temperature as it would if it moved slower.
- The higher the flow rate, the higher velocity and pressure drop there will be too.
- Increasing the pipe sizes will reduce the velocity and pressure drop if they exceed the maximum recommendations, 1m/s and 350 pa/m respectively
- The recirculation pump is best located adjacent to the actual heat pump.
- They are commonly installed on the heat pump’s feed or return side.
- As the temperature is cooler on the return side, some industry experts argue that it’s the better location as it extends its life.
Implications of Incorrect Sizing of Recirculation Pumps
Sizing the recirculation pump correctly in a heating or cooling system is equally as important as pipe sizing.
Both undersized and oversized recirculation pumps can lead to operational problems and inefficiencies.
Problems with Undersized Recirculation Pumps
1. Inadequate Flow Rates: An undersized pump may struggle to deliver the required flow rate, compromising the system’s overall performance and comfort levels.
2. Increased Wear and Tear: A pump that is too small for the system’s requirements may have to work harder and run longer to meet the demand, leading to accelerated wear and tear.
3. Inefficient Energy Usage: With the pump operating continuously to meet the demand, energy consumption and costs may rise.
Problems with Oversized Recirculation Pumps
1. Higher Initial Costs: Oversized pumps typically cost more to purchase and install, leading to unnecessary initial expenses.
2. Energy Inefficiency: Bigger pumps consume more energy, leading to higher operational costs, especially if the pump runs at full capacity when unnecessary.
3. Noise and Vibration: Oversized pumps can generate excessive noise and vibrations, causing discomfort and potential structural issues over time.
4. Short Cycling: An oversized pump can lead to rapid on/off cycling, reducing the pump’s lifespan and increasing maintenance needs.
In summary, the correct sizing of the recirculation pump is key to maintaining efficient operation, reducing unnecessary costs, and extending the lifespan of your heating or cooling system.
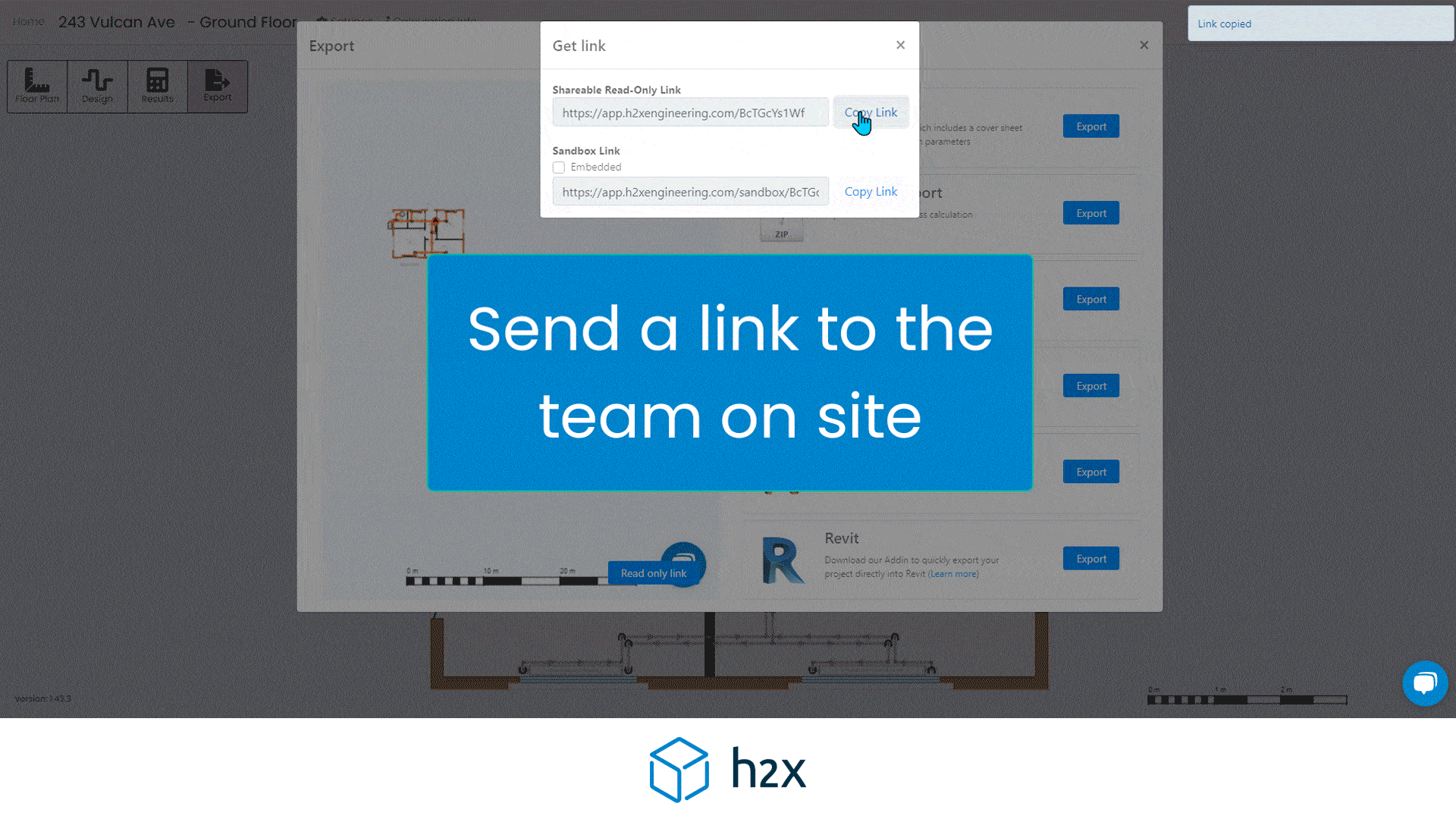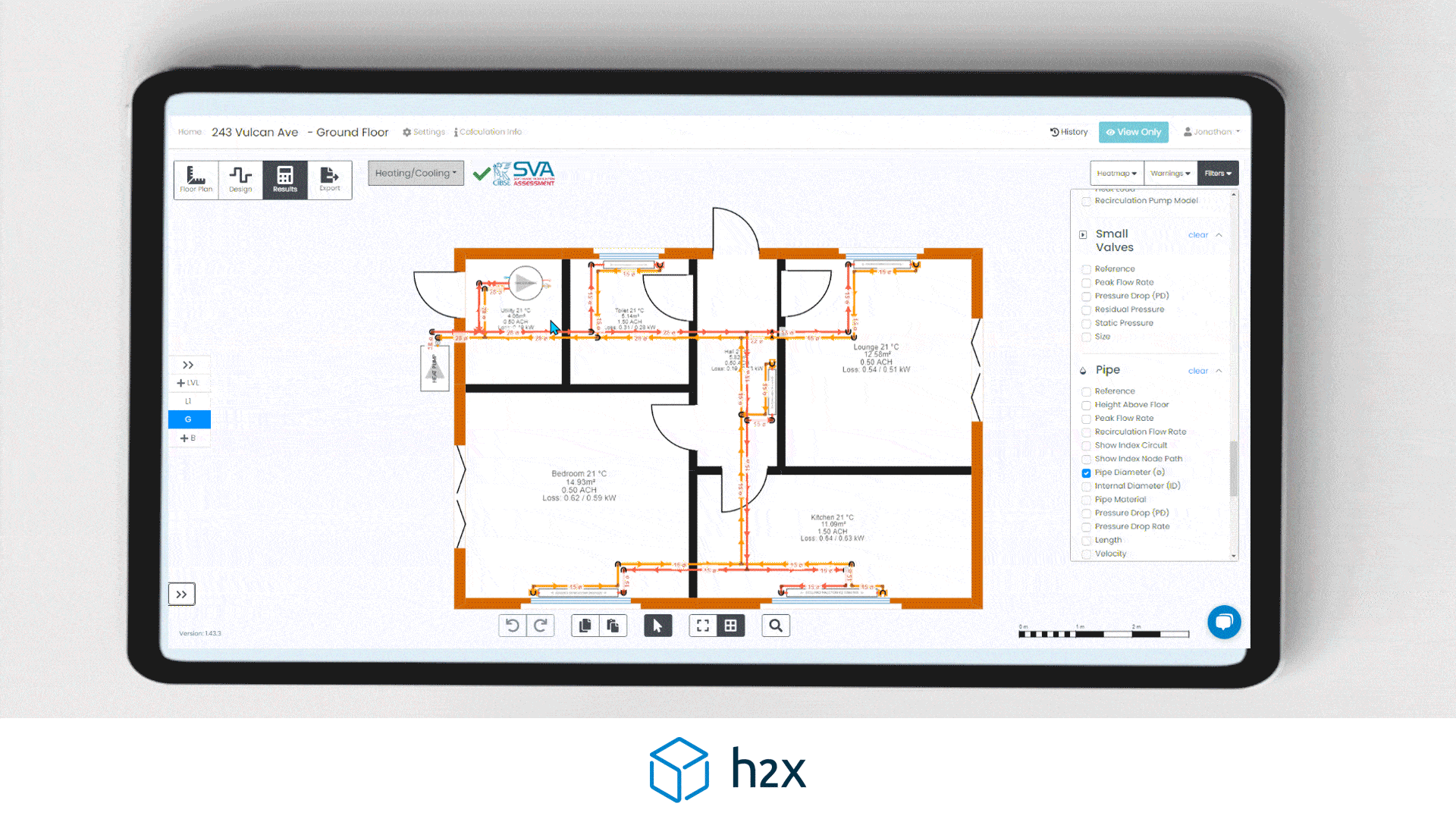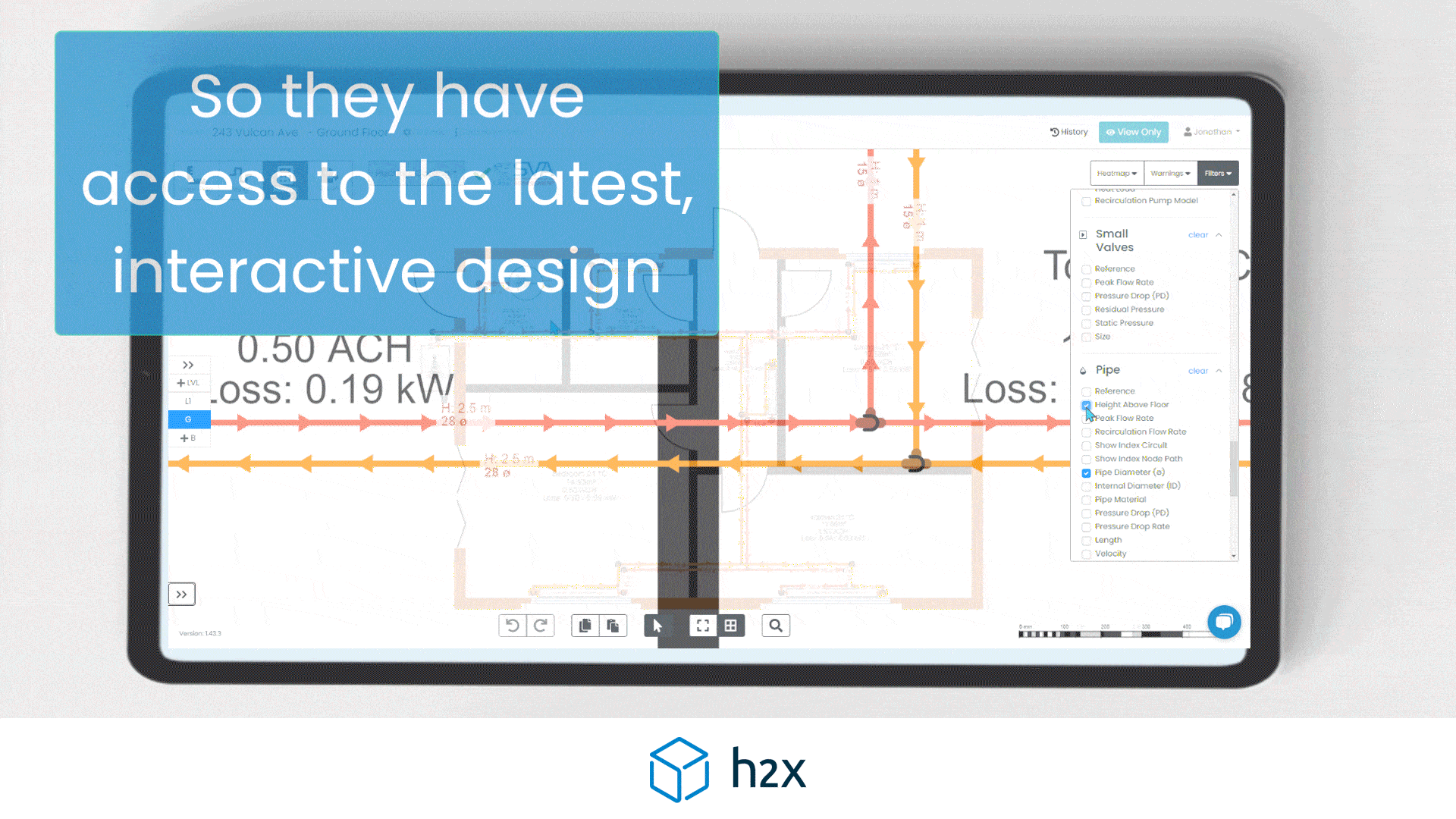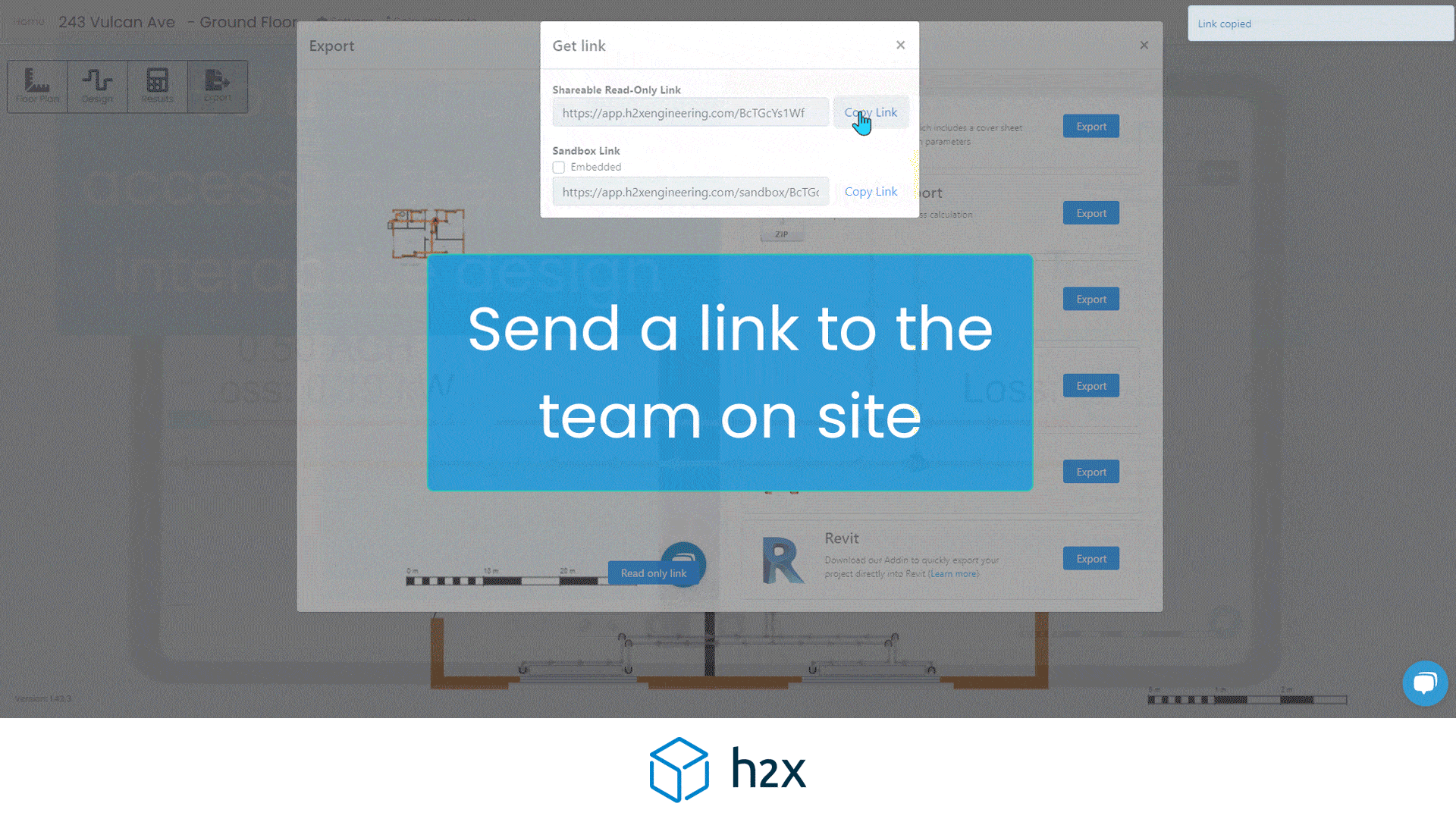
How to Size a Recirculation Pump Correctly
There are two parts to defining the recirculation pump duty:
1. The flow rate of the system
2. The pressure drop through the index circuit, generally the furthest circuit from the heat pump*
*It is important that you do not cumulate the pressure drop through every part of the system. The pressure only needs to overcome the circuit with the most pressure drop (the index circuit) and that will ensure there is enough pressure to overcome all of the other circuits.
Recirculation Pump Sizing Example:
Pump Flow Rate
This matches the flow rate that you size the heat pump for.
e.g. 11 kW / 0.53 L/sec
Refer to our blog Calculating Heat Loss for reference material relating to calculating the load of heat emitters.
Pump Pressure Drop
The index circuit has pressure drop through the following:
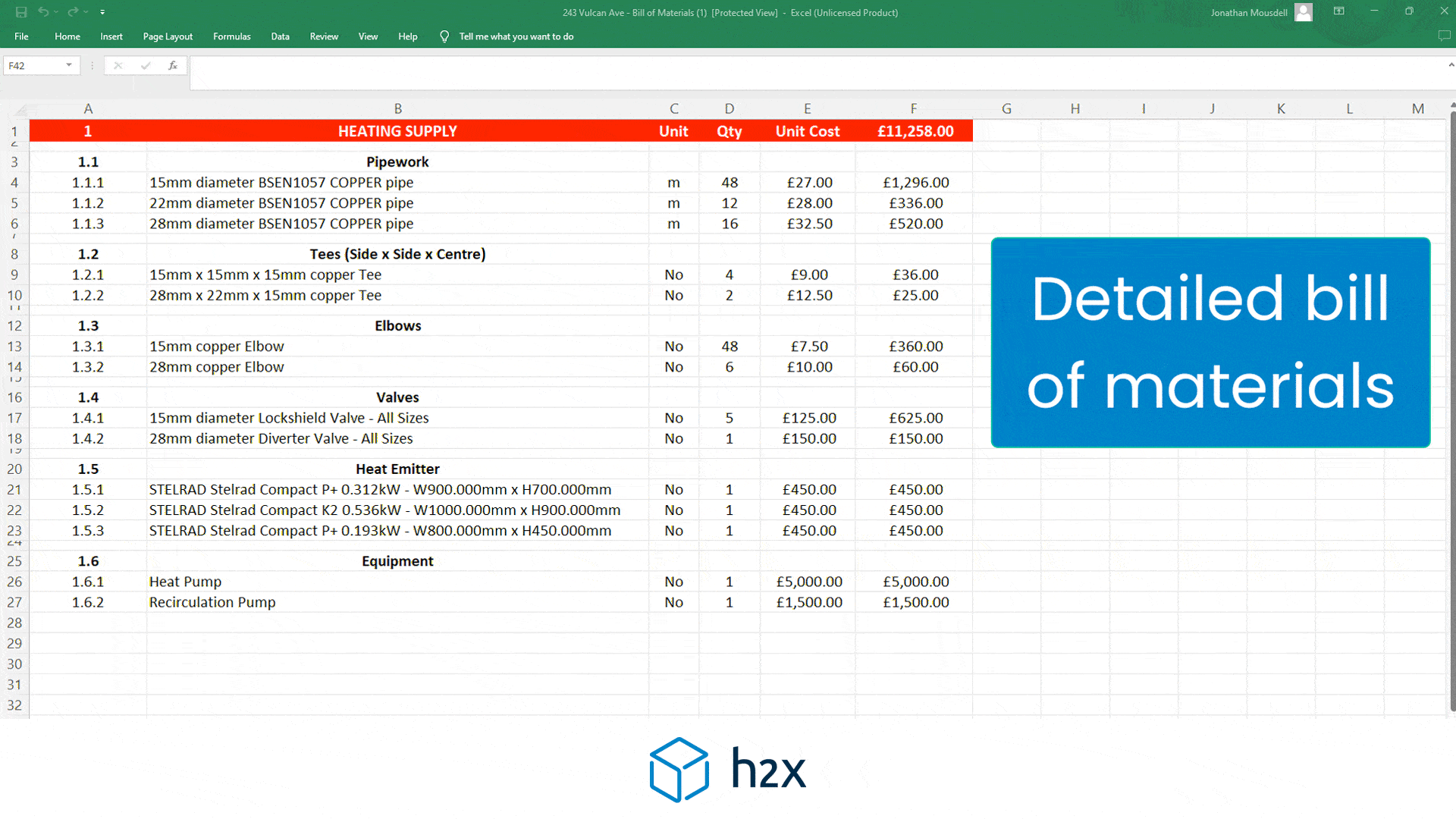
Pipes:
The pressure drop through pipes is calculated using the below formula:
Pressure Drop (bar) = (Friction Factor x (Pipe Length (m) / Pipe Diameter (m)) x (Velocity (m/s)^2 / 19.62)) x 9084
25m x 35mm pipe = 3345Pa
22m x 28mm pipe = 4455Pa
18m x 22mm pipe = 4716Pa
15m x 15mm pipe = 2322Pa
Total Pipe Pressure Loss = 14838Pa / 0.149bar
Try our free pressure drop calculator.
Heat Emitters:
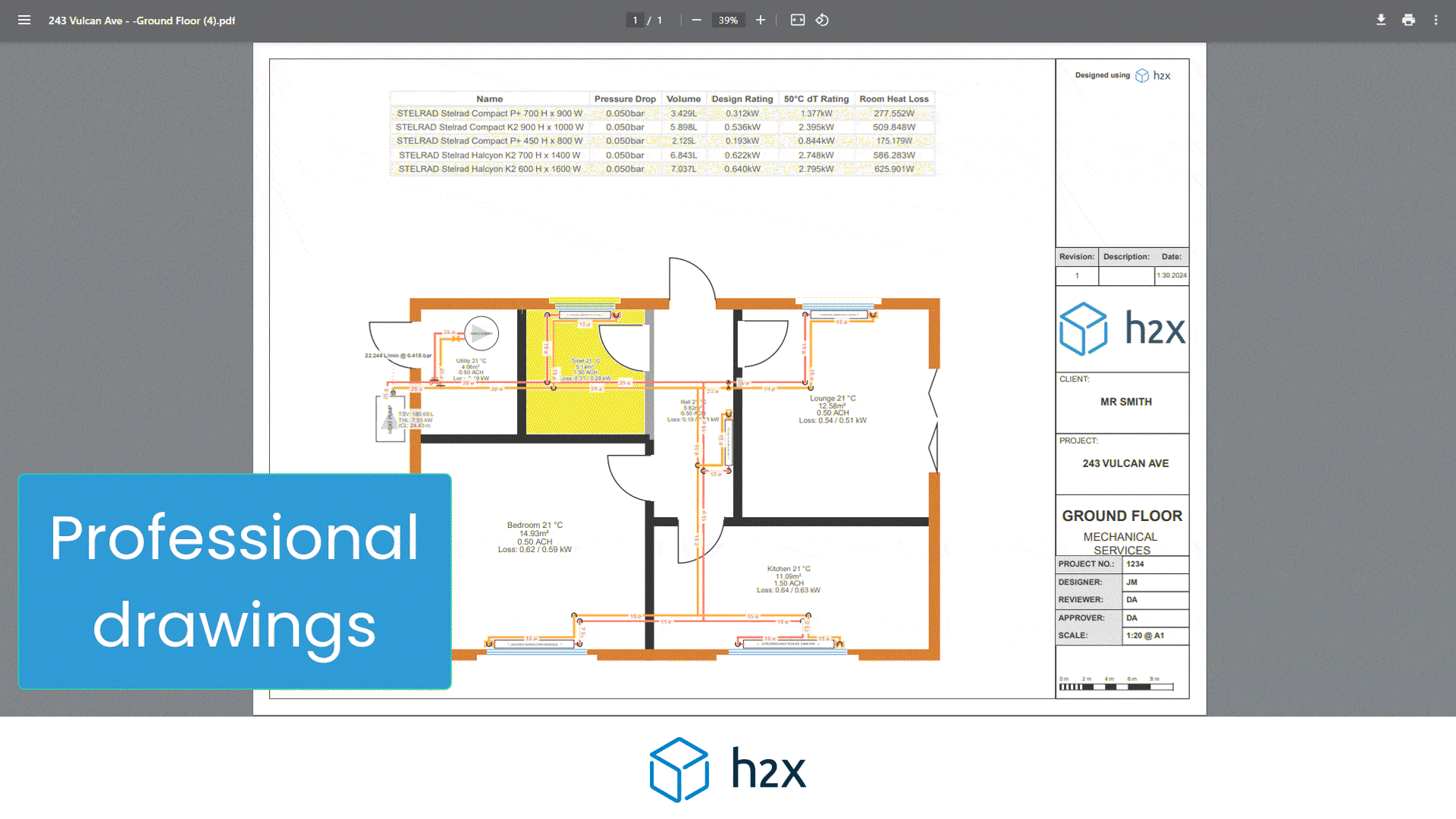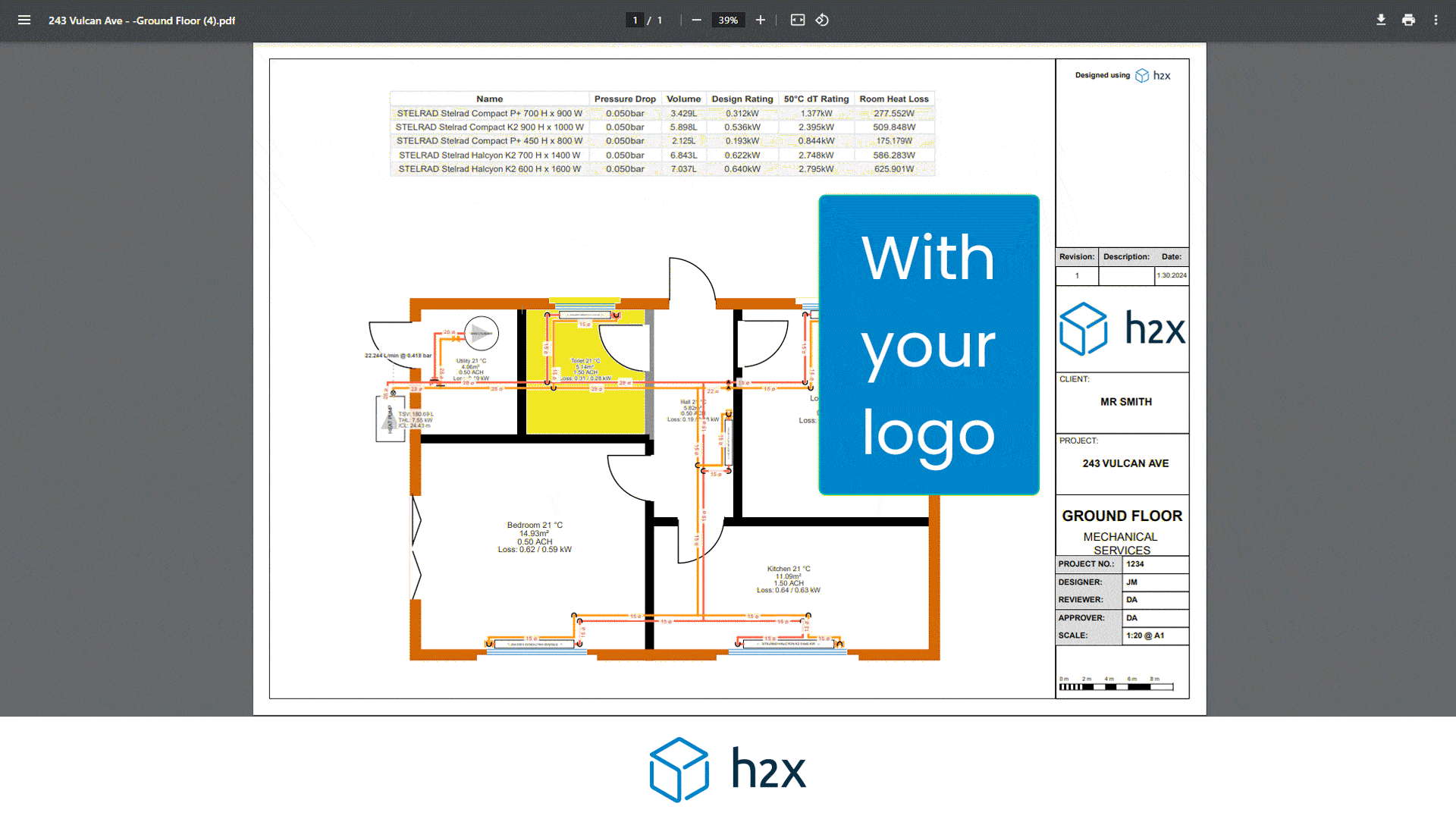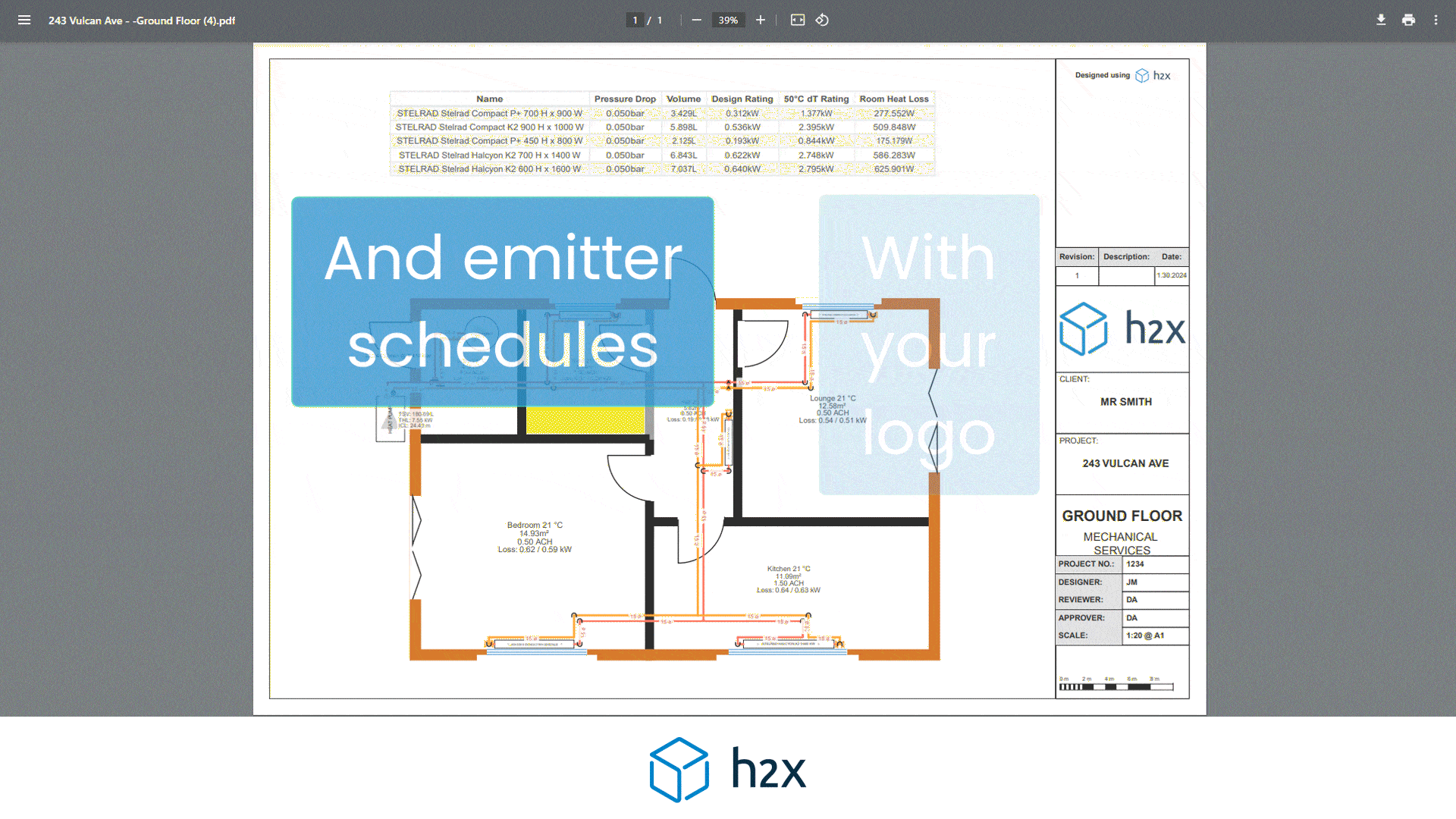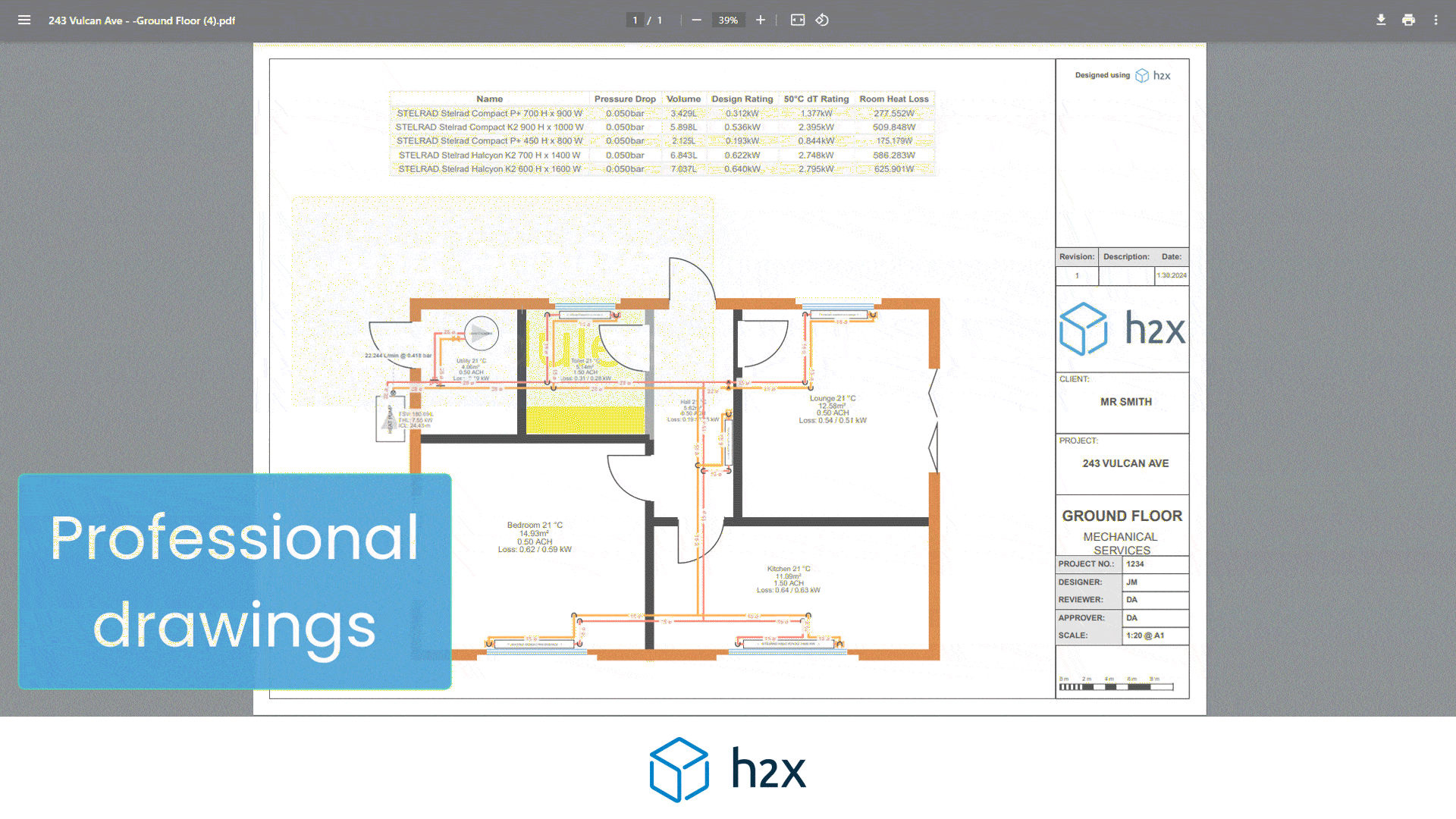
It is best to check the technical data from the manufacturer for the pressure drop through the heat emitter.
In this example, we will use 1000Pa per radiator.
1 x Radiator = 1000Pa
There is also a pressure drop through the lockshield valve, this is usually 10000Pa / 0.1bar on the index circuit.
Total Heat Emitter Pressure Loss = 11000Pa / 0.11bar
Valves and Fittings:
The pressure drop through valves and fittings are calculated using their K (also known as Zeta) values.
It is best to check the technical data from the manufacturer for the valve/fitting K value.
The pressure drop is then calculated using the below formula:
Pressure Drop (bar) = (K Value x (Velocity (m/s)^2 / 19.62)) x 9084
1 x 15mm TRV = 0.74 K Value = 55Pa
2 x 35mm Isolation Valve = 0.06 K Value = 9Pa
4 x 35mm Elbow = 0.63 K Value = 184Pa
2 x 28mm Elbow = 0.66 K Value = 98Pa
1 x 22mm Elbow = 0.69 K Value = 52Pa
6 x 15mm Elbow = 0.75 K Value = 224Pa
Total Valve and Fitting Pressure Loss = 622Pa / 0.00622bar
Total Pressure Drop
The total pressure drop through the whole system is:
Pipes = 14838Pa
Heat Emitters = 11000Pa
Valves and Fittings = 622Pa
Total Pressure Drop = 26460Pa / 0.26bar
Pump Duty
The recirculation pump duty is 0.53L/s @ 0.26bar.
» Click here to download our free eBook that breaks down everything engineers need to know about heat pump design!

The transformation of industries by the digital revolution is a story told many times over, and heating system design is no exception.
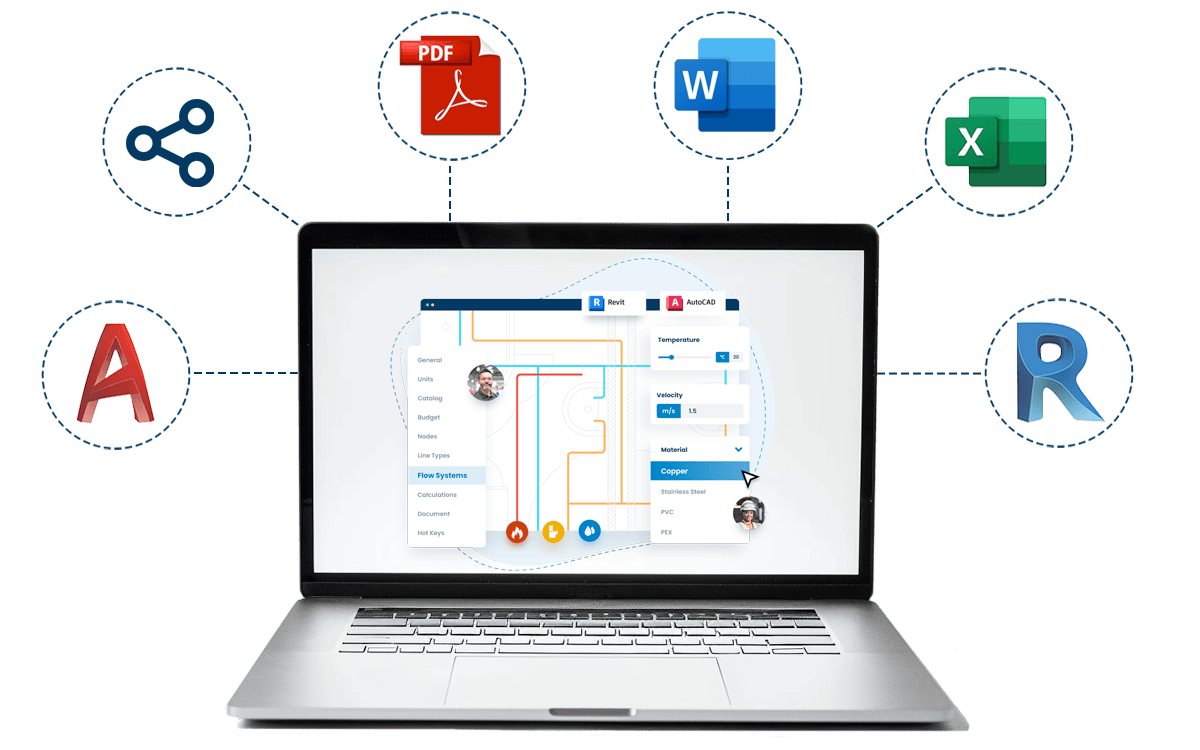
With the right software, like h2x Engineering’s Heating Design Software, you can drive efficiency and accuracy in your heating system projects.
Embracing the digital revolution in the form of heating design software, like that offered by h2x Engineering, is crucial for professionals who wish to stay competitive in the industry.
It offers a blend of convenience, precision, and efficiency that traditional methods cannot match.
Give your heating system designs the h2x advantage and experience the difference by booking a demo or by starting your free trial today!
h2x: All-In-One Tool for Calculating, Designing, Estimating, and Paperwork
What's in the Pipeline?
Get technical resources delivered to your inbox weekly!
Testimonials
What Installers Say
What Consultants Say
A game changer for the humble plumber. Incredible.
Brad Winkel
Director at Queenstown Plumbing
Brilliant, simple and easy to use. Game changer.
James Major
Director at Hubb
Big time game changer to the industry!
Viv Jude
Director at UHC
Incredible software! Super user-friendly and allows you to save so much time.
Devni Gamage
Engineer at DMA
h2x is great software, our company use it nearly every day. It is easy to use with direct conversion from h2x to Revit.
Callum Craig
Engineer at WDE
h2x is fantastic software. It is very easy to use and the ability to output to Revit is a fantastic time saver.
Joe Kirrane
Engineer at MEP