Water Storage Tanks
A water storage tank is a container used to store and hold water. Tanks are typical for the following systems: Rainwater collection/irrigation systems...
What is a water storage tank?
A water storage tank is a container used to store and hold water.
What systems commonly require a water storage tank?
Tanks are typical for the following systems:
-
Rainwater collection/irrigation systems;
-
Domestic water supply; and
-
Fire suppression systems.
Why are water storage tanks required?
The most common scenarios where water storage is required include the following:
-
Water main failure: Water storage tanks provide a backup water source in case of a failure in the main water supply, such as a broken pipe or power outage affecting pumping stations. This ensures a continued water supply for essential drinking, cooking, and sanitation needs.
-
Water main flow rate limitations: Water storage tanks can be helpful in situations where the main water supply cannot meet the flow rate demand, such as during peak usage. By storing water in advance, a water storage tank allows for a consistent and steady water supply, even if the main water supply cannot provide enough flow.
-
Rainwater collection: Water storage tanks help collect rainwater because they provide a convenient and efficient way to store and conserve this precious resource. Rainwater is a free, renewable resource that can be used for various purposes, such as irrigation, landscaping, and washing. Collecting rainwater in a water storage tank can reduce your reliance on municipal water supplies, which can be expensive and face challenges such as droughts or water scarcity.
Overall, a water storage tank helps store and manage water resources in various scenarios.
How do storage tanks work?
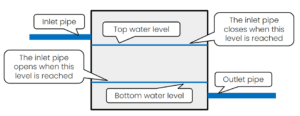
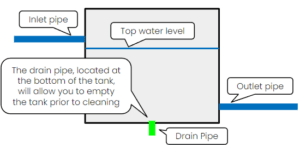
The water is typically fed into the tank through the inlet pipe.
Tanks usually have level indicators to stipulate the water level in the tank; these control the flow of the inlet pipe.
On the outlet side, tanks use gravity or a pump to distribute the water.
The tank should also have an overflow pipe to prevent flooding and drain pipes to assist in cleaning the tank.
Where should you locate the tank?
Water storage tanks can be located either above-ground or underground.
The primary considerations when making your decision are:
-
Above-ground tanks are easier to access and maintain
-
Above-ground tanks, assuming they are at the top of the building, can still gravity-feed water to the building in the event of a power/pump failure
-
Above-ground tanks require space within the building, which architects will not want to provide
-
Above-ground tanks will add significant load to the structural design
-
Above-ground tanks may need a booster pump to supply them with water
-
Underground tanks are difficult to access and maintain
-
Underground tanks will not be able to supply water to the building in the event of a power/pump failure
-
Underground tanks do not require space within the building, which makes them easier to coordinate with architects
-
Underground tanks do not add significant load to the structural design
-
Underground tanks do not need a booster pump for water to fill them
In general, it is essential to carefully consider the location of a water storage tank to ensure that it is safe, functional, and fit for purpose.
Can you have multiple storage tanks?
You should have multiple water storage tanks in most scenarios.
Firstly, each type of usage will require a dedicated tank to prevent cross-contamination. For example, a separate tank will be required for domestic water, fire impression, and rainwater collection.
Secondly, having two water storage tanks (or a division wall within the tank) is a good idea to ensure the whole building’s water supply is not disrupted during maintenance.
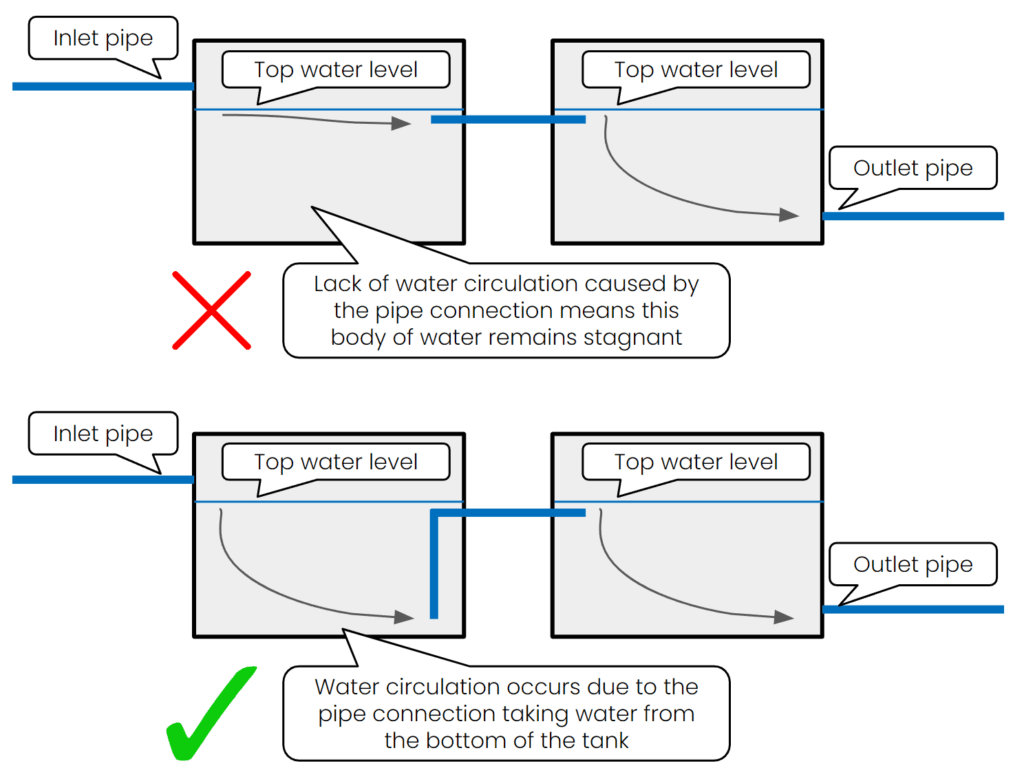
How do you connect multiple tanks?
There are a couple of options for connecting multiple water storage tanks:
-
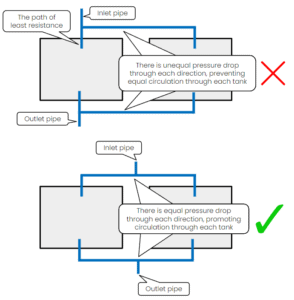
In parallel: There must be an equal flow manifold between the tanks to promote water circulation
-
In series: The inlet of the second tank must come from the bottom of the first tank to promote water circulation
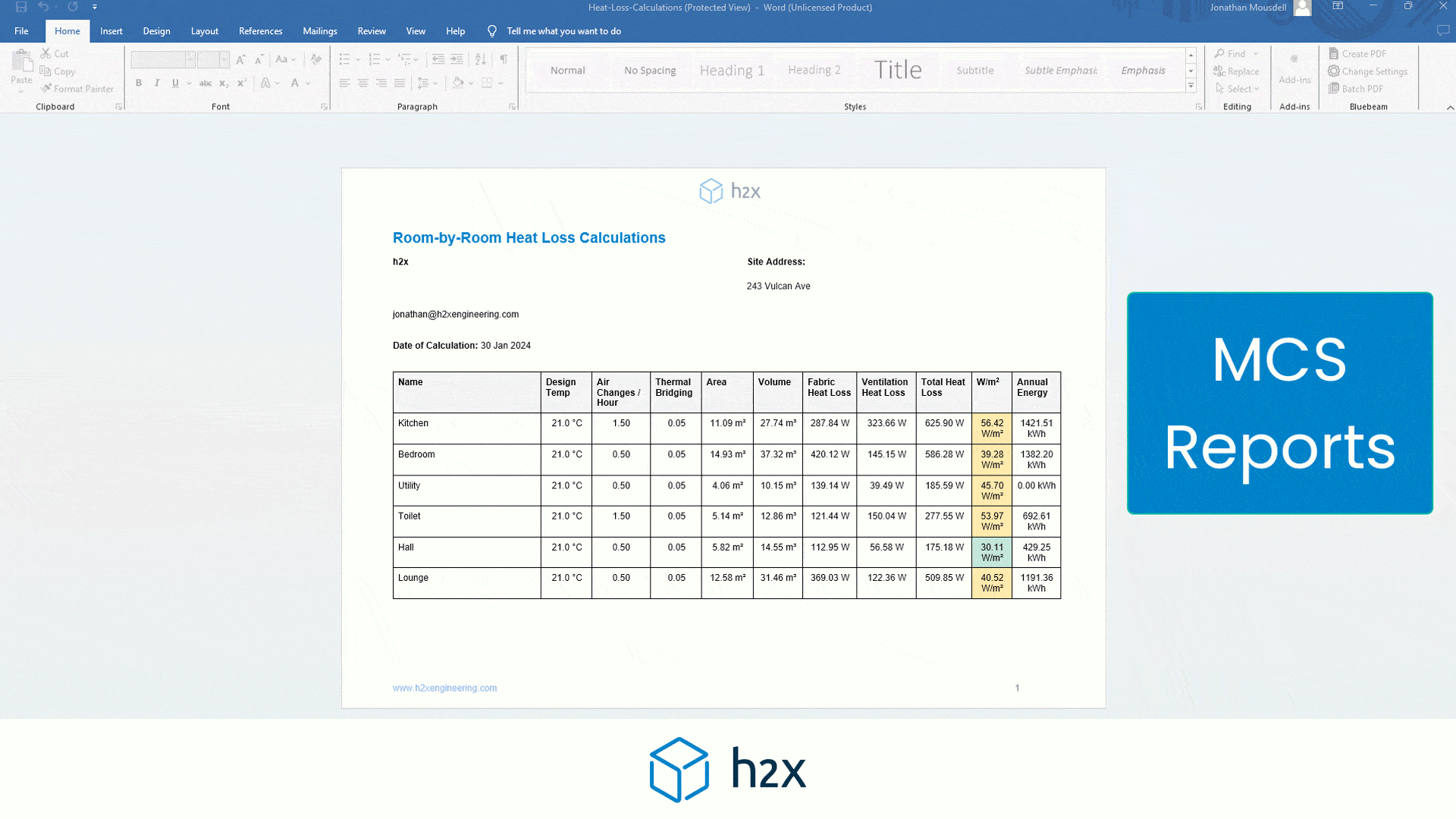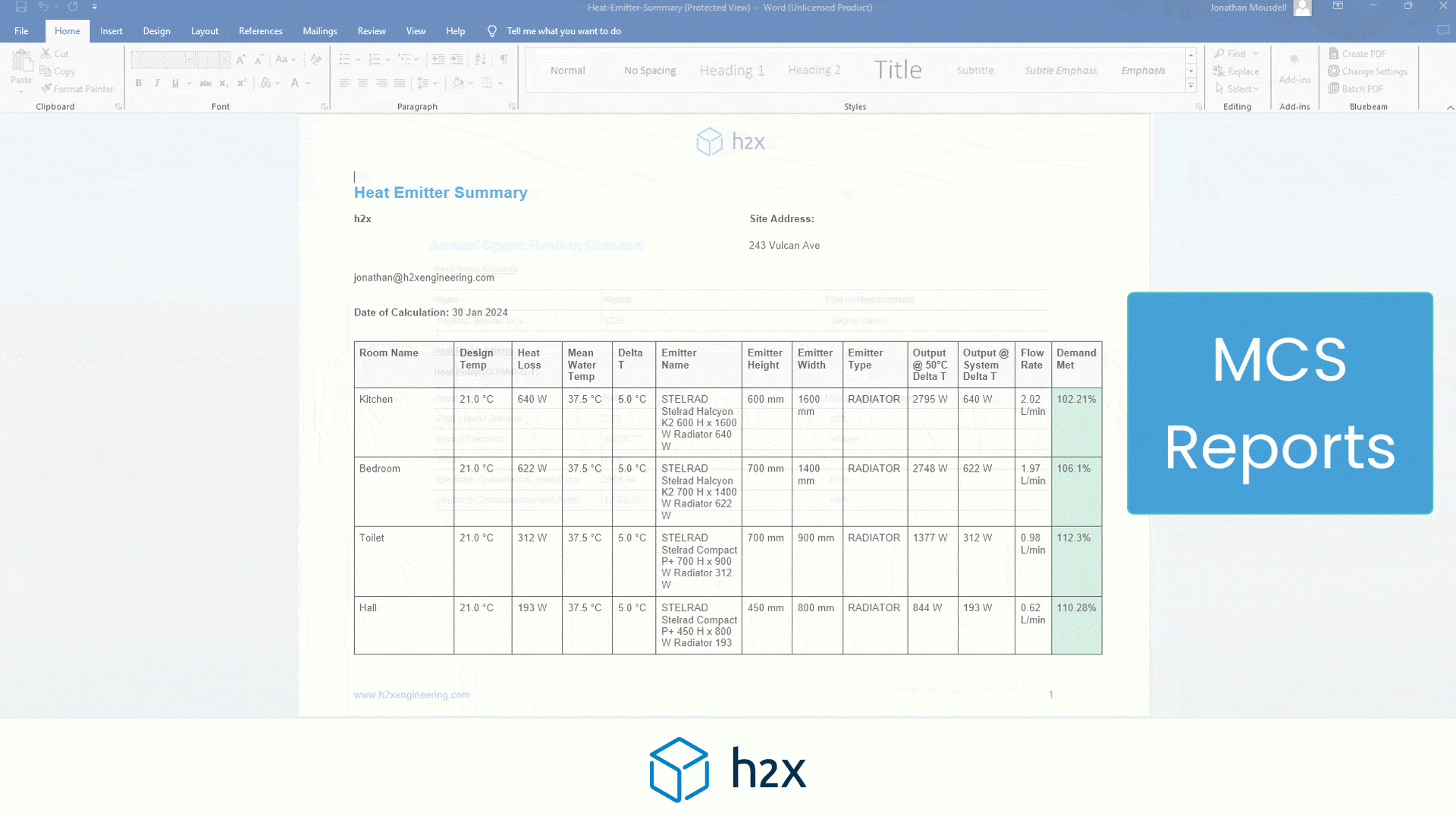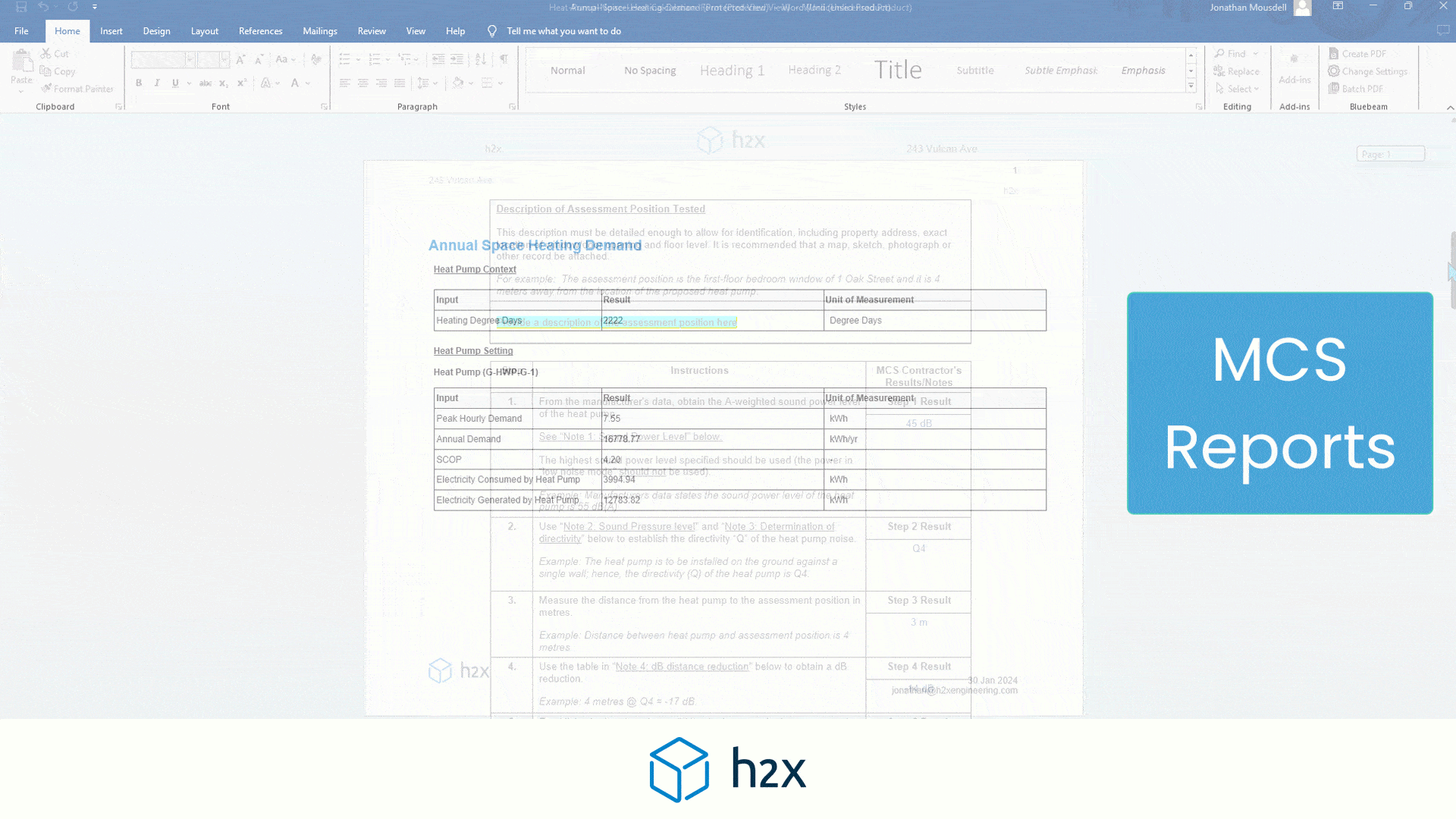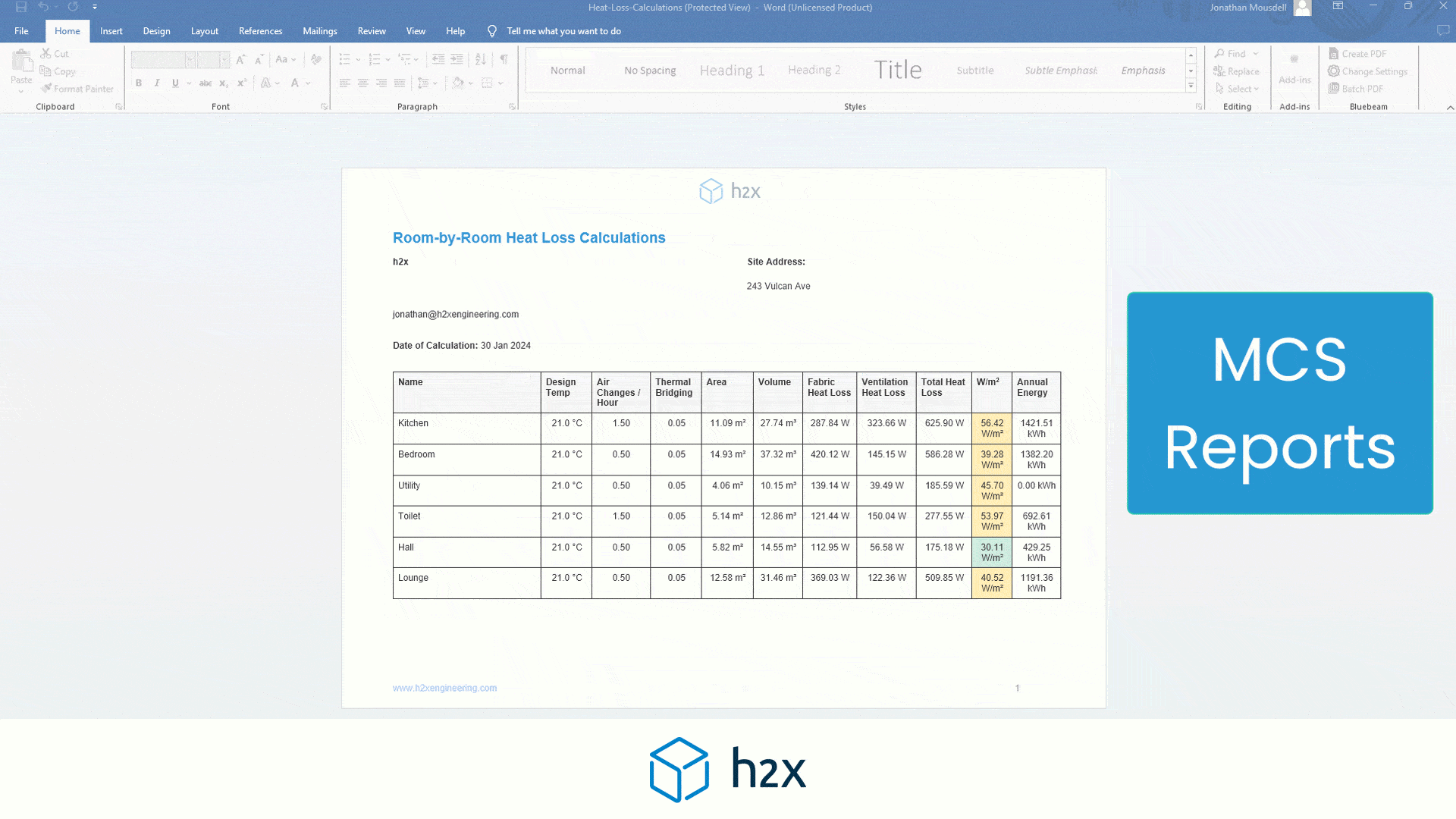
What size/capacity should my tank be?
When sizing a water storage tank, knowing how long you need to store water is important.
For example, in a domestic scenario, it may only be 20 minutes of the peak flow rate. Whereas in a hospital, it may need to be hours or days of storage.
Discussing this with your client is best, as the tank size has considerable implications on the design and the building.
Once you know how long you need to store water, to determine the size of the tank, you can use the following formula:
Tank size (litres/gallons) = Peak flow rate (l/sec / gpm) x Minutes of storage
Tank size (litres/gallons) = Daily usage (litres/gallons) x Days of storage
For example, if your household uses 300 litres/gallons of water per day and wants to store enough water for three days, you would need a tank with 300 x 3 = 900 litres/gallons capacity.
Should the tank be connected to the BMS?
Connecting a water storage tank to a building management system (BMS) is a good idea in some scenarios.
A building management system (BMS) is a computer-based system that monitors and controls systems in a building.
Connecting a water storage tank to a BMS makes sense if the water supply is essential because you can install sensors to measure various aspects, such as the water level.
The BMS will then send warnings if the water levels get too high or low, highlighting the potential problem to you before it becomes a critical issue.
Does the tank need overflow pipes?
Including overflow pipes in a water storage tank is critical.
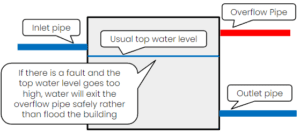
Overflow pipes allow excess water to be safely discharged from the tank if there is a fault and the water level gets too high, preventing the tank from causing damage or flooding.
The overflow pipe is installed higher than the tank’s inlet. When the water level in the tank rises above the level of the inlet pipe, the excess water flows out of the overflow pipe.
It’s crucial to ensure that the overflow pipes are correctly sized (based on the maximum incoming flow rate) and that they discharge to a visible area where overflowing water can be easily seen.
Suggested Reading: This article discusses calculating maximum (peak) flow rates.
How do you drain tanks?
Including (sludge) drains in a water storage tank is critical.
They are used to drain the tank during maintenance or repair scenarios.
These drains are located at the bottom of the tank and are used to drain the entire tank.
Water quality considerations?
There are a few key water quality considerations to keep in mind when storing water in a tank:
-
Contamination: It is crucial to prevent contaminants from entering the tank. This can be done by installing filters or screens on the inlet pipes, regularly cleaning and maintaining the tank, and avoiding locating contaminants (like non-potable water pipes) above the tank.
-
Algae growth: Algae can grow in water storage tanks, particularly in warm, sunny conditions. To prevent algae growth, ideally, you can locate the tank in an area where sunlight can’t reach the water.
-
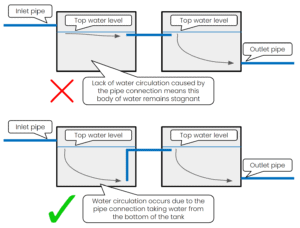
Bacterial growth: Bacteria can grow in water storage tanks, mainly if the water is not circulated regularly. To prevent bacterial growth, it is recommended to design the inlet and outlet pipes on opposite sides. You can also use chemicals and install an ultraviolet (UV) light system to kill bacteria.
-
pH: It is crucial to maintain the pH of the water within a safe range (typically between 6.5 and 8.5). You can use chemicals such as sodium hydroxide or sulfuric acid to adjust the pH.
It’s essential to regularly test the water in your storage tank to ensure it meets the appropriate quality standards.
How often should you clean a tank?
How often you should clean a water storage tank depends on a few factors, including the quality of the water being stored, the tank’s size, and the tank’s location.
It is generally a good idea to clean the tank at least once a year and more frequently if necessary.
How do you clean a water storage tank?
Here are a few steps you can follow to clean a water storage tank:
-
Drain the tank: The first step is to drain the tank completely
-
Clean the inside of the tank: Once the tank is empty, clean the inside of the tank
-
Disinfect the tank: After cleaning the inside, you need to disinfect it to kill bacteria or other contaminants
-
Flush the system: Once the tank is clean and disinfected, you must flush the system to remove any remaining debris or disinfectant
It’s essential to follow proper safety precautions when cleaning a water storage tank, including wearing protective clothing and using appropriate cleaning products.
How much space does my tank need?
Here are a few factors to consider when determining the space needed for a water storage tank:
-
Tank size: The size of the tank will be the main factor in determining the space required. Make sure to measure the area where you plan to install the tank to ensure it will fit with sufficient clearance around the tank for maintenance.
-
Tank shape: The shape of the tank can also affect the space required. For example, a round tank may require less space than a rectangular tank of the same capacity.
-
Tank location: If you plan to install the tank indoors, you will need to consider the height of the ceiling and the size of any doors or openings the tank will need to pass (unless it is a panel tank). If you plan to install the tank outdoors, you must consider the surrounding landscape and any structures or utilities that may be in the way.
-
Tank support: The tank will also need a foundation or other support to hold it in place. Make sure to allow for sufficient space for the support structure, as well as any equipment or piping that will be connected to the tank.
What are the access requirements?
There are a few essential access requirements to consider when installing a water storage tank:
-
Tank location: The location of the tank will be a key factor in determining access requirements. If the tank is located in a hard-to-reach area, you may need to provide access for maintenance and repair purposes. This could include installing a ladder or other access platform or creating a clear path to the tank.
-
Tank size: The size of the tank will also be a factor in determining access requirements. Larger tanks may require more space for access and maintenance purposes.
-
Tank features: The features of the tank, such as inlet and outlet valves, filters, and overflow pipes, will also need to be accessible for maintenance and repair purposes. Make sure to allow for sufficient space around these features for easy access.
-
Safety considerations: It’s essential to consider safety when providing access to a water storage tank. Install any necessary guards, handrails, or other safety features to prevent accidents.
- Confined Space: Some tanks are defined as confined spaces requiring side access hatches.
Planning for tank access when it is designed rather than trying to retrofit access later is essential.
What are the structural requirements?
There are a few vital structural requirements to consider when installing a water storage tank:
-
Tank size: The size of the tank will be a key factor in determining the structural requirements. Larger tanks will be heavier (more water and materials) and require a more robust support structure to hold them in place.
-
Tank shape: The shape of the tank can also affect the structural requirements. For example, a round tank will require a different support structure than a rectangular tank.
-
Tank location: The location of the tank will also be a factor in determining the structural requirements. For example, a tank on the 20th level will require more support than a tank on the ground level.
-
Soil conditions: If the tank is inground, the soil conditions must also be considered. The tank may require additional support or stabilisation if the soil is unstable or prone to movement.
- Earthquake: The tank will require extra structural support if the water supply needs to be maintained during a catastrophic event like an earthquake.
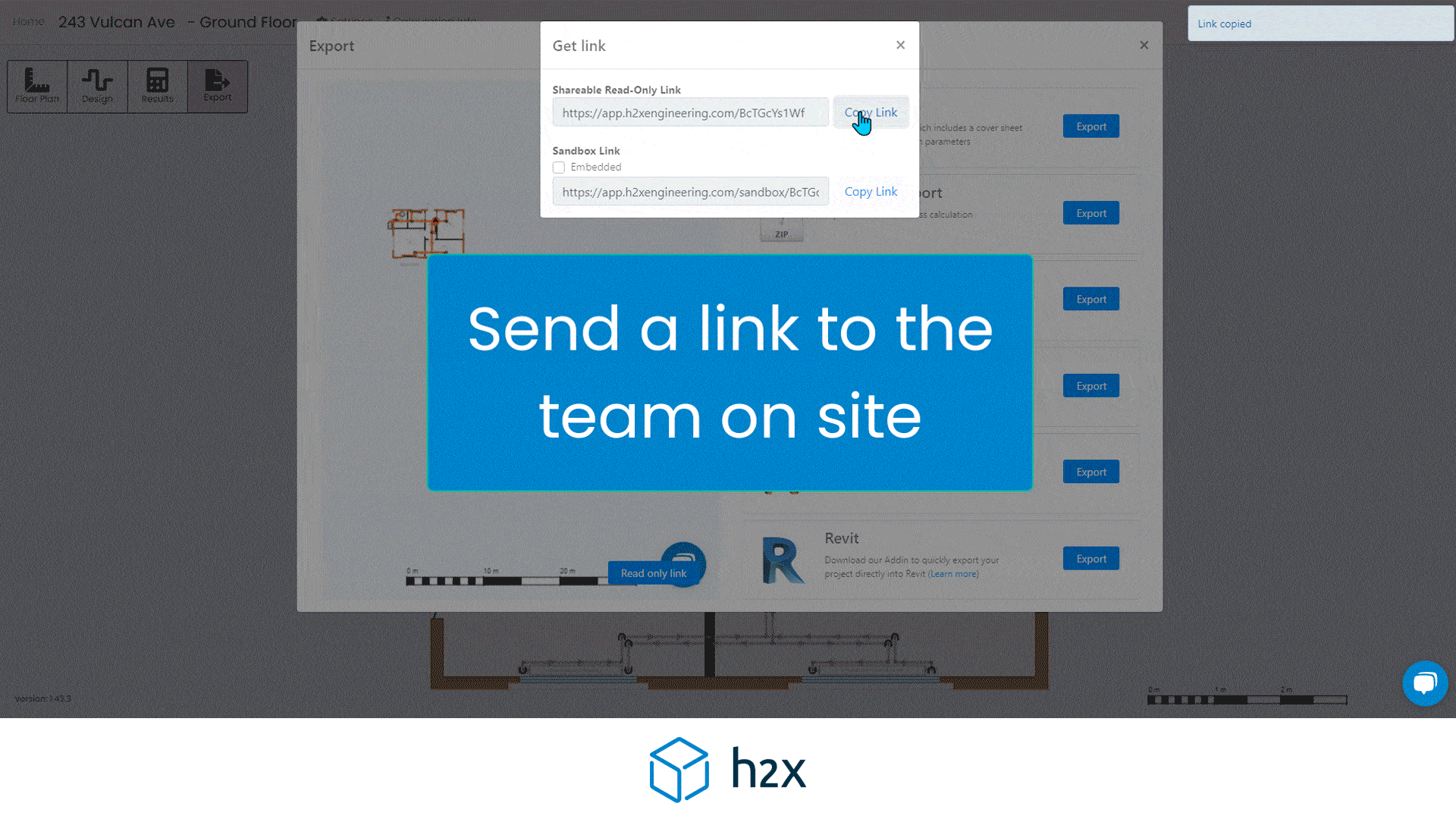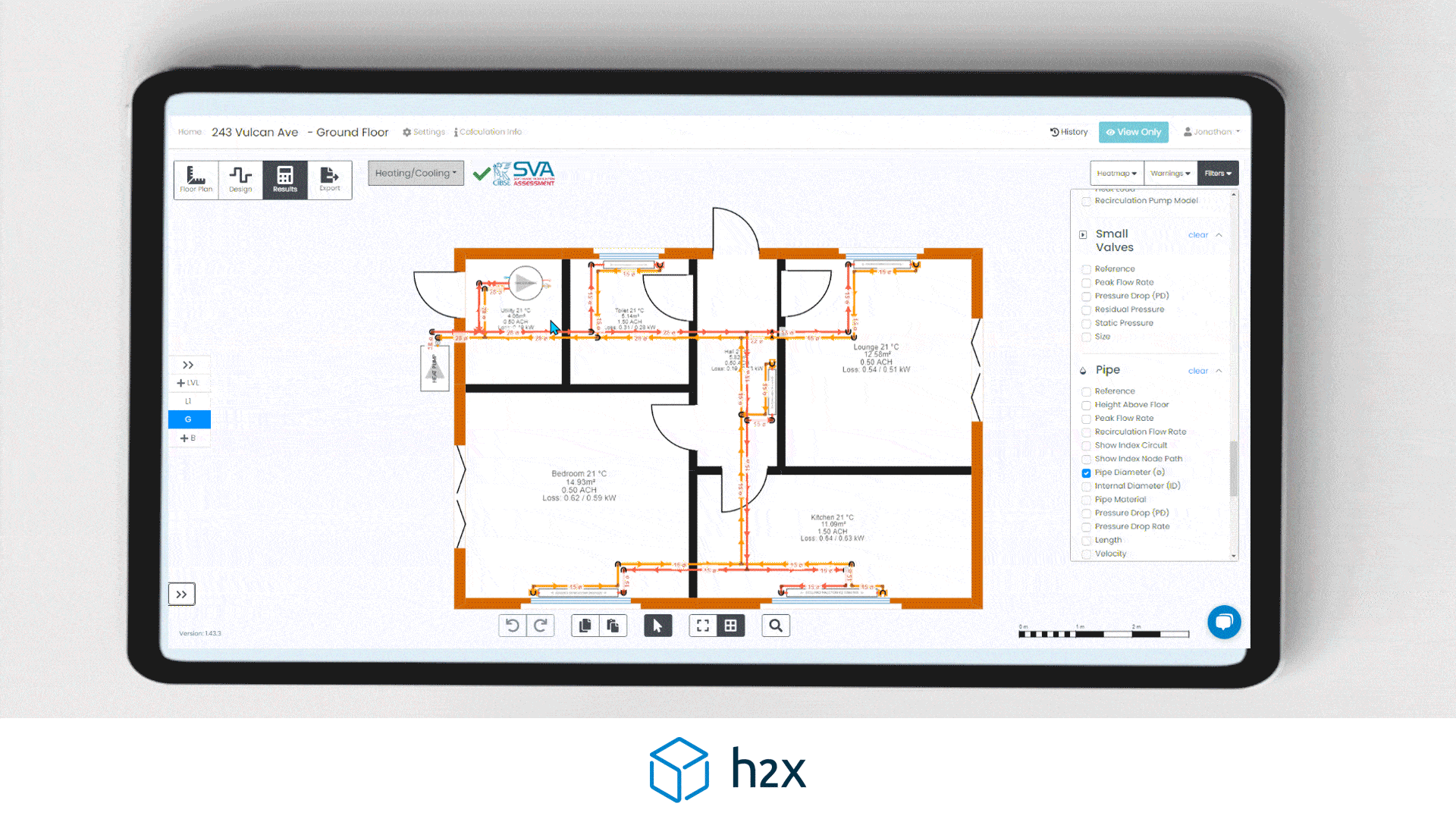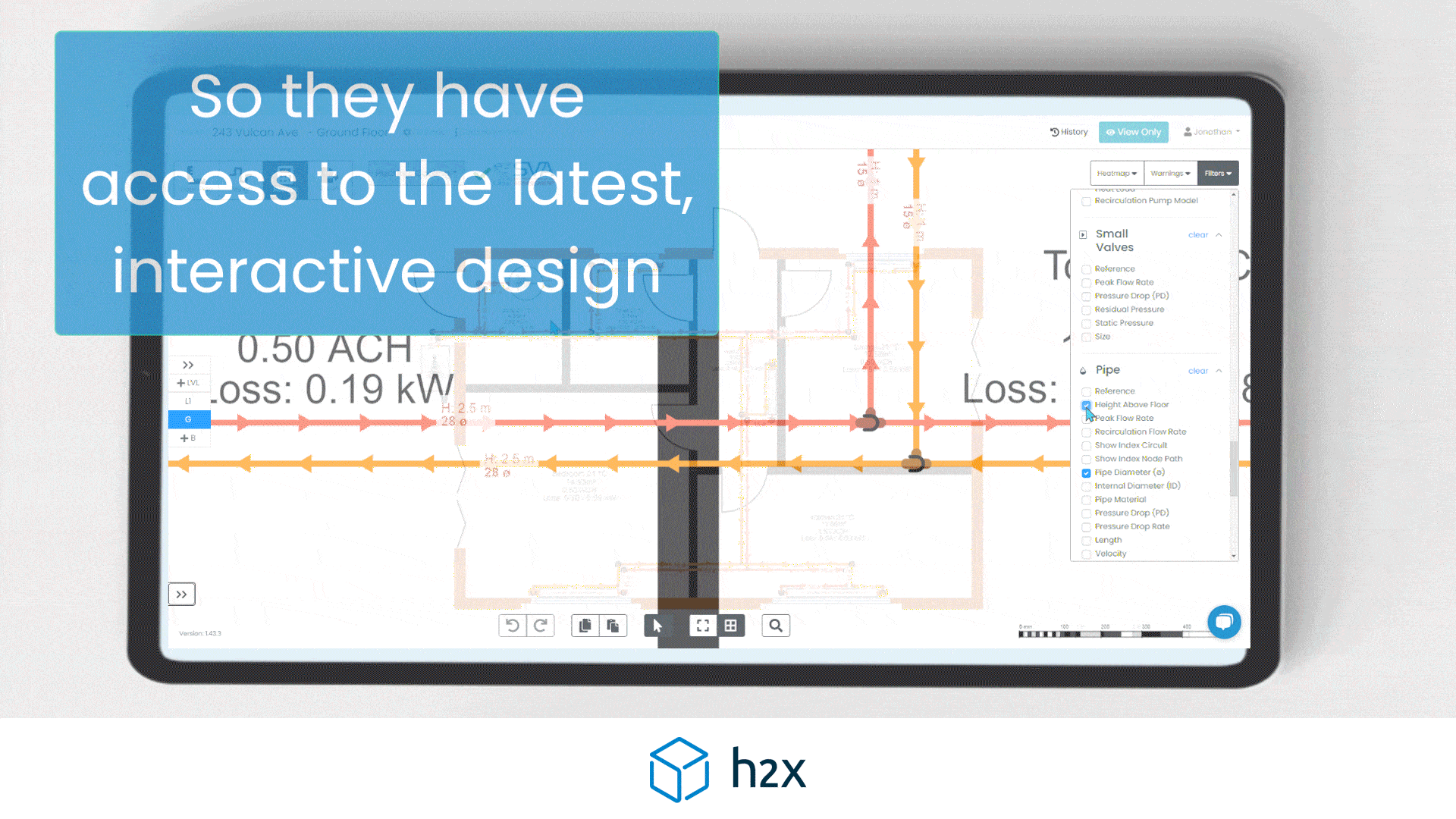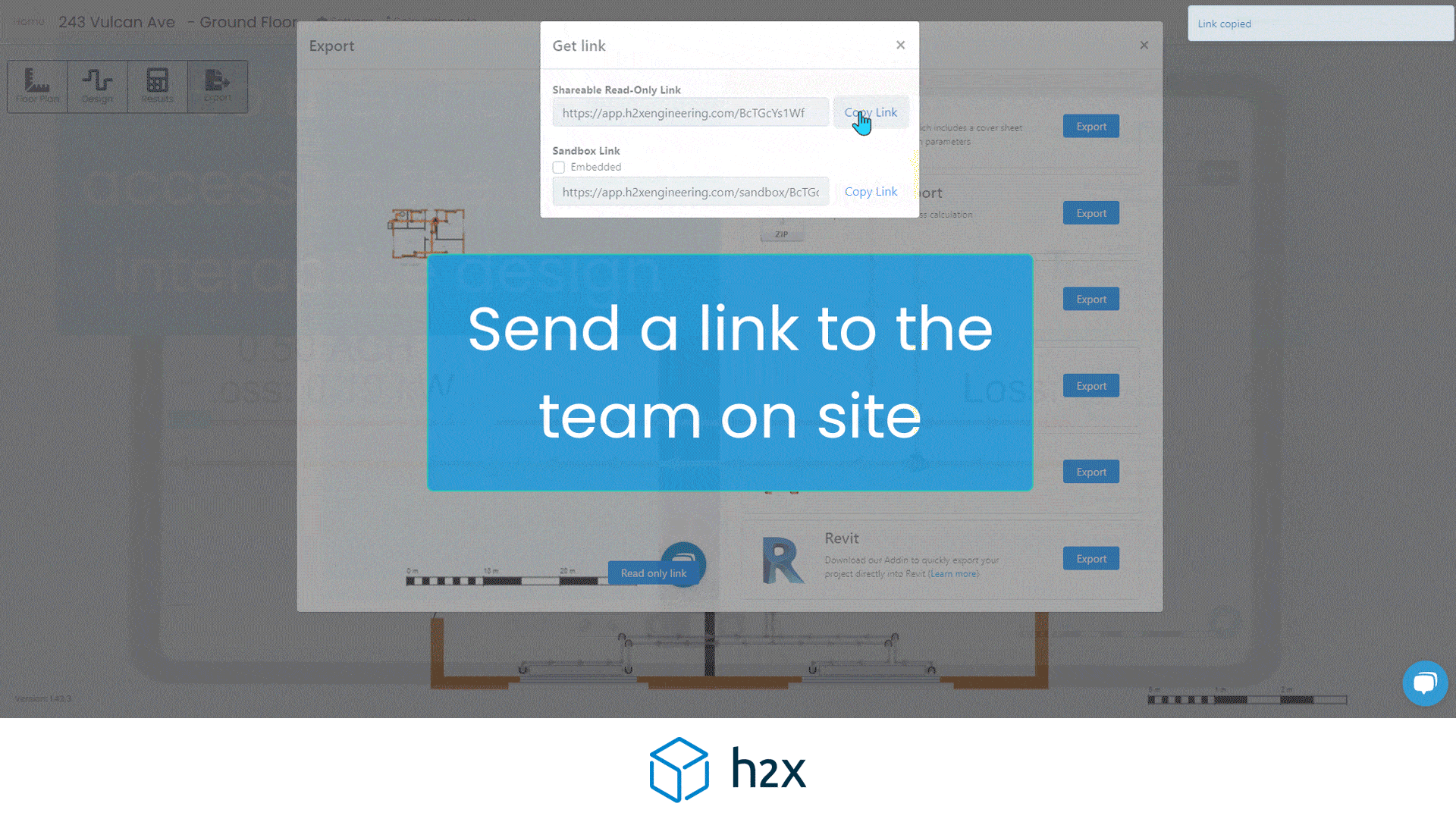
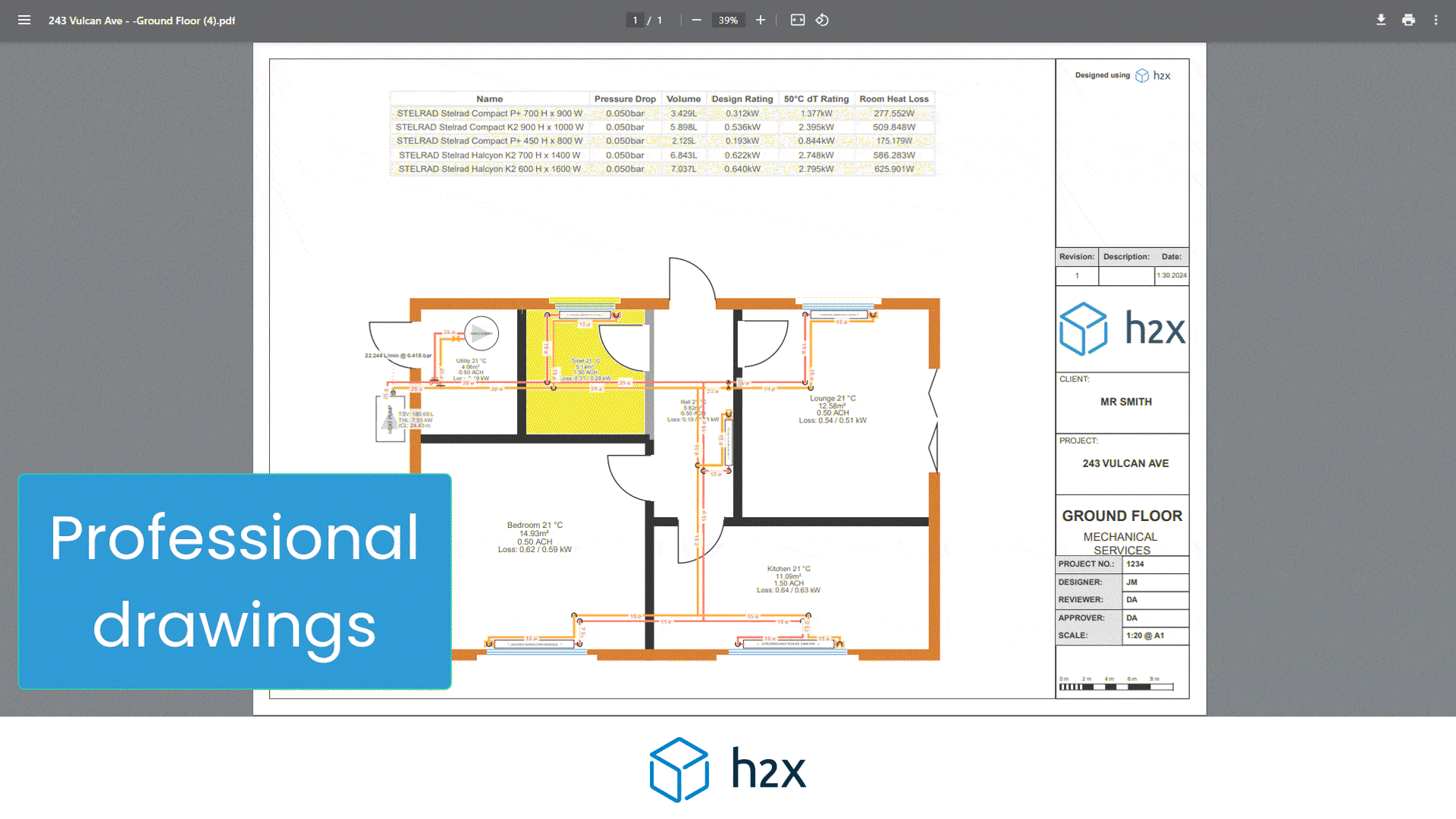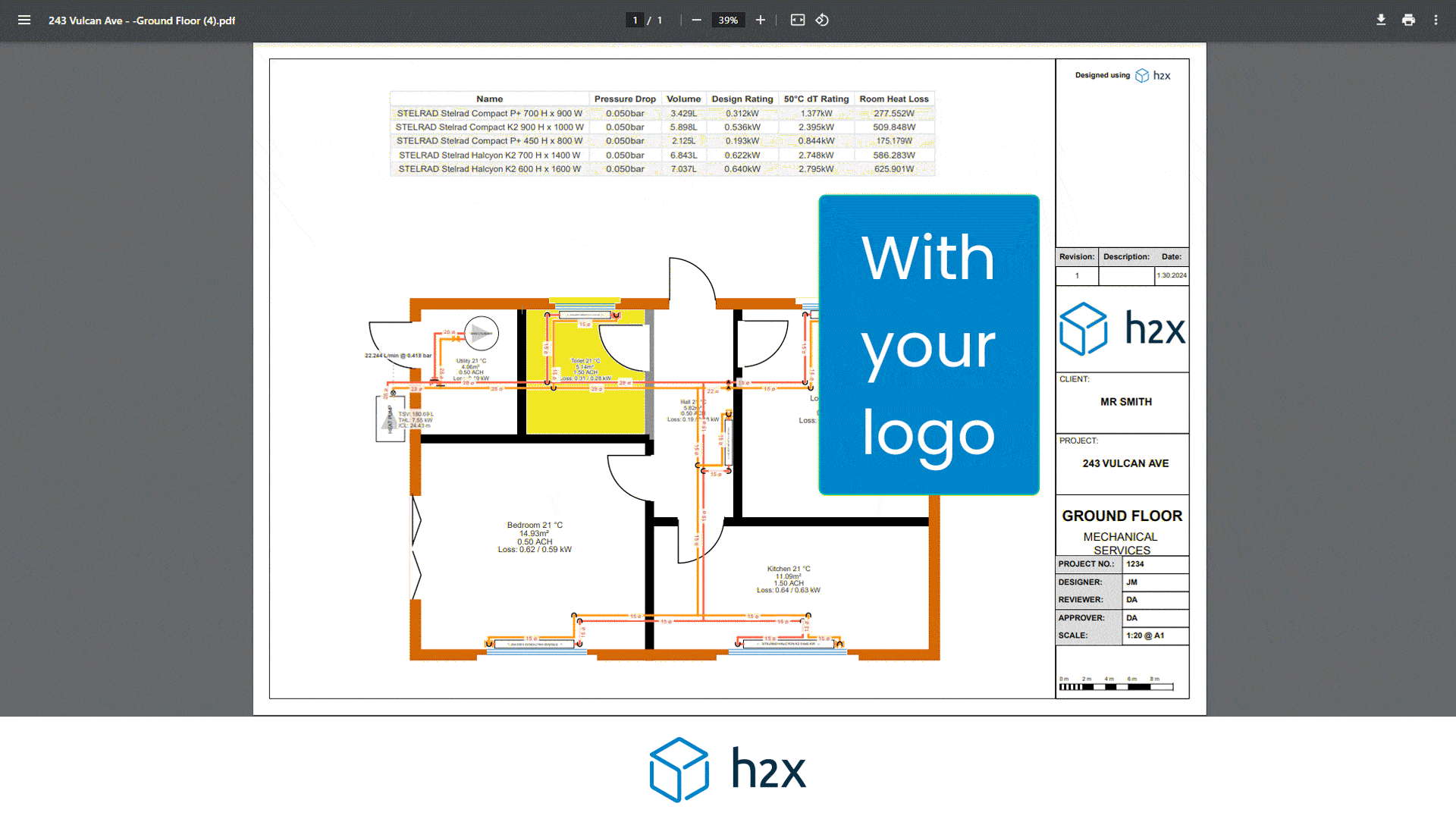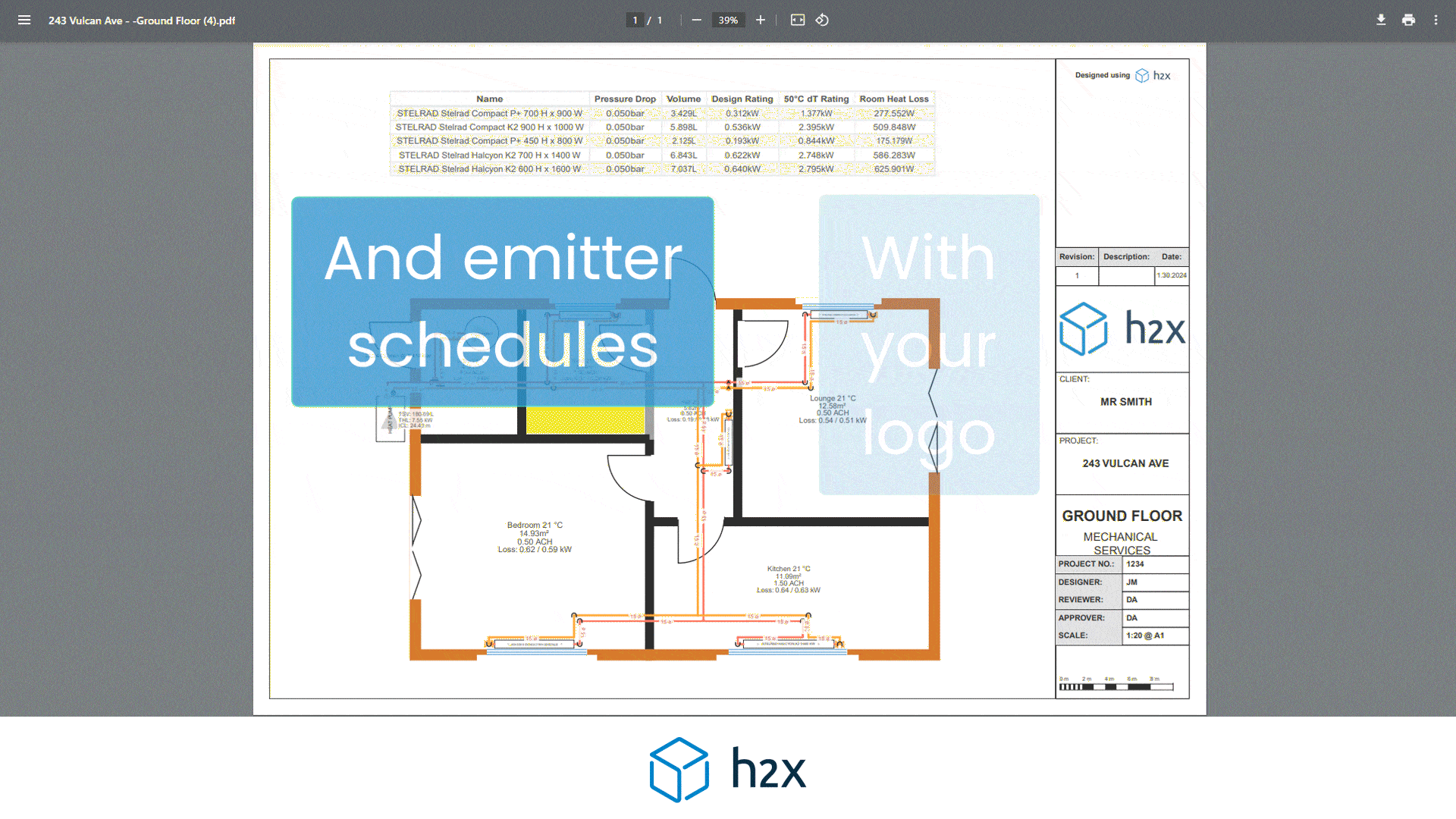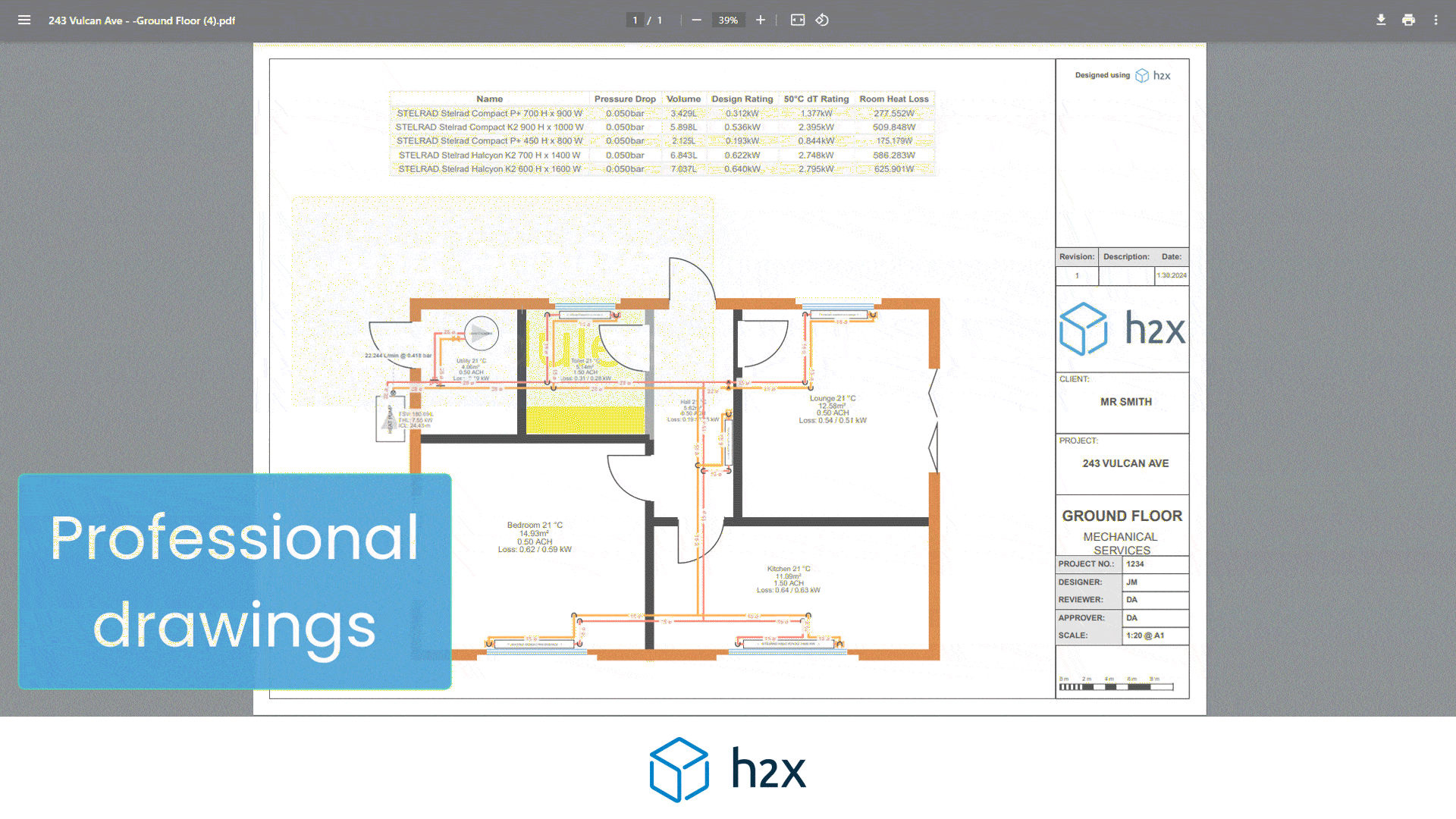
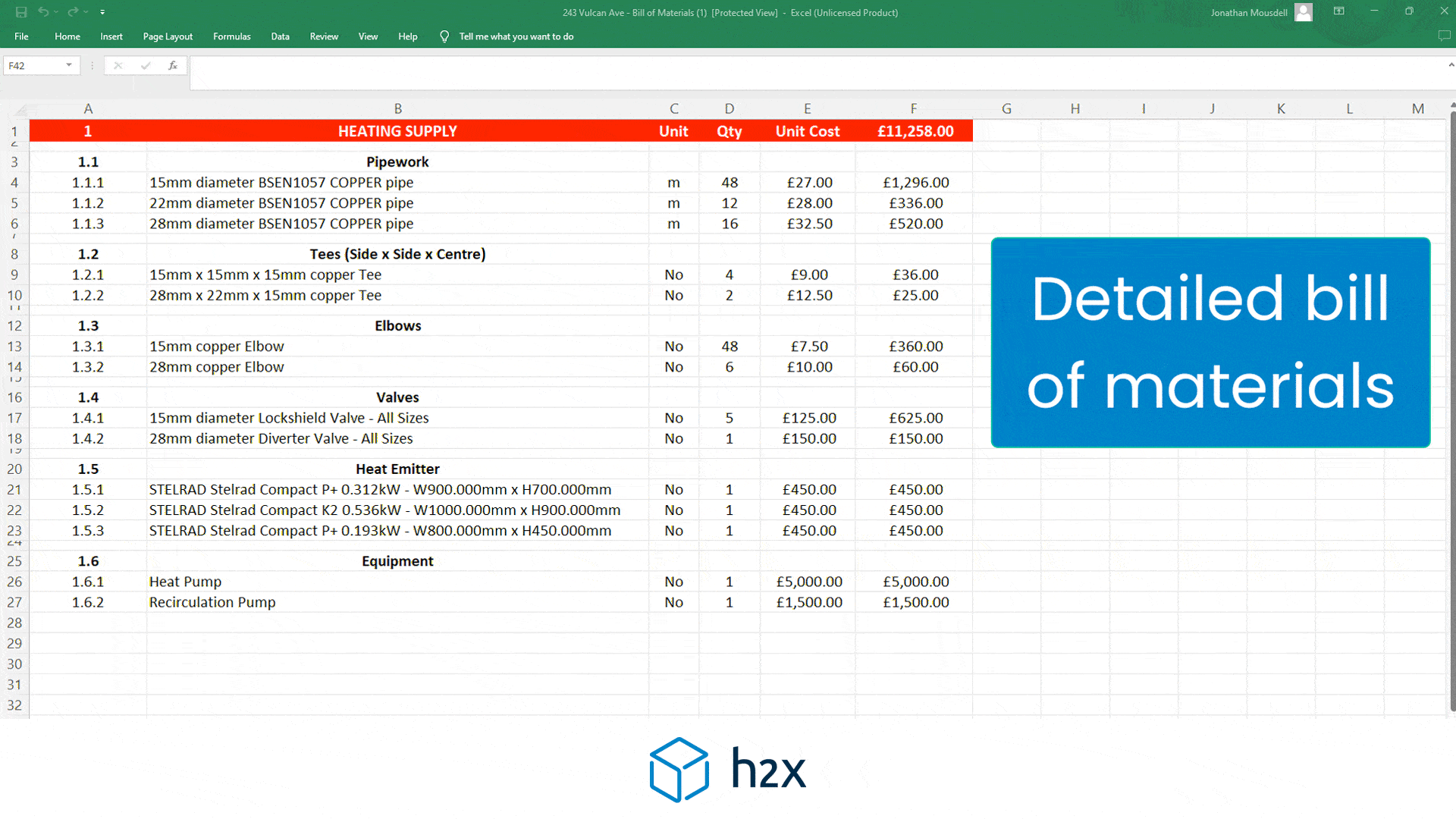
h2x is a plumbing system design software built to ensure compliance, efficiency, accuracy and collaboration.
Mains water pipe size calculator provide automated calculations for flow rates, velocities, pressures, pump duties, plant sizing, and recirculation systems mean that you can focus on your project’s design instead of undertaking tedious calculations.
h2x’s straightforward user interface helps engineers produce high-quality designs and work more efficiently, all while adhering to industry regulations.
The software has already been used to size millions of kilometres of pipes in projects across the world.
Book a demo with us today to discover how H2X can help you improve your design and calculation workflow.
h2x: All-In-One Tool for Calculating, Designing, Estimating, and Paperwork
What's in the Pipeline?
Get technical resources delivered to your inbox weekly!
Testimonials
What Installers Say
What Consultants Say
A game changer for the humble plumber. Incredible.
Brad Winkel
Director at Queenstown Plumbing
Brilliant, simple and easy to use. Game changer.
James Major
Director at Hubb
Big time game changer to the industry!
Viv Jude
Director at UHC
Incredible software! Super user-friendly and allows you to save so much time.
Devni Gamage
Engineer at DMA
h2x is great software, our company use it nearly every day. It is easy to use with direct conversion from h2x to Revit.
Callum Craig
Engineer at WDE
h2x is fantastic software. It is very easy to use and the ability to output to Revit is a fantastic time saver.
Joe Kirrane
Engineer at MEP