Media, UV, and Cartridge Filters Explained: An Engineer’s Guide

Water filtration and purification play a critical role in industrial water use for businesses. Unlike domestic use, industries often require vast quantities of water for various processes, such as manufacturing, cooling, and cleaning.
Water sources can contain various contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and sediments. Ensuring the quality and purity of this water is not only crucial for consumer and patient safety but also for the operational efficiency, environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance of businesses.
Understanding the differences between various water filters is crucial because not all filters are created equal. Different filters employ distinct mechanisms to remove contaminants, and their effectiveness can vary widely.
Some filters use physical barriers like mesh or activated carbon to trap particles and chemicals, while others rely on chemical reactions to neutralise harmful substances.
By selecting the right filtration system, businesses can optimise their processes, reduce maintenance costs, and minimise their environmental footprint.
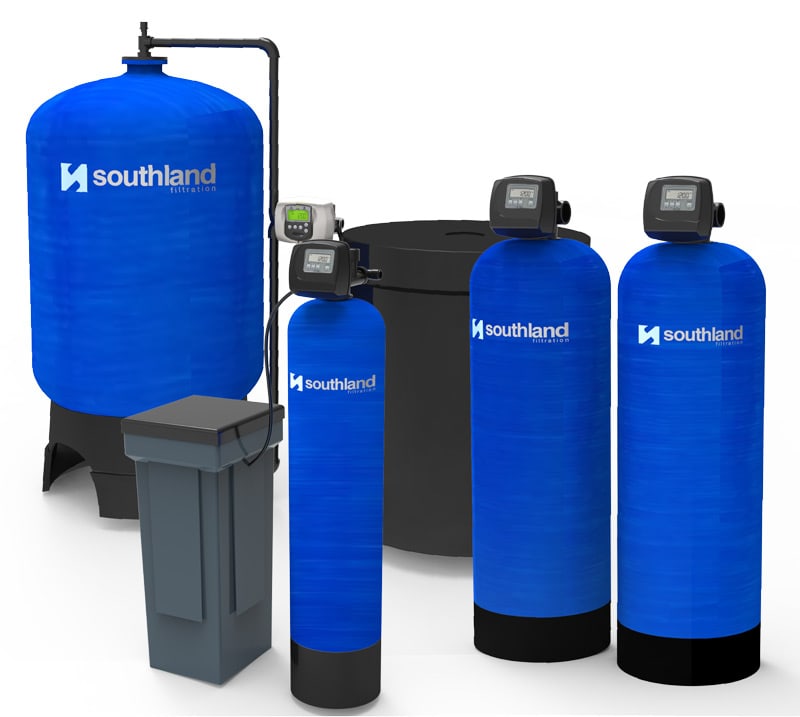
Media Filters
How They Work
The working of backwashing media filters involves a cyclical process.
- Water flows through a filter bed containing a filtering medium (such as sand, anthracite, or activated carbo)
- As the water passes through, the filtering medium captures contaminants, such as sediment, debris, or even microscopic impurities.
- Over time, this accumulation reduces the filter’s efficiency.
- Periodically, these filters initiate a backwash cycle. During this phase, the direction of water flow reverses, dislodging and flushing trapped contaminants from the filtering media.
- The cleansed filter bed is then ready to filter for optimal water quality.
Media Filters.
Typical Use Case
Industrial backwash filters find their niche in various sectors and scenarios, proving their worth in demanding industrial environments such as:
- Manufacturing facilities rely on them to purify process water, ensuring the quality of products and the longevity of equipment.
- Power plants employ these filters to safeguard cooling systems against clogs and damage from debris.
- Wastewater treatment plants use backwash filters to recycle water and reduce environmental impact.
- The mining industry depends on them to extract and treat water from mines, preventing environmental contamination.
- In municipal water treatment plants, they are used to purify drinking water by removing sediments and microorganisms.
- Industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, rely on backwash filters to maintain the quality of their products and protect their equipment from clogs and damage caused by contaminants.
- In wastewater treatment, these filters help in recycling and reusing water, reducing environmental impact.
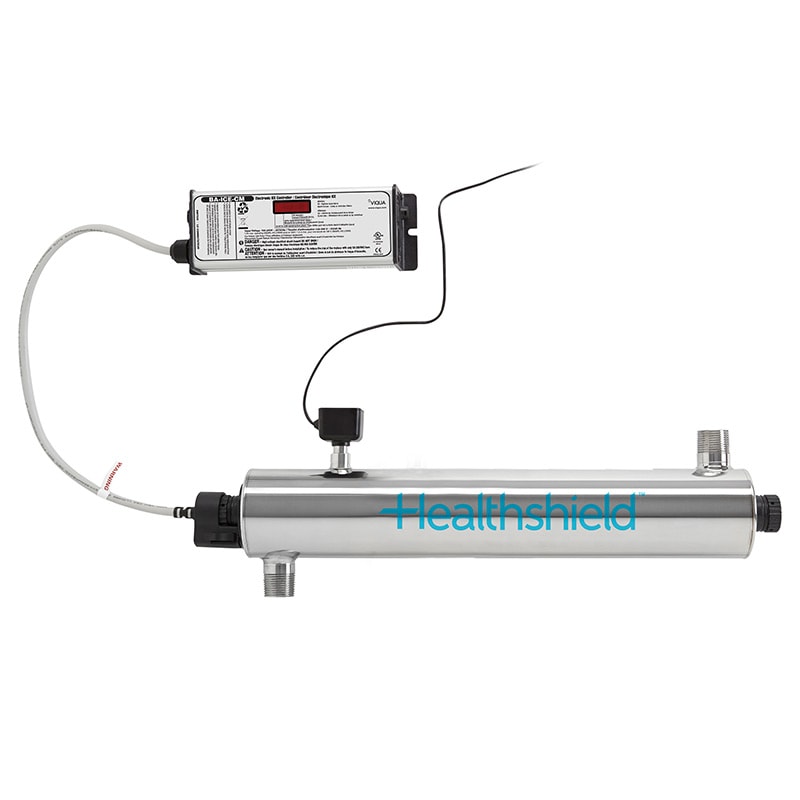
UV Disinfection Systems
How They Work
UV disinfection systems protect system integrity against microorganisms and pathogens by using ultraviolet light to disinfect water effectively.
The damaging effect of UV-C rays on the DNA of microorganisms renders them incapable of reproduction and eliminates the risk of contamination.
- As water flows through a UV filter chamber, it is exposed to a high-intensity UV-C light source.
- This light, at a specific wavelength (typically 254 nanometers), penetrates the cell walls of microorganisms, disrupting their genetic material.
- The result is that Microorganisms become inactive and unable to reproduce.
While the UV-C light works, water passes through the chamber unaltered, with no added chemicals or byproducts. This ensures that the treated water remains safe for hydraulic systems without introducing any potential contaminants.
UV Filters.
Typical Use Cases
Engineers employ UV systems in a range of critical scenarios where water quality and sterility are non-negotiable.
- Healthcare for maintaining the sterility of CSSD, renal dialysis, endoscopy suits and laboratories where the purity of water is essential to patient safety and infection control.
- Cooling water systems for power plants, preventing the growth of harmful organisms that can foul heat exchangers and reduce system efficiency.
- In industrial processes, UV filters are deployed to safeguard hydraulic fluids from microbial contamination, ensuring that costly equipment remains in peak condition.
- In municipal water treatment, UV filters are an indispensable component, eliminating the risk of waterborne diseases by neutralising pathogens.
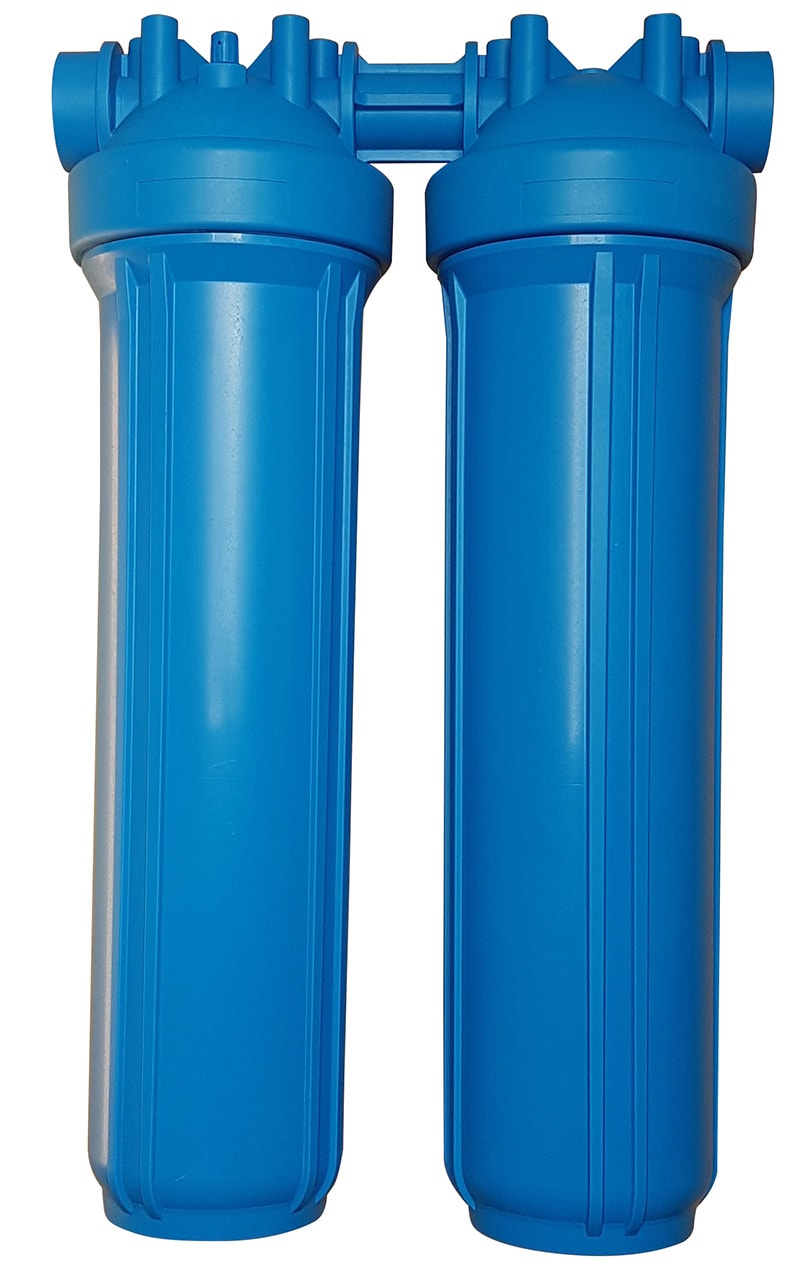
Cartridge Filters
How They Work
Cartridge filters efficiently trap and remove contaminants from water sources. These filters operate based on a principle known as depth filtration, where the filter medium captures impurities as water flows through it.
The filter medium itself is typically composed of materials like pleated paper, spun polypropylene, or porous ceramic.
- As water passes through the filter housing, it encounters the cartridge.
- Contaminants in the water, whether they are sediment, particles, chemicals, or microorganisms, get entrapped within the filter medium.
- Clean, filtered water emerges on the other side, free from the potential hazards posed by impurities.
Over time, as the cartridge accumulates contaminants, it can be replaced easily, restoring the filter to its optimal performance.
This modular design ensures that water treatment systems continue to deliver clean, safe water without significant downtime or disruptions.
Cartridge Filters.
Typical Use Cases
Cartridge filters find versatile applications across various water treatment scenarios, where maintaining water quality is paramount.
In industrial water treatment, cartridge filters play a crucial role in removing suspended solids, chemicals, and microorganisms from process water.
These filters are employed to safeguard product quality and equipment integrity in:
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Electronics industries
- Municipal water treatment plants clarify water by capturing particulates and enhancing the efficiency of downstream treatment processes
- Pre-filtration for reverse osmosis systems, protecting delicate membranes from fouling
Efficiency and Contaminant Removal
Each filter is effective at removing and neutralising different contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and sediments.
The table below summarises their differences, including the limitations of each type of water filter.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Consideration needs to be given to the design and maintenance of the water filters to ensure the design can operate sustainably.
Water wastage in backwash filters
Water wastage can be a concern in backwash filters, especially in the context of water treatment and filtration.
During the backwashing process, where the filter media is cleaned by reversing the water flow, a substantial amount of water is often flushed out, carrying away trapped contaminants.
While this is a necessary step to maintain filter efficiency, it can result in water loss, which is a critical issue in regions facing water scarcity or where conservation is a priority.
To mitigate this, modern filtration systems incorporate strategies to optimise backwash cycles, using sensors and controls to trigger backwashing only when necessary and to minimise the volume of water used.
In some applications, if the infrastructure is already there, the water that is discharged during the backwash cycle can be recycled and used for applications such as irrigation and flushing toilets.
This approach helps strike a balance between the need for clean filters and the imperative to reduce water wastage, contributing to sustainable water treatment practices.
Electrical consumption in UV filters
UV filtration systems rely on powerful UV lamps to emit ultraviolet light for disinfecting water by neutralising microorganisms.
These lamps do consume electricity, and the energy requirement can vary depending on the size and capacity of the UV system.
It’s essential to factor in electrical consumption when using UV filters, especially in applications where energy efficiency is crucial.
Routine maintenance, such as replacing UV lamps when they reach the end of their lifespan, can help ensure that the system operates efficiently and consumes electricity as intended, ultimately contributing to both effective water treatment and responsible energy use.
Disposal of cartridge filters
Once Cartridge filters reach the end of their lifespan or become saturated with contaminants, they should be handled and disposed of responsibly.
Proper disposal involves removing and replacing the used cartridges according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
In many cases, cartridge filters can be disposed of as solid waste or recycled, depending on the materials used in their construction.
It’s essential to follow local regulations and guidelines for the disposal of used cartridge filters to minimise their impact on the environment and ensure that they do not contribute to water pollution or other ecological concerns.
Maintenance and Longevity
The frequency of maintenance for all these filters may vary based on factors such as water quality, usage patterns, and manufacturer recommendations.
Adhering to proper maintenance schedules ensures that these filters continue to provide clean and safe water while extending their longevity and preventing potential system issues.
Optimising size and specification
The key to successful water purification lies in custom-sizing the system for your specific needs. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Off-the-shelf solutions may not address your specific contaminants or flow rates effectively. Every water treatment application is unique, always source a supplier who will develop a solution specific to your needs.
- You’ll save on time and resourcing costs in the long run as custom-sized systems ensure that water treatment is efficient, and effectively meets the required quality standards.
- You’ll save on overspending on unnecessary features or capacity if you get a system that precisely matches your needs.
To achieve these benefits and get the best value, partner with suppliers who understand the intricacies of water treatment where they can:
- Conduct thorough water quality analysis to identify contaminants and their concentrations
- Evaluate flow rates and system demands to determine the appropriate size and capacity
- Design and supply custom-tailored solutions that address your unique water treatment challenges.
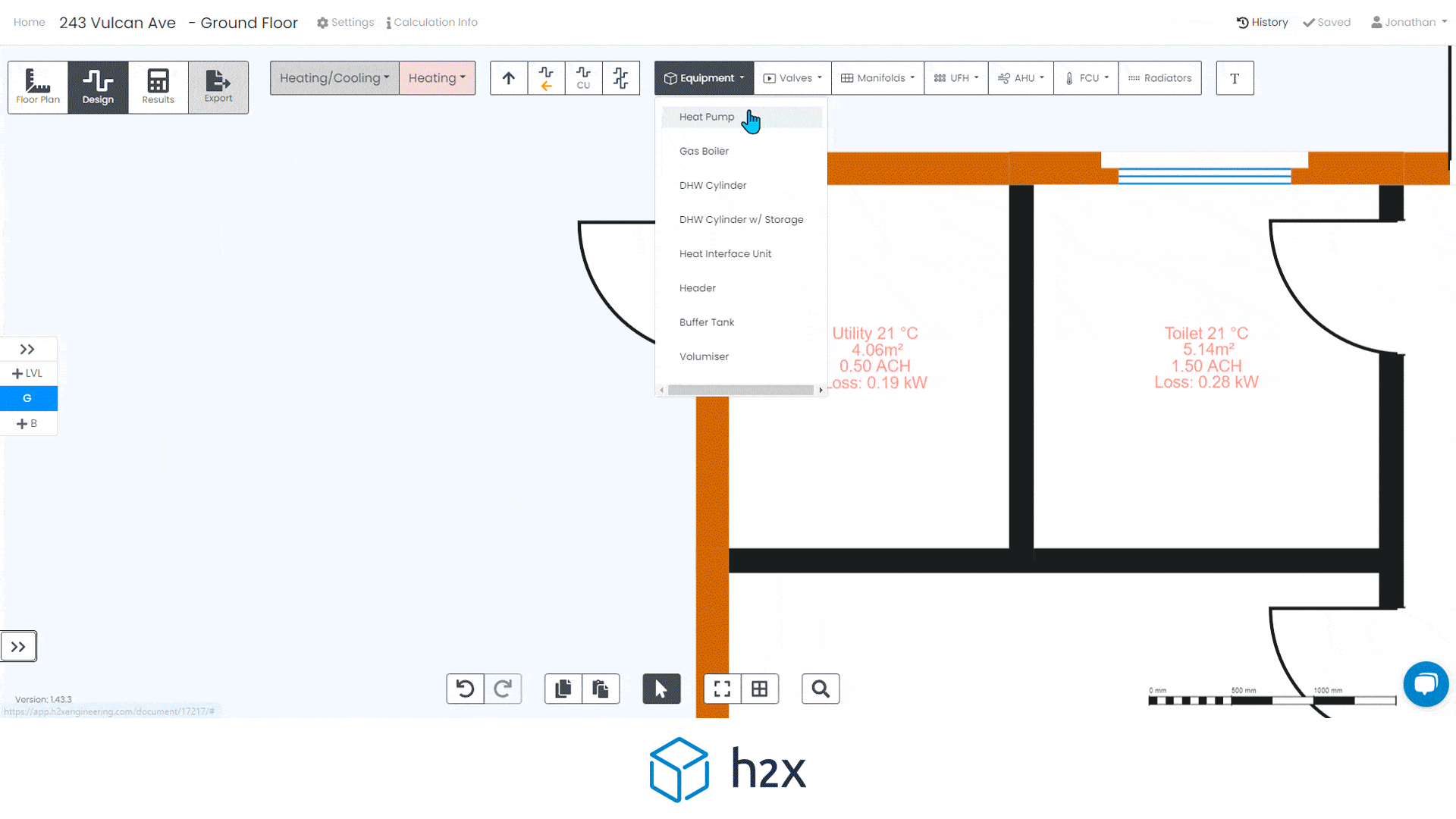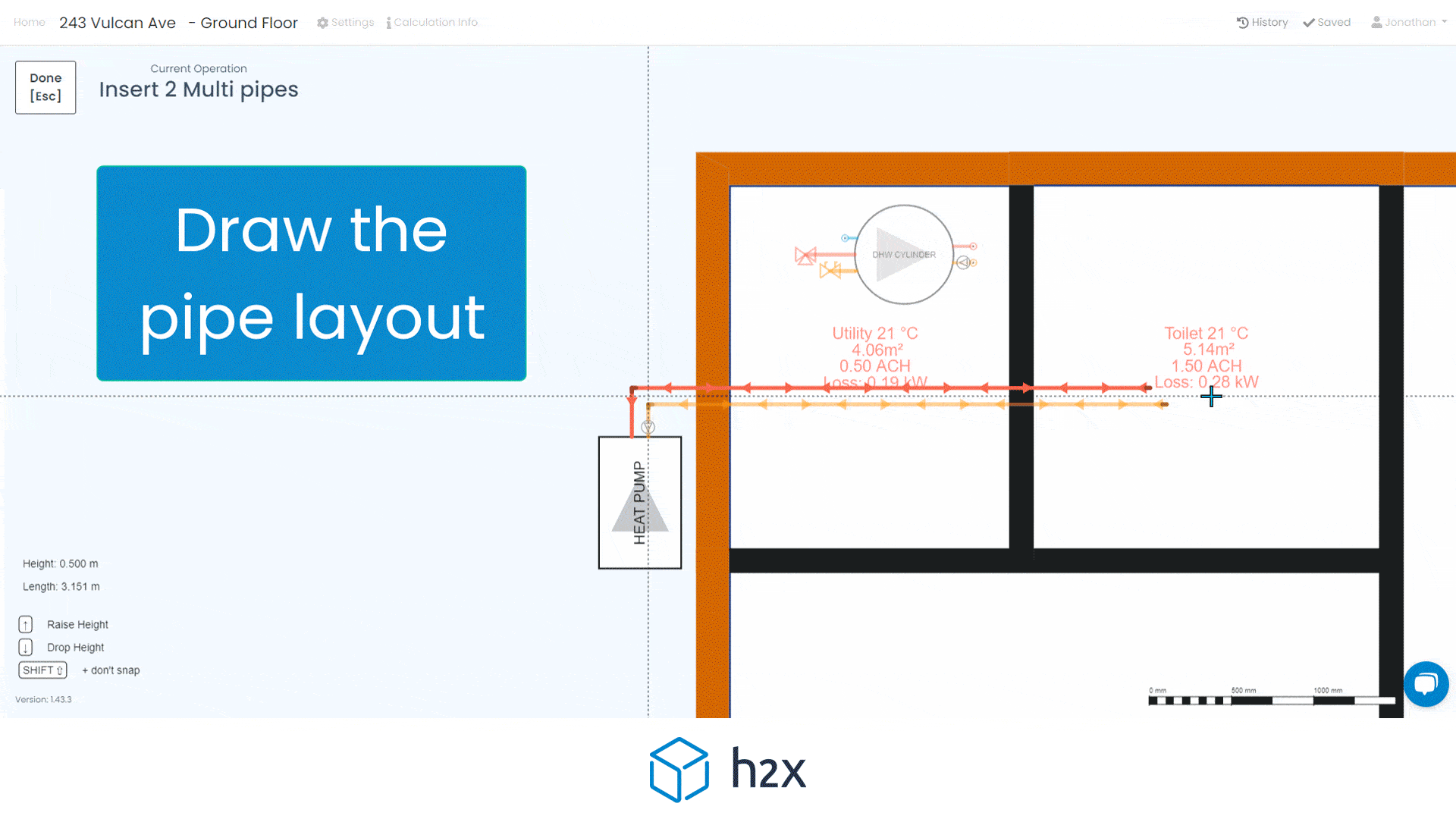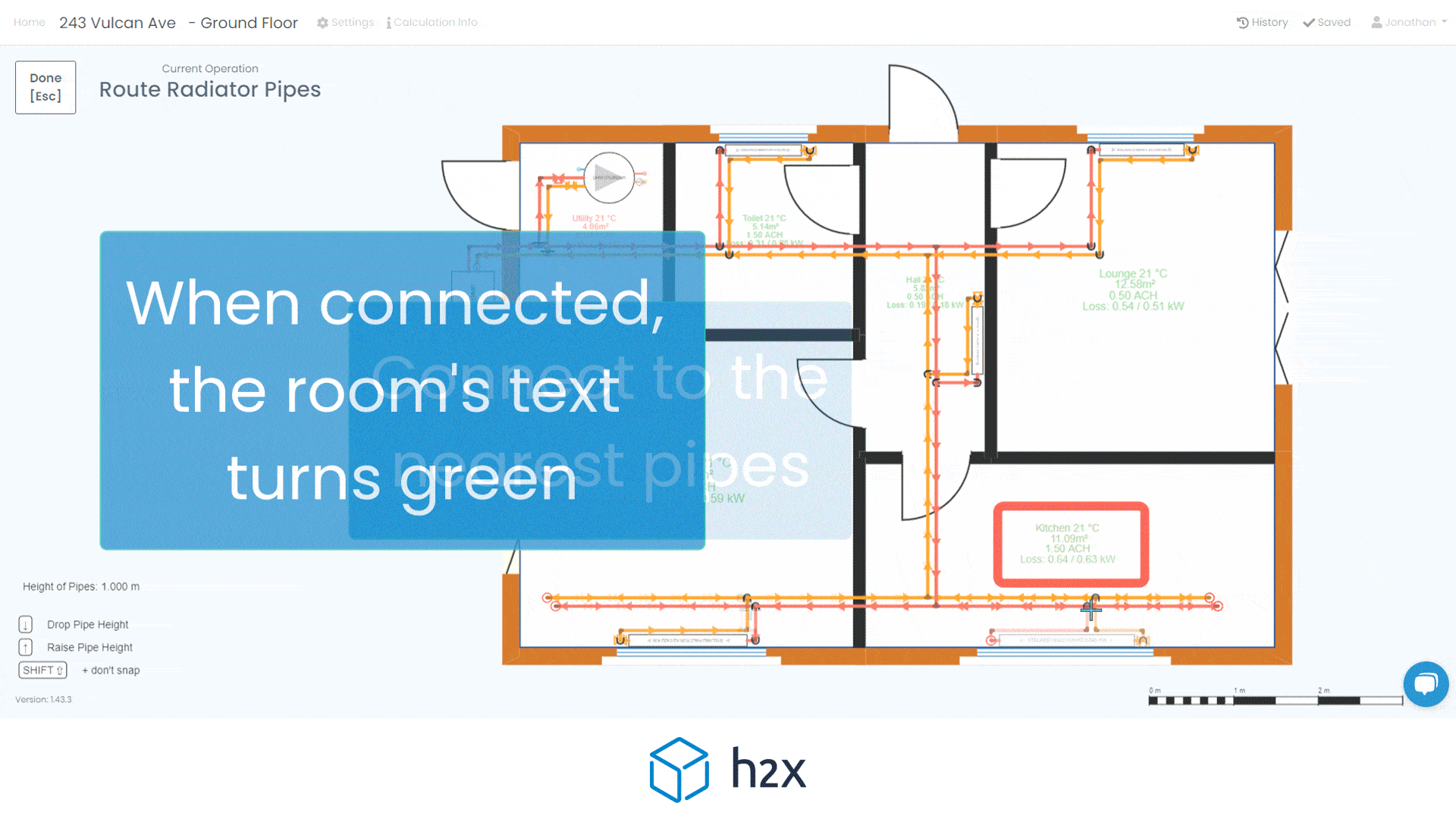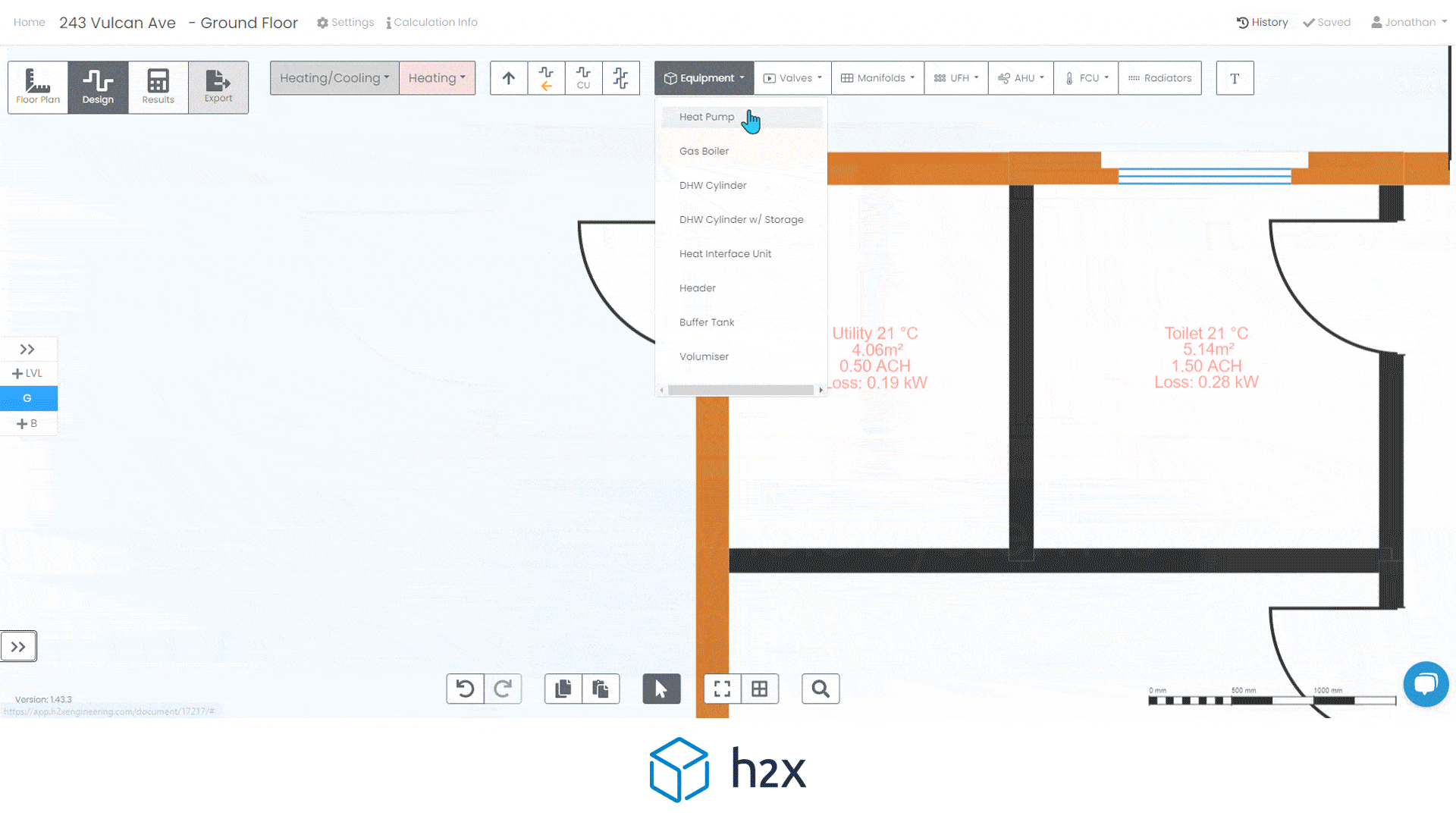
Automated filter sizing and specification
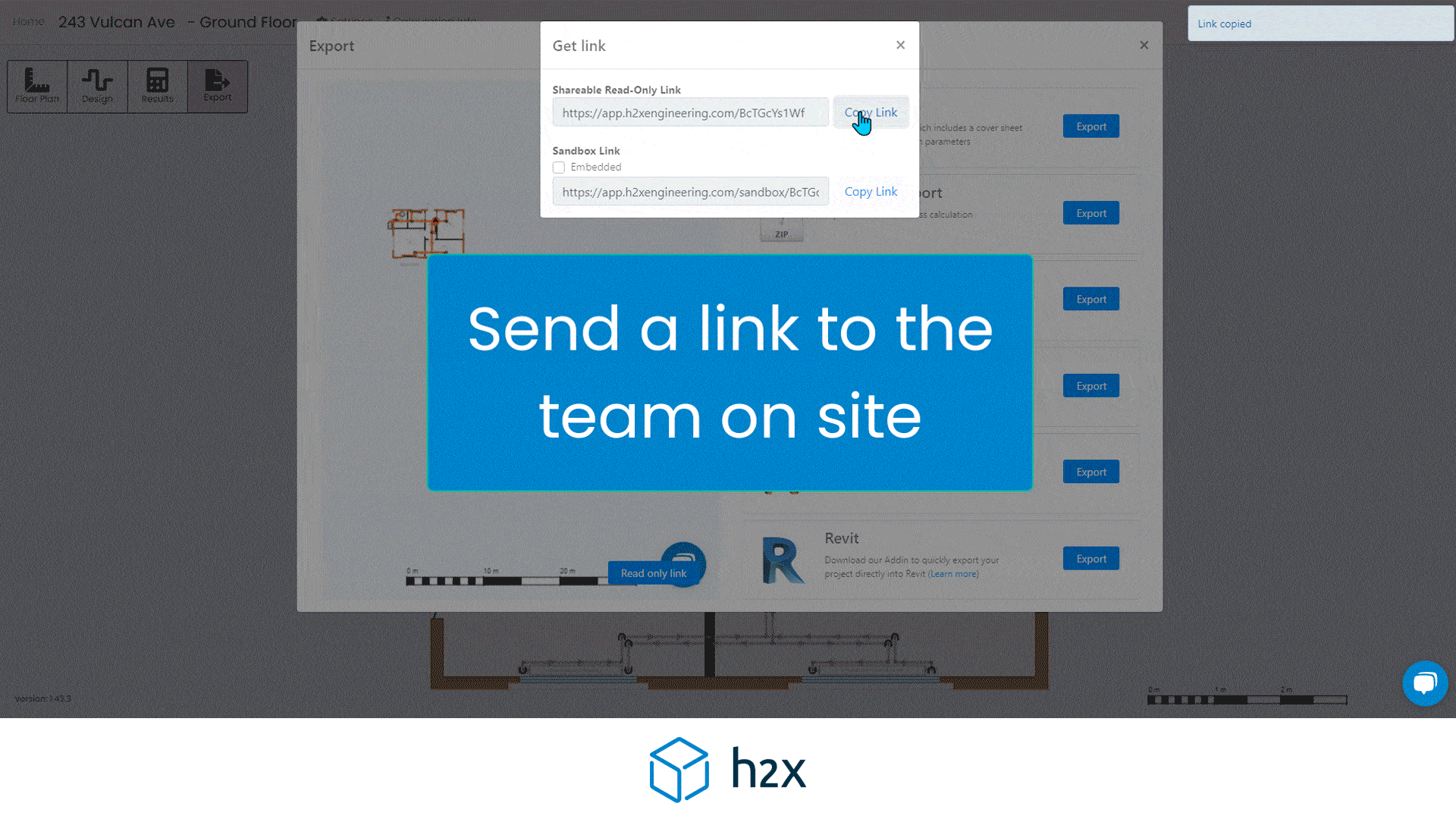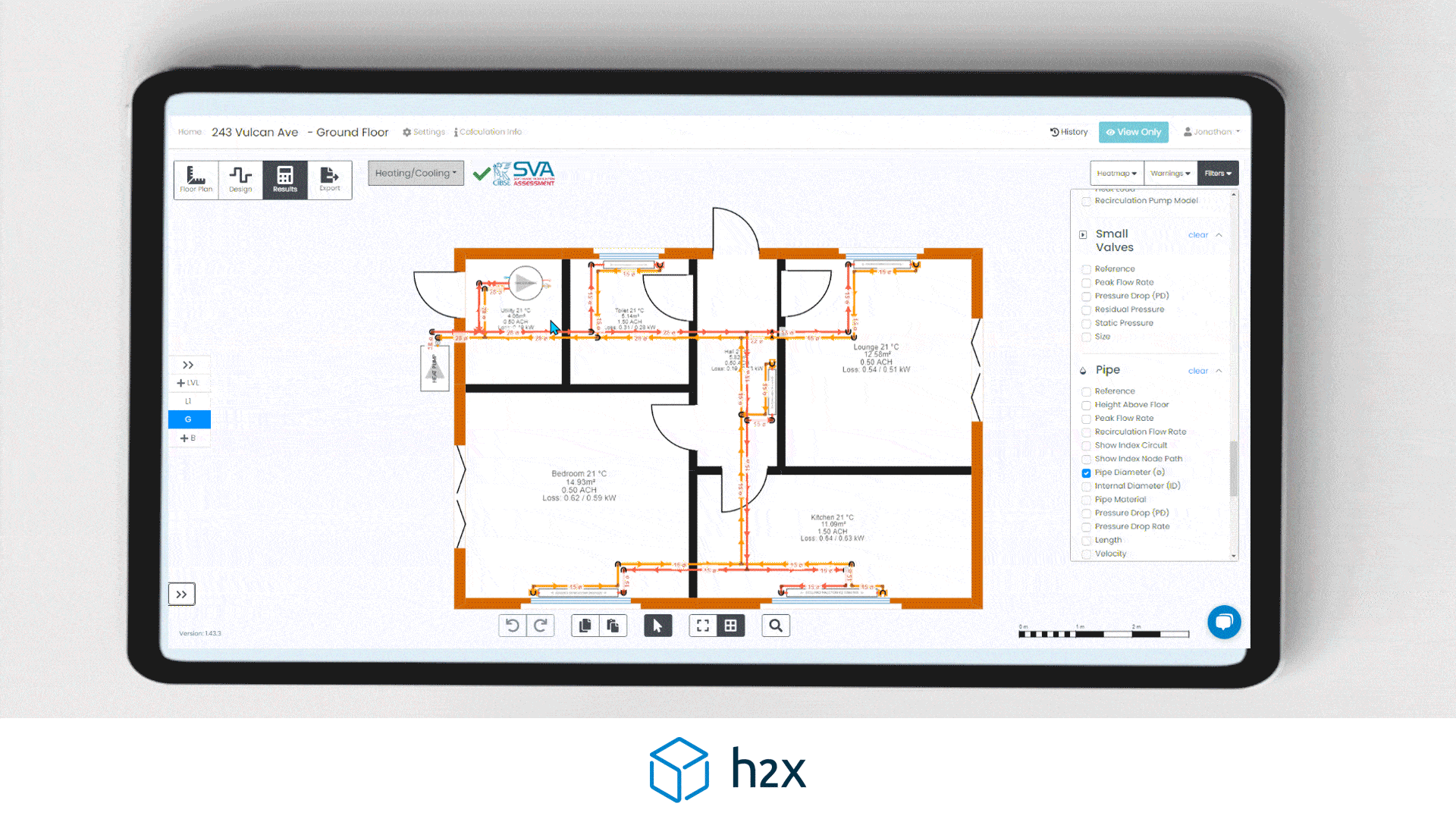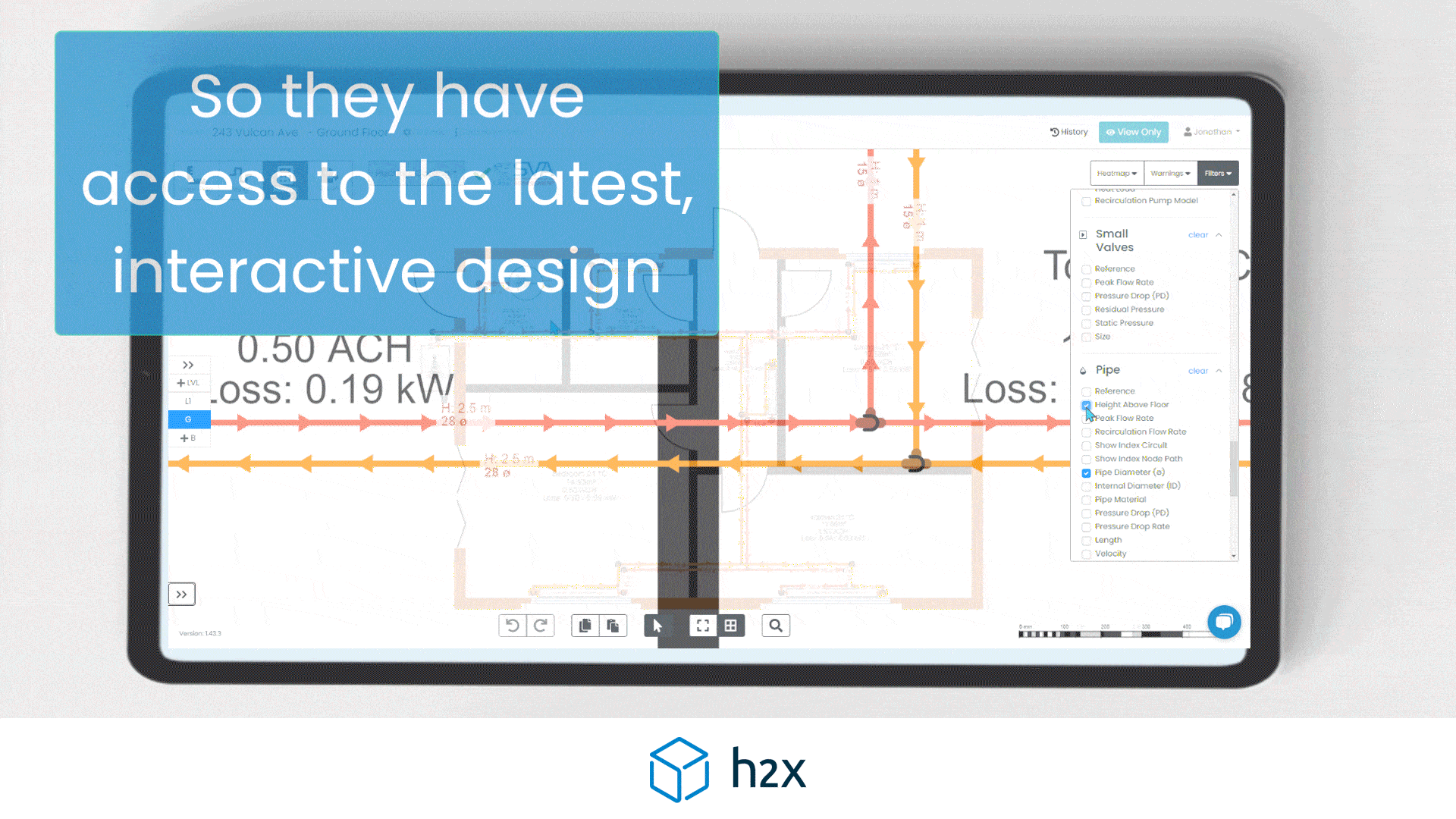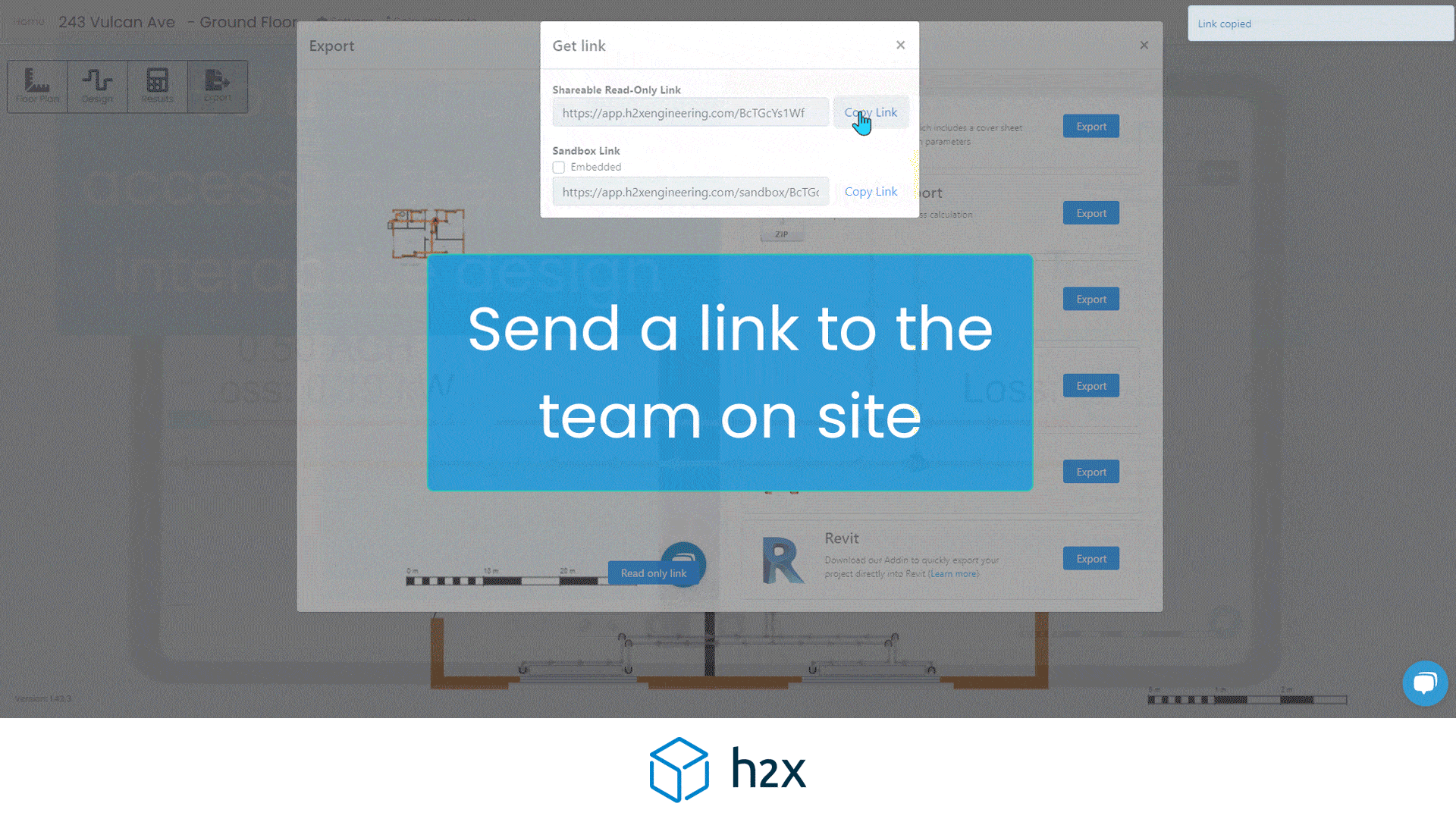
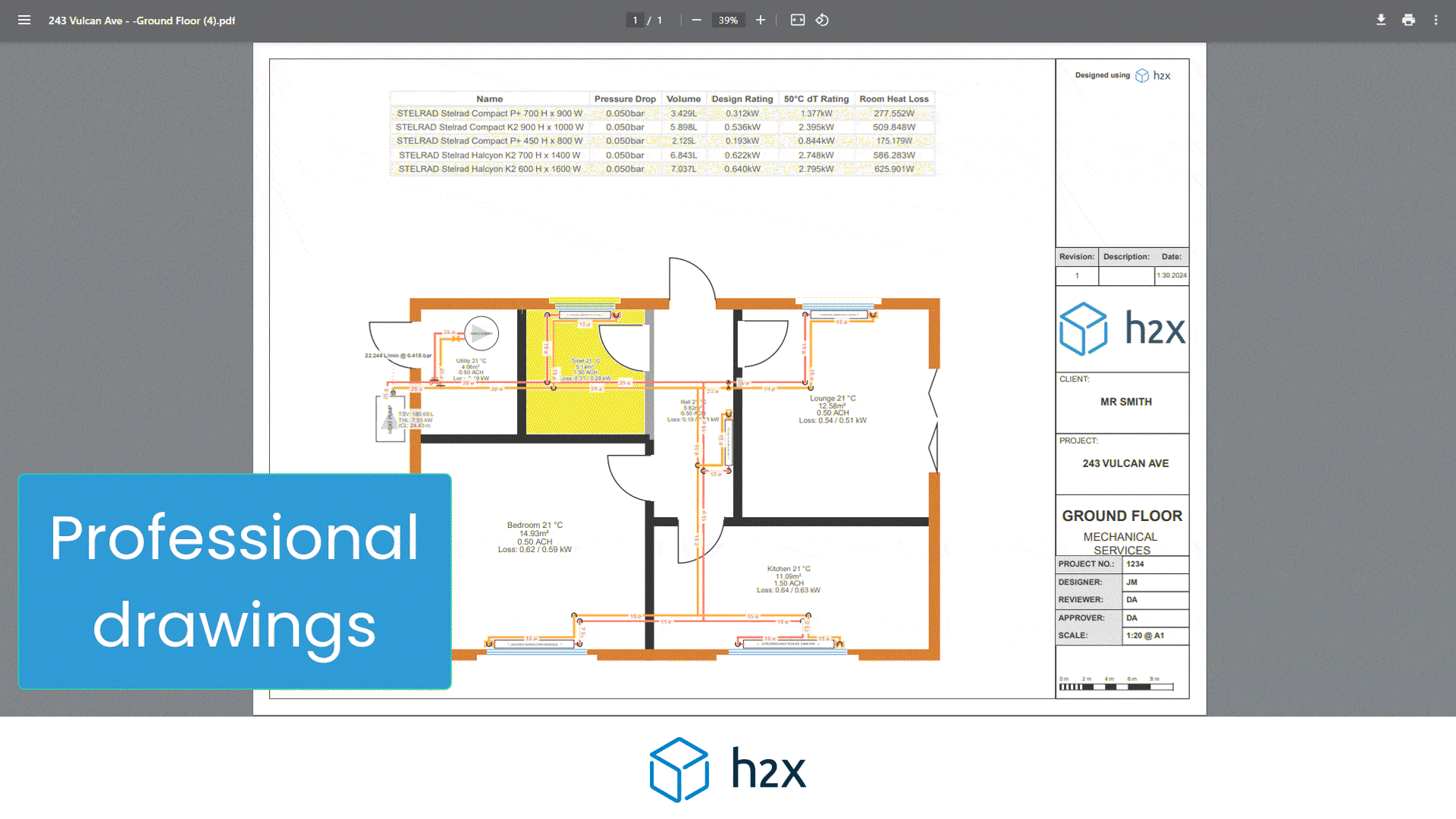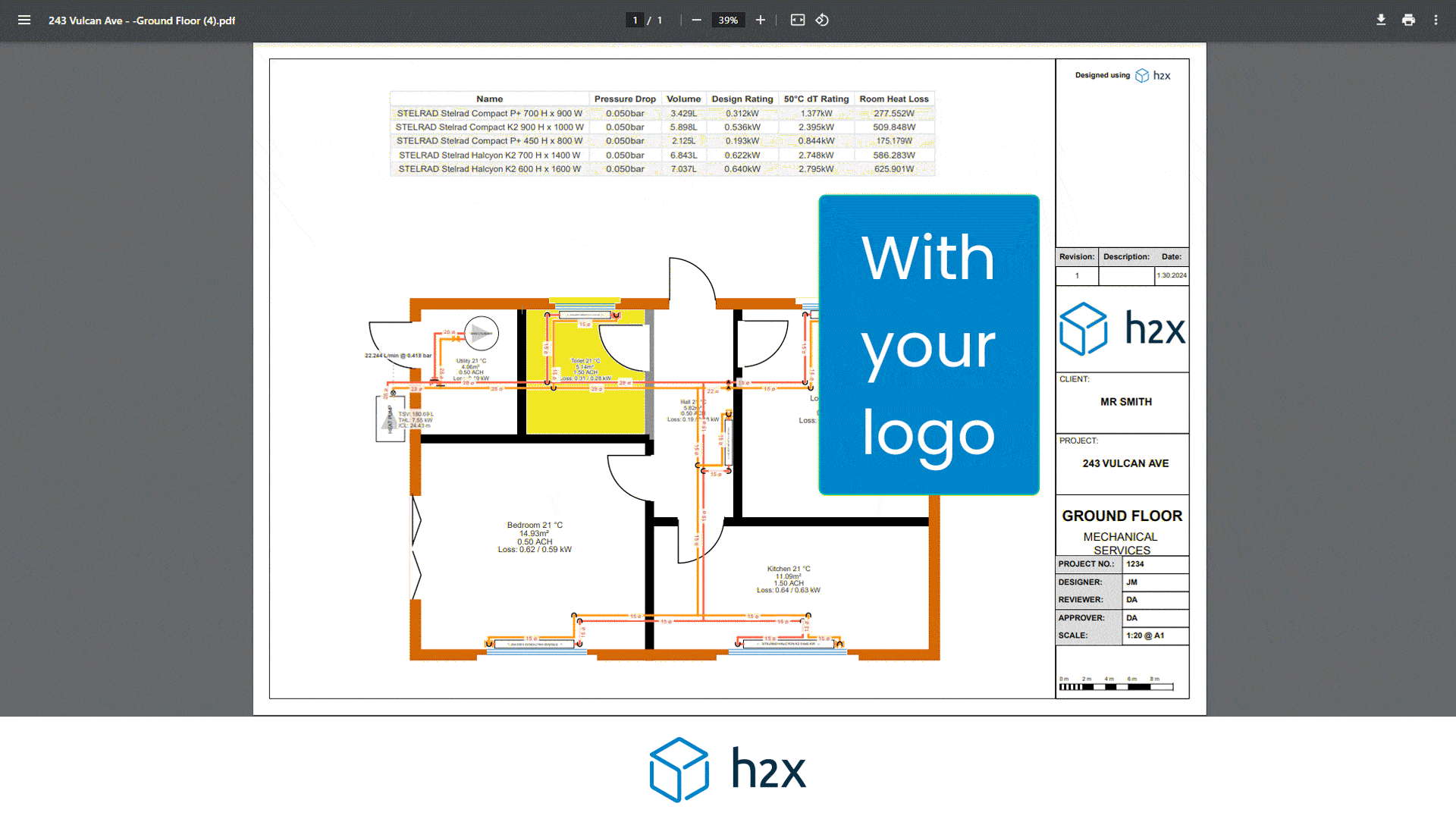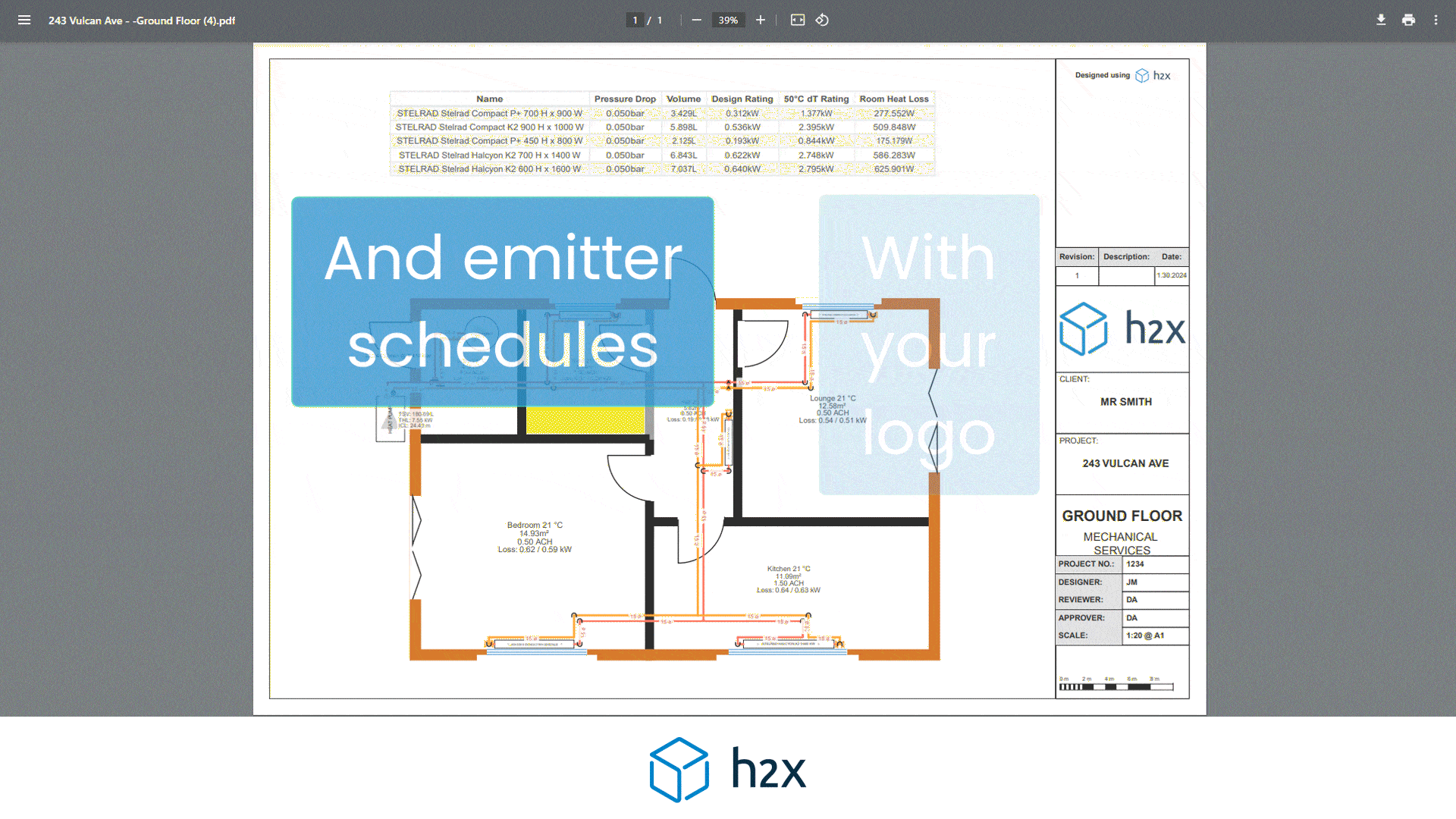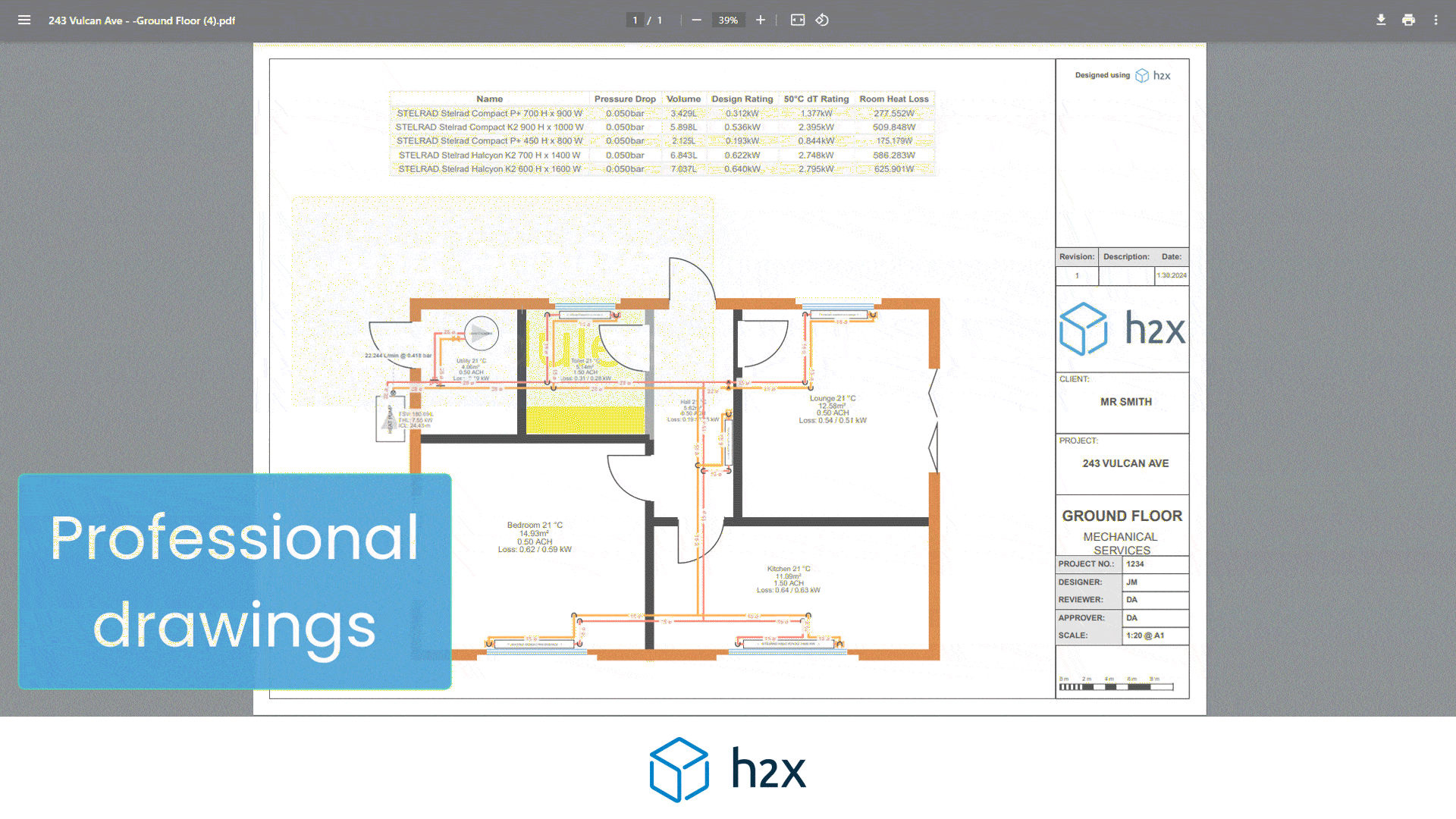
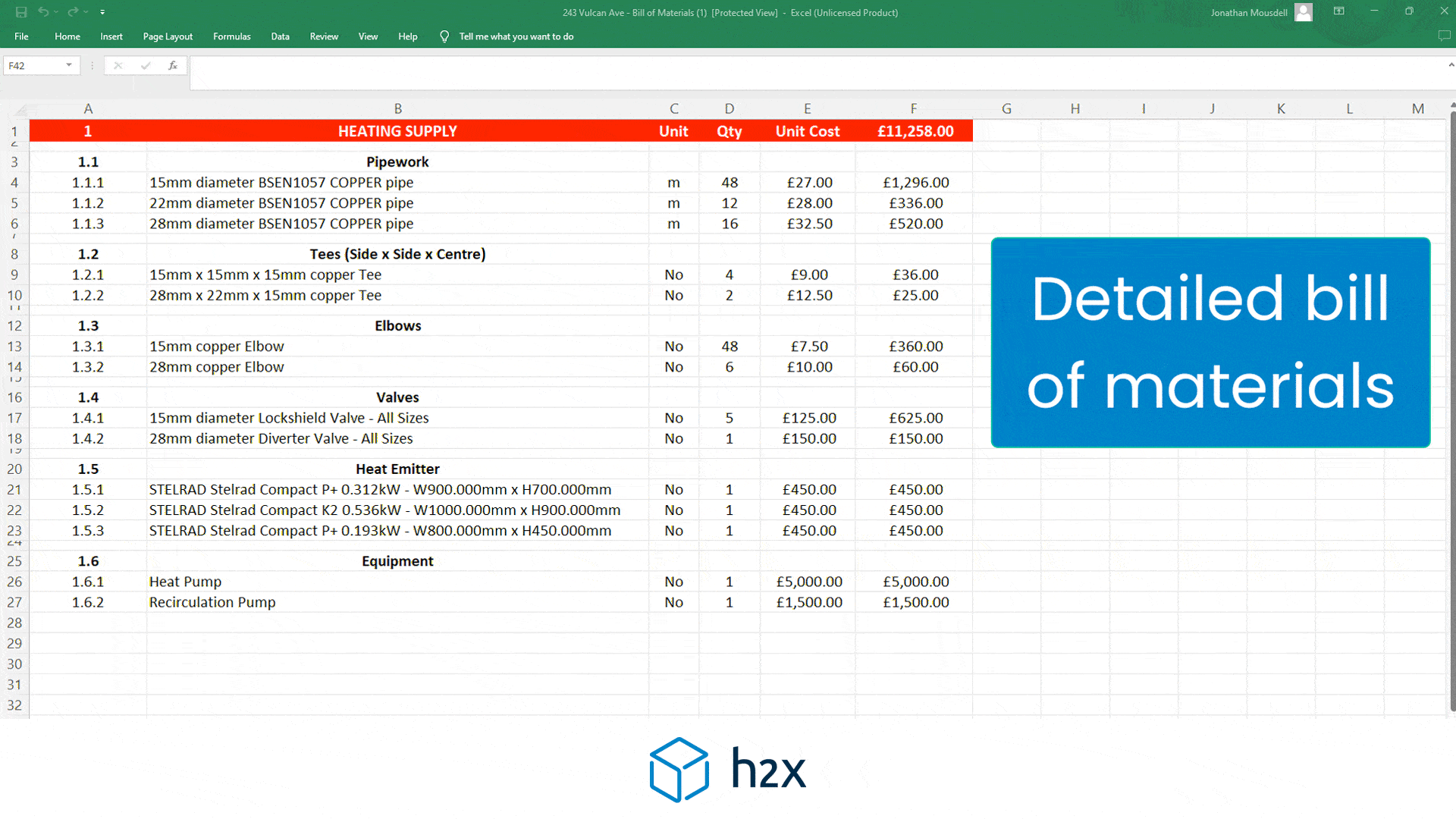
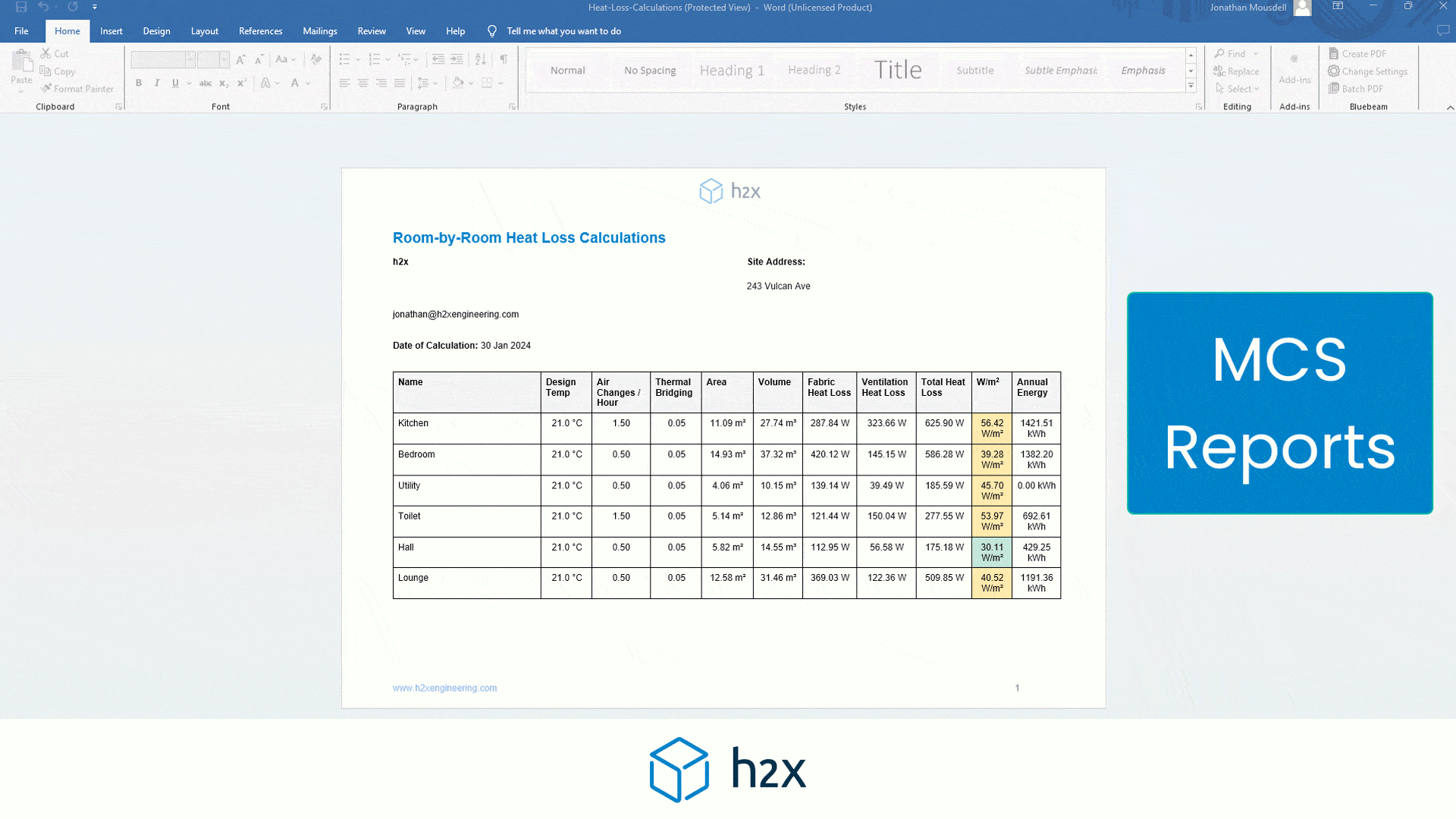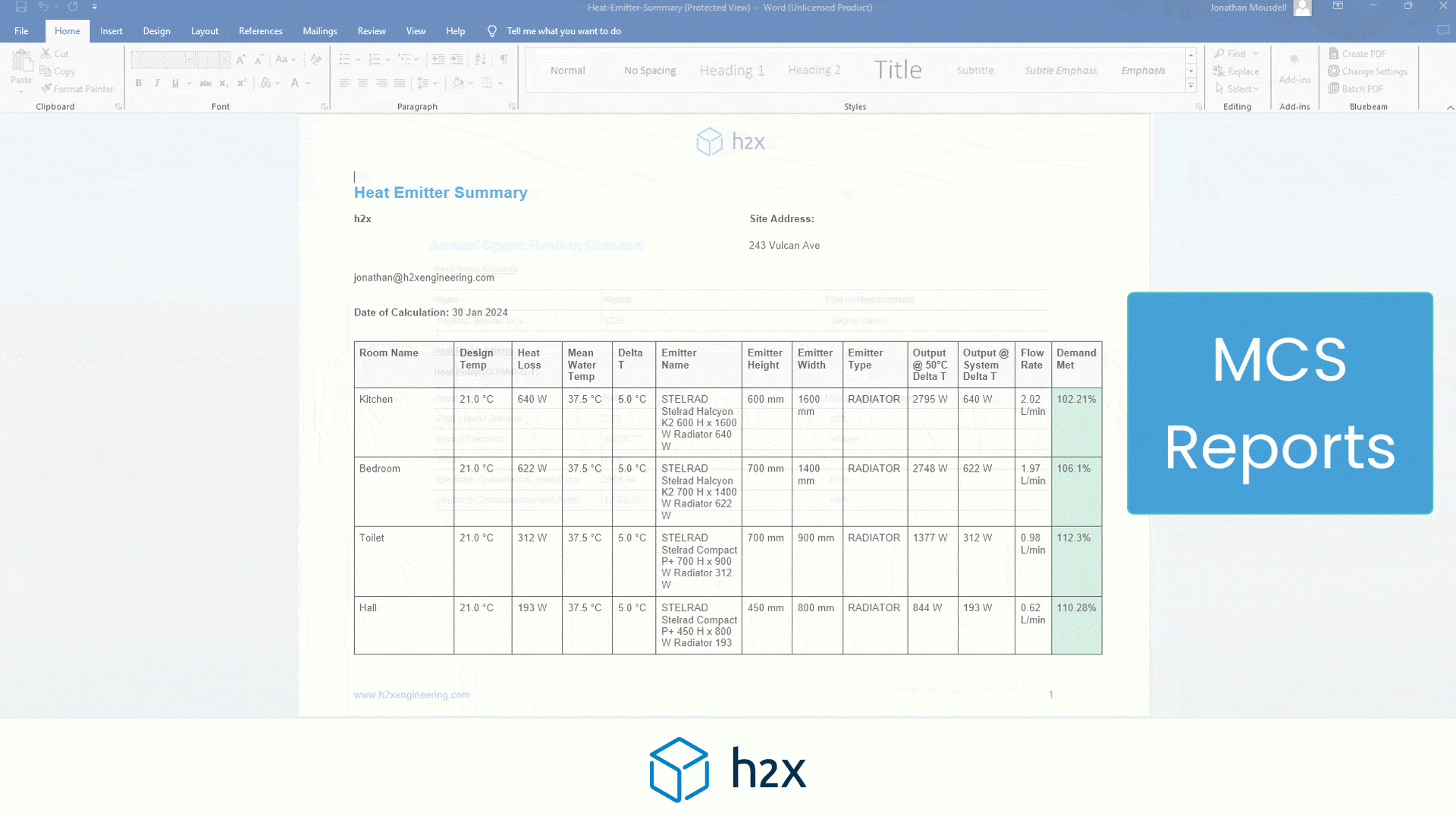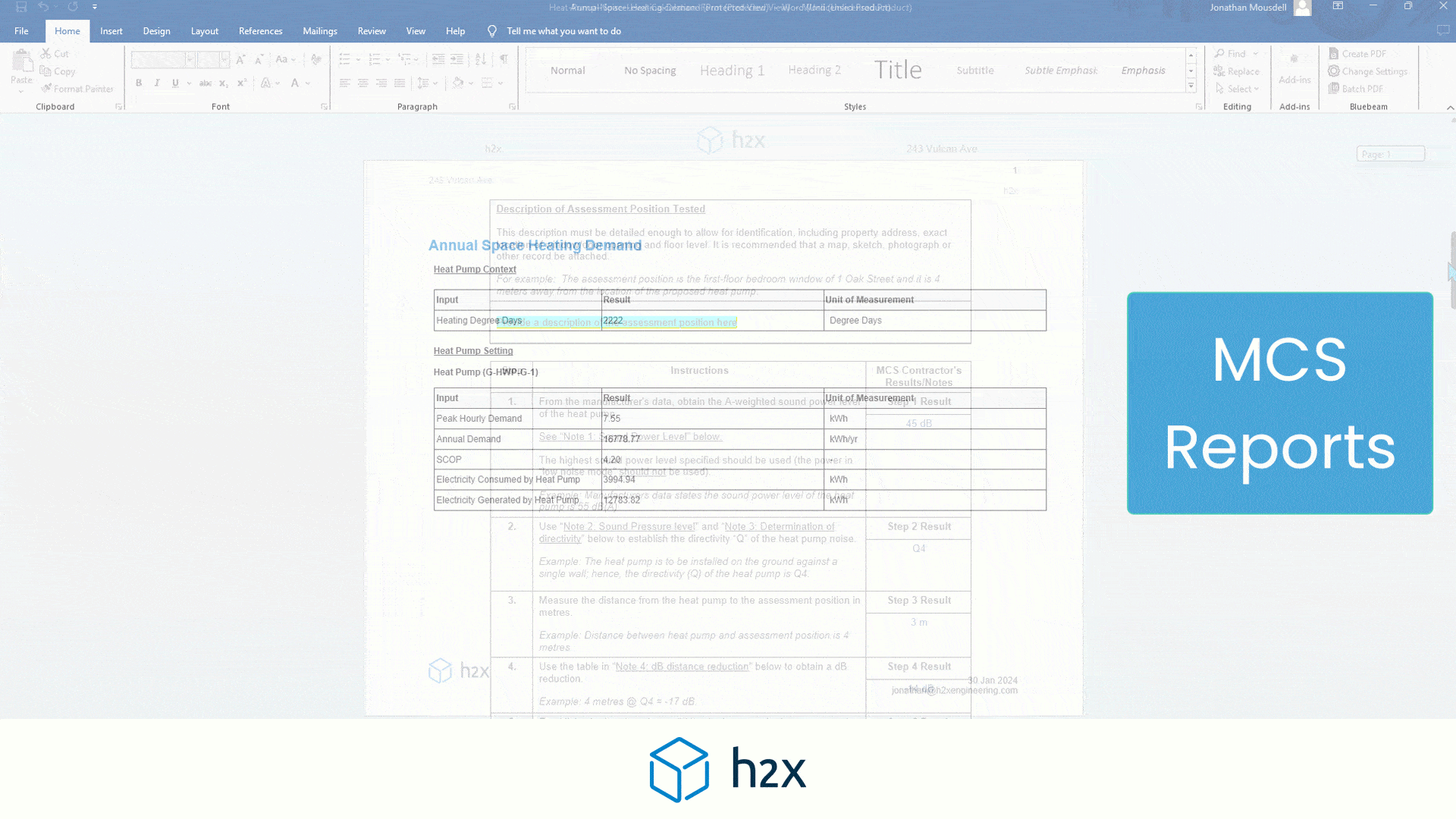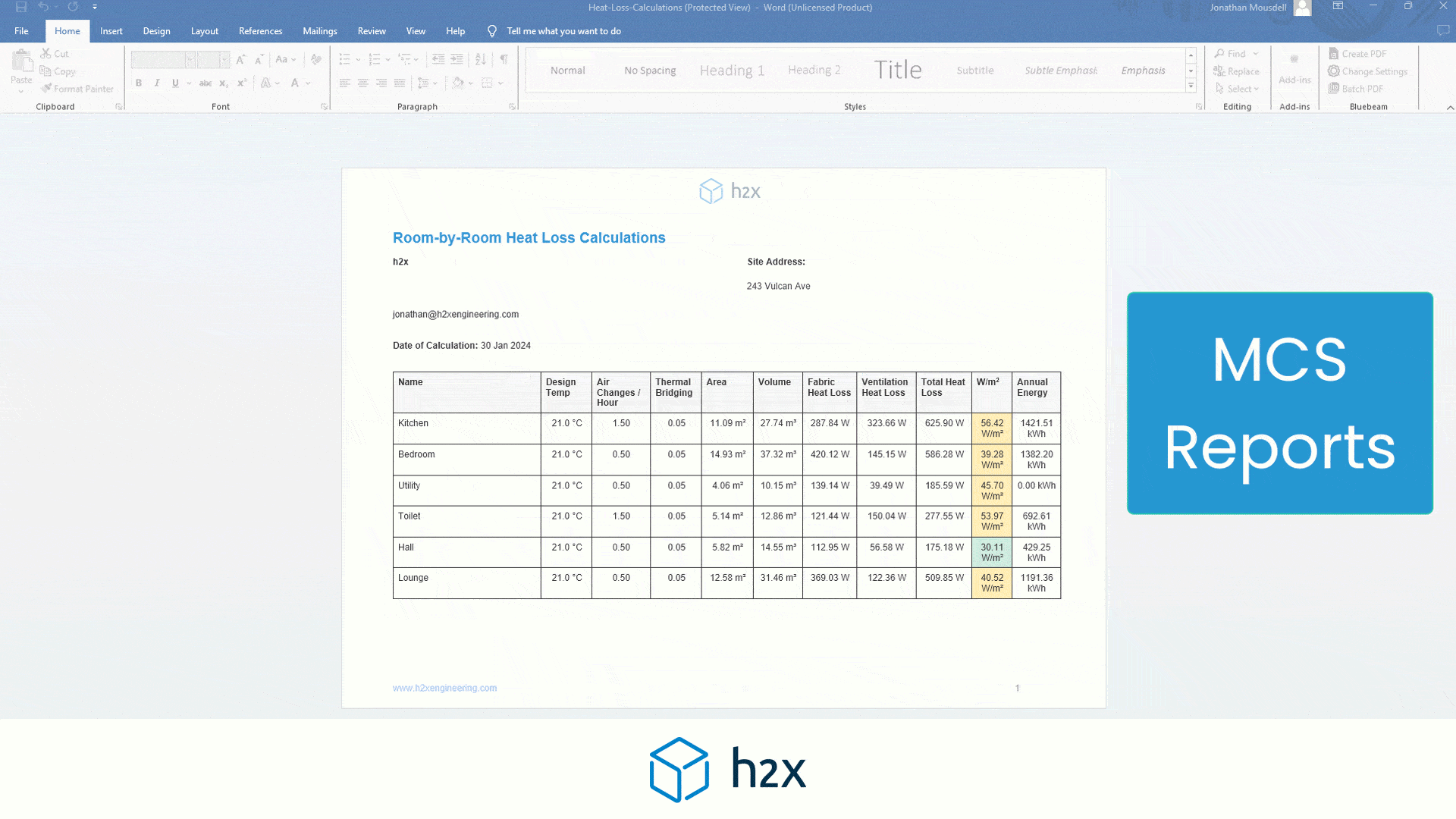
h2x has partnered with Southland Filtration to simplify the process of accurate sizing and specifying the correct water filter for your project.
Choose from a range of water filters to add to your system layout, and based on the calculated flow rate, h2x will accurately size and specify the correct model, the associated pressure drop, and provide warnings if you do not meet the minimum and/or maximum pressure limits.
h2x: All-In-One Tool for Calculating, Designing, Estimating, and Paperwork
What's in the Pipeline?
Get access to our monthly roundup of news and insights
You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy.
Testimonials
What Installers Say
What Consultants Say
A game changer for the humble plumber. Incredible.
Brad Winkel
Director at Queenstown Plumbing
Brilliant, simple and easy to use. Game changer.
James Major
Director at Hubb
Big time game changer to the industry!
Viv Jude
Director at UHC
Incredible software! Super user-friendly and allows you to save so much time.
Devni Gamage
Engineer at DMA
h2x is great software, our company use it nearly every day. It is easy to use with direct conversion from h2x to Revit.
Callum Craig
Engineer at WDE
h2x is fantastic software. It is very easy to use and the ability to output to Revit is a fantastic time saver.
Joe Kirrane
Engineer at MEP